The full form of DOCSIS is Data over Cable Service Interface Specification. This standard enabled cable to connect people to the web by serving as a reliable way. So, what is DOCSIS exactly? Let’s go through this article to learn about it in detail.
Previously, cable in the home was used for some particular reasons, mainly for television. However, in recent times, many people don’t use it to watch television. Instead, they use it for connection to the Internet which has become a necessity nowadays. At present, the Internet has become a basic service that every household needs.
What Is DOCSIS?
DOCSIS is a telecommunications standard which is recognized globally. It helps to transfer high-bandwidth data through the coaxial cable systems which are available already and mainly used to transmit cable television program signals (CATVS). Currently, this standard is in its 3rd generation.
The Bigger Picture:
Cable networks started to lose their ground because of the rise of high-speed fiber-optic internet. But now some old technologies are still alive. The Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification has been improved and modified a lot since its inception in 1997 with the evolution of data transfer technology. This standard’s aim is to offer faster speeds.
Besides, it can provide improved support for VOD, VoIP, and other advanced services. You should know that VOD stands for Video on Demand, whereas VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. The 4.0 version is its latest version, which could support the fastest symmetrical downstream and upstream speeds.
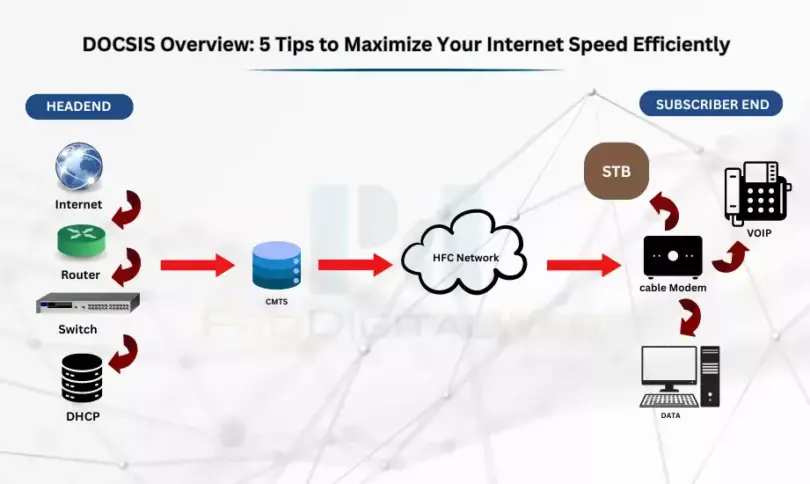
Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification offers Internet services via a cable TV system. In this case, it allows cable operators to use unused bandwidth on cable TV systems so that they can let customers access high-speed Internet.
Before knowing how it works, you need to know about the system’s key components, including — the cable modem, the cable modem termination system, and the coaxial cable infrastructure.
-
Cable Modem:
It helps to connect your device to the cable operator’s network. The modem is used to modulate and demodulate signals. Besides, it performs error correction ensuring that data will be transmitted securely.
-
Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS):
Its location is at the cable operator’s site. CMTS is used to assist in communicating with cable modems of the customers. It can be used to route traffic between the internet and the cable modem. It helps to perform network management functions such as QoS or quality of service and authentication control.
-
Coaxial Cable:
It carries data between these previous two key components. The infrastructure includes some coaxial cables, amplifiers and filters, which help to transmit signals.
How Does DOCSIS Work?
It divides the cable TV network’s bandwidth into many channels. Every channel can carry a particular data type. Thus, operators can provide quick data services without creating any problems with the television service.
In order to request any specific channel for data transfer, your DOCSIS modem starts communication with CMTS at the ISP’s headend. With the help of CMTS, it becomes possible to manage data flow between your modem and the internet. It makes sure that you, as a customer, can get the requested bandwidth.
The data flow can go both upstream and downstream. Traditionally, people wanted downstream traffic more than the other. However, this technology aims to strive toward a 10G vision according to the consumer’s requirements. This vision is going to provide symmetrical service speeds— both upstream and downstream.
Why Is Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications Important?
In recent times, we have seen a lot of advancements in technology. Therefore, Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification plays a vital role in offering internet access to users globally. The reasons why it is important are as follows:
-
Faster Internet Speed:
Compared to DSL Internet or dial-up Internet, it lets you download and upload content quickly because of the cable TV network’s increased bandwidth.
-
Cost-effectiveness:
It is a cost-effective way that can offer all customers high-speed Internet access. As cable TV networks are available already in place, users are not required to invest money to build new infrastructure. Thus, Data over Cable Service Interface Specification can be available at a lower price than other Internet access methods.
-
Wide Availability:
You can get it available in urban, suburban, and rural areas. So, you can implement this technology by changing a little bit to the infrastructure on these networks.
-
Compatibility With Existing Hardware:
This telecommunications standard supports routers and cable modems which are available already. There is no need to buy new equipment to upgrade Internet speeds.
Above all, a lot of people can get high-speed Internet connections with this technology cost-effectively.
A Little of History:
-
DOCSIS 1.0:
This first version was introduced in March 1997. The 1.0 version is able to obtain up to 40 Mbps and about 10 Mbps bandwidth in the downstream and upstream channels, respectively. Later, in April 1999, version D1.1 was upgraded, where the bit rates remained the same to implement VoIP services for cable TV subscribers. This standard is complemented with elements of QoS. It allows the technology to fulfill the security needs required to transmit DES 56 data.
-
DOCSIS 2.0:
This one offered more symmetrical transport bandwidth to respond to the enhanced requirements for network bandwidth. Its maximum download speed is 40 Mbps, whereas the upload speed is 30 Mbps. In order to make it happen, it was necessary to make a wider band available in the upstream direction and implement more effective modulation schemes.
-
DOCSIS 3.0:
This version was introduced in 2006 to deliver the channel bonding (combining downstream and upstream channels), IP multicast, AES encryption, and IPv6 functionality. Additionally, it can connect 6 or 8 MHz channels in the downstream direction. As a result, the maximum speed for DOCSIS is 340 Mbps, whereas 440 Mbps is for EuroDOCSIS. When it comes to the upstream direction, 120 Mbps is the possible speed. This version has now become the fundamental technology of operators who are working in HFC networks.
-
How The Implementation of This Standard Helped The Industry?
Implementing this standard helped to develop HFC technology, playing a vital role in the telecommunications industry. Coaxial cables are used in the infrastructure of the HFC (Hybrid Fiber-Coax) network topology. These cables have a connection with an optical node offering electric-to-optical conversion. You can use optical nodes to power an amplifier that is connected to the coaxial cable. The central location is known as CMTS or Cable Modem Termination System. It works as a hub for modems that have a connection with a distributed HFC network.
-
DOCSIS 3.1:
This version was introduced in 2013. It helped to implement GigabitEthernet services in all the available HFC networks. In addition, D3.1 brings PHY, a new generation of physical layers, integrating FEC and OFDM mechanisms. The standard form of OFDM is Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing, whereas FEC stands for Forward Error Correction. In the upstream direction, this combination helps to boost efficiency by 66% while 50% in the downstream. All credits go to the use of enhanced modulation (from 1024 QAM to a maximum of 4096 QAM).
-
More Information About This Version:
It uses the existing channel bandwidth in other paths. Previously, 6 or 8 MHz channel widths were featured in old iterations. But now, narrower OFDM subcarriers have replaced it. As a result, a block spectrum is produced having a width of 200 MHz. Therefore, it will be compatible with 10 Gbit/s downstream and 1 or 2 Gbit/s upstream. It was essential to develop separate standards for versions before D3.1 for the US and Europe due to some major differences between the two systems.
The European cable TV adopted the PAL or SECAM, USA has adopted the national television system committee broadcast color system. As they are operating in different RF channels which are 6 MHz in the United States and 8 MHz in Europe, regarding the channel bandwidth, it has consequences. In the architecture of EuroDOCSIS, 8 MHz allows more bandwidth to be assigned downstream.
-
DOCSIS 4.0:
It allows multi-gigabit symmetrical services to use the full spectrum of the cable plant simultaneously in upstream and downstream directions to provide low-latency service in the pursuit of 10G. Digital certificates and TLS or Transport Layer Security encryption are a few security improvements which this version supports. These features ensure that transmitted data remains secure from tampering.
What Are The Important Features Of DOCSIS 4.0?
It is considered the next-generation of broadband technology over HFC networks of cables. Let’s see the features that it can offer.
-
Enhanced Speeds:
The maximum upstream and downstream capacity supported by this version is 6 Gbps and 10 Gbps, respectively. By offering such substantial rise in the speeds of downstream and upstream, it can ensure that you as a user can enjoy multi-gigabit symmetrical services over Hybrid fiber-coaxial network.
-
Support For Emerging Applications:
The symmetrical speeds that Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications offers are now very relevant because of some emerging new applications and technologies, including —
- Interactive video conferencing,
- Remote learning,
- Healthcare applications,
- Internet of Things,
- And
Virtual reality.
-
Efficient Use Of Existing Infrastructure:
This version helps to make the existing cable broadband networks more effective, and there is no need for extra cabling, resulting in cost-effectiveness, while making sure that the infrastructure is future-proof.
What Are The Benefits Of Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications?
This telecommunications standard can offer advantages to both operators and consumers:
Operators:
- New services are simple to deploy
- Infrastructure cost is low
- Various service levels to fulfill consumer requirements.
Consumers:
- Supports existing home cable connection.
- Compatible with many devices and internet users.
- High-speed internet access, which is reliable and secure.
What Technology Does Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications Use?
This technology works as a bridge between CMTS and cable modems. The connection can occur over HFC that helps to combine coaxial cables and the high data-transfer rates of fiber optics. Additionally, Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications uses multiple technologies to offer enhanced security and higher speeds.
-
Channel bonding:
Channel bonding was introduced in D3.0 to let you use many channels simultaneously to transmit data. Thus, it can offer redundancy and boost bandwidth. As a result, the connection remains consistent despite any problems with one channel.
-
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM):
OFDM is a crucial feature of D3.1 and beyond. It can divide a single data stream across many carriers. This feature helps to reduce interference and optimize data transfer.
-
Full Duplex Communication:
With the help of this standard, it is possible to transmit and receive data simultaneously. As a result, upload and download speeds become symmetrical, which is important for several applications like online gaming and video conferencing.
-
Extended Spectrum Capabilities:
The DOCSIS 4.0 gives a push towards the use of a broader frequency spectrum, which ensures more channels to transfer data at higher speed and achieve more reliable connections.
What DOCSIS Version Do You Need?
D3.0 modem is suitable for most users, but for gigabit cable packages, its 3.1 version is important.
The D1.0 or 1.1 and D2.0 modems have become historical footnotes now. This is because cable internet providers do not support or use them.
-
DOCSIS 3.0 Is Still Fine For Most People:
It can be expected that most people will enjoy the D3.0 even for some upcoming years. It is able to handle a 30 Mbps down or 3 Mbps up connection. In addition, it can handle a 500 Mbps down/50 Mbps up connection. You have to consider whether or not it comes with sufficient channels for handling the maximum speed of the cable internet tier for which you spend money.
Every channel includes a maximum bandwidth capacity. If the number of channels is unable to handle the internet plan’s full capacity, you will pay for bandwidth that you never use completely.
Suppose you invest your money in a 500/50 package, a cable modem having at least a 4×4 channel configuration. If this is the case, 172 Mbps is the maximum speed for upstream and downstream. Although it can easily cover the entire upload speed, it is only capable of covering around a third of the download speed.
So, it is essential to have enough bonded channels for 500/50 connections. In order to ensure that, you need to use a 16×4 modem at least. It offers maximum speed for upstream and downstream — 172 Mbps and 686 Mbps respectively. For other packages, like the more modest 30/3 tier, you can easily go with the D3.0 4×4 ones. It provides space to bump up to the next tier or two, and does not even need an upgrade.
-
DOCSIS 3.1 Is Essential For Gigabit Cable Packages:
The D3.0 standard is able to support near-gigabit speeds. However, cable internet providers want you to use the D3.1 version for their top-tier packages. There is no need to spend twice as much or more on D3.1 for people in the lower speed tier. If your internet package has 800+ Mbps range, you will require a D3.1 one. If you are willing to skip the rental fee of your ISP modem and need gigabit speeds, you have to choose a pricier one.
Although D3.1 is suitable for gigabit plans between 800 Mb per second and cable provider’s 940-1000 Mb per second, it is not necessarily recommended. There is not so much of a price difference between multi-gigabit modems and good gigabit modems. Instead of purchasing a new modem, you should pay a little extra when your cable provider gives multi-gig offerings.
Always consider the role your Wi-Fi router plays in home internet experience. You should not pair a new DOCSIS 3.1 modem and a costly gigabit cable package with a router that needed to be replaced years ago. Is your WiFi router over three years old? Then, you should replace it now.
Is This Standard Secure?
Each web-based technology includes a few inherent risks. But this standard is secure. As this standard travels between the ISP’s headend and the customer’s modem, it uses encryption to keep data secure. Every new version of Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications has connections with the updated security measures. For instance, the most upgraded generation 4.0 version brings several new advanced security controls like forward secrecy, mutual authentication, etc. Also, its 4.0 version introduces improved security for private keys and other network credentials.
Customer and network data security is going to come down to the measures taken by operators. ISPs can get benefits from the built-in security features, which are useful in stopping fraud detection, denial of service (DoS), fraud detection and mitigation.
How Do You Provision and Manage CPE Devices Over DOCSIS Networks?
In the section on how Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications works, you can see the mention of the connection between the ISP and the customer. You can see here more detailed information which lets you learn how devices are managed in the customer’s home. A few steps are followed to provision and manage CPE or customer premises equipment devices over DOCSIS networks to ensure that the connectivity is secure.
A CPE device needs to make a connection with the network first. Then, the device sends a DHCP or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server request to obtain an IP address. This protocol server provides a unique IP address to every device to let it communicate with the network.
After that, a configuration file will get downloaded based on this technology in the DOCSIS CPE device. The file has information related to the parameters and network settings, like the encryption keys, downstream and upstream frequencies, modulation schemes, etc. In order to set up a connection with the network, the CPE device uses the information. Moreover, using the information the device can communicate with other devices which are available on the network.
As soon as the device is provisioned and makes a connection to the network, it becomes possible to manage the device as well as monitor remotely. For instance, you can perform firmware upgrades which ensures that your device has the most recent software version. You can reboot your device to address the connectivity problems if required.
If you are one of the network administrators, you are capable of using the specialized software tools with the help of which you can both manage and monitor DOCSIS CPE devices and identify and fix problems that can arise.
Above all, you need to provision and manage DOCSIS CPE devices properly to ensure that you will get a secure network infrastructure.
DOCSIS vs EuroDOCSIS:
The frequency plan concerning the downstream path makes these two different. Modems that support EuroDOCSIS can implement a flexible frequency scheme. In this case, the center frequencies start at 112 MHz, whereas it ranges up to 858 MHz, however in small 250 kHz frequency hops.
On the flip side, the Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification is compatible with three frequency plans, including- HRC/IRC/STD. 867 MHz is the maximum frequency at the center. However, it needs frequency hops of only 6 MHz.
How To Manage DOCSIS Devices:
Now, Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications have become a popular standard globally. But Internet Service Providers could see the multiplicity of subscriber devices and cable modems throughout the industry as a threat. According to an estimate, almost 5000-8000 CPE models that are compatible with different versions of the standard come from many manufacturers. So, managing so many unsupported devices is going to be very difficult without a comprehensive device management solution, especially for carriers with several deployments and small-scale enterprises.
How Does This Technology Affect Your Future?
There are some important aspects that matter to technologists — connection speeds, low latency, reliability, etc. These factors can affect the future directly. Now, high-speed internet connectivity plays a crucial role in modern life. People are now capable of streaming in 4K. Also, they can play online games with all people, collaborate on video chat, drive connected cars, etc.
Rapid advancements in Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification technologies are making these things possible, while helping to boost the download and upload speeds, lowering lag or latency to deliver a seamless experience. In addition, it enables you to improve security to keep online information secure.
Its 4.0 technology is going to enable symmetrical multi-gigabit services. This technology will be beneficial in many different industries and applications like entertainment, education, healthcare, collaboration technologies, autonomous vehicles etc. We can expect to view innovative learning and work applications, advanced health monitoring services, etc, in the near future.
Additionally, the technology may bring visually rich VR/AR, holodecks, omnipresent AI assistants, etc. It could even introduce some game-changing innovations which people couldn’t even think about. The HFC infrastructure of cable serves as the backbone of the 10G future and DOCSIS combined with advanced network technologies will help to reach the near future.
The Bottom Line:
In order to offer Data and Voice services with TV Channels over the HFC Network that exists already, CATV Service Providers can choose DOCSIS. While its 3.0 version offers low latency, it can boost the security level. In addition, this version is compatible with the Mulitcasts and IPV6. Also, this version uses the AES Encryption. While Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications have been a broadband service enabler, its 4.0 version is not going to be the last one. So, you can expect to see newer advancements, which will enable ISPs to use the CATV infrastructure in a better way.