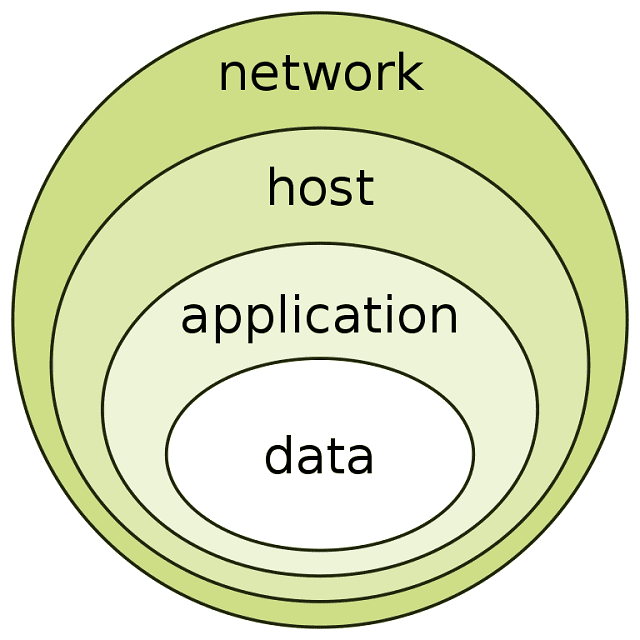
Introduction to Defense-in-Depth Strategy (DiD)
In today’s digital world, cyber threats have become more sophisticated. It is more frequent. And it is more dangerous than ever before. Cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to breach networks and steal sensitive data. In response, organizations are turning to a defense-in-depth strategy. It is a novel concept that originated in the military. And it has been adapted to cybersecurity.
The defense-in-depth strategy involves implementing multiple layers of security controls across the organization. The implication includes the organization’s network, applications, and data. This approach is designed to provide a comprehensive and resilient defense against cyber threats. The threats include malware, phishing attacks, and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
It is the application of multiple countermeasures in a layered manner to achieve security objectives. It involves layering heterogeneous security technologies in the common attack vectors. This one ensures that attacks missed by one technology are caught by another.
The core principle of it is to ensure that if one layer of security is breached, there are other layers in place to prevent or mitigate the damage. The multiple layers include access control, network segmentation, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, antivirus software, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions.
Implementing a defense-in-depth strategy improves the organization’s security posture. And it reduces the risk of data breaches. Using multiple layers of protection, organizations increase the chances of detection. And they can respond to cyber threats promptly and on time. Additionally, implementing it helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements. And it avoids costly fines.
In the rest of this article, we’ll explore the layers of a defense-in-depth strategy, its benefits, and the best practices for implementing it effectively. By the end of this article, you’ll better understand how to protect your organization against cyber threats and ensure that your data remains secure.
Definition of Defense-In-Depth Strategy (DiD)
A defense-in-depth strategy is a cybersecurity approach that involves implementing multiple layers of security controls to protect against a range of cyber threats. This approach can provide a comprehensive and resilient defense against attacks. It ensures that if one layer of security is breached, other layers are in place to prevent or mitigate the damage.
The multiple layers include access control, network segmentation, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, antivirus software, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions. The core principle of it is to create a layered defense that makes it difficult for attackers to penetrate an organization’s network. And it increases the chances of detecting and responding to cyber threats on time.
Importance of Defense-In-Depth Strategy in Cybersecurity
Defense in Depth or DiD is an information security approach in which a series of security mechanisms and controls are layered. It is a cybersecurity approach that uses multiple layers of security for holistic protection. The importance of defense-in-depth strategy in cybersecurity cannot be overstated.
Cyber threats have become more sophisticated and frequent. And organizations must be prepared to defend against them. Implementing it improves an organization’s security posture and reduces the risk of data breaches. Here are some reasons why a defense-in-depth strategy is so critical:
Protection against Multiple Attack Vectors
Cyber attackers use various techniques and attack vectors to penetrate an organization’s network. The attackers use phishing emails to trick users into revealing their login credentials. Or they may exploit vulnerabilities in software or hardware to gain unauthorized access to the network.
The defense-in-depth strategy ensures that multiple layers of security controls are in place to protect against different types of attacks. These layers include access control, network segmentation, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, antivirus software, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions. Organizations reduce the likelihood of a successful attack by using multiple layers of protection. And they increase the chances of detecting and responding to cyber threats on time.
Resilience against Attacks
The core principle of defense-in-depth is to create a layered defense. That layered defense makes it difficult for attackers to penetrate an organization’s network. Even if one layer of security is breached, other layers are in place to prevent or mitigate the damage. This approach makes it more challenging for attackers to succeed in their attacks.
They need to overcome multiple layers of protection to reach their targets.
Additionally, a defense-in-depth strategy minimises the impact of a successful attack on the organization. Suppose a cyber attacker can breach one layer of security and gain access to a specific system or application. The network segmentation can contain the attack and prevent the attacker from moving laterally within the network.
Compliance with Regulations
Many industries and organizations are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate implementing specific security controls. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) require healthcare organizations to implement access controls, encryption, and other security measures.
It is to protect patient data. Similarly, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) requires organizations that process credit card payments to implement specific security controls. Implementing defense-in-depth strategy help organizations comply with these regulations and avoid costly fines. Additionally, implementing it helps organizations demonstrate to regulators, customers, and partners that they are taking proactive steps to protect sensitive data.
Protection against Insider Threats
Whether intentional or unintentional, insider threats pose a significant risk to an organization’s security. For example, an employee with sensitive data access may accidentally disclose or intentionally steal it. The defense-in-depth strategy helps to protect against insider threats by implementing access controls, monitoring user behaviour, and detecting anomalies in the network. By implementing these controls, organizations minimize the risk of insider threats. And these also quickly detect and respond to any suspicious activity.
Peace of Mind
Implementing DiD gives organizations peace of mind as they have taken steps to protect their network and data against cyber threats. Cybersecurity is an ongoing process. And implementing a defense-in-depth strategy is just one part of a comprehensive security program. However, by implementing multiple layers of protection, organizations reduce the risk of a successful attack. And they increase their resilience against cyber threats. Additionally, implementing it helps build trust with customers and partners concerned about data privacy and security.
Defense-in-depth strategy is critical in today’s cybersecurity landscape. Organizations must be proactive in their approach to security and implement multiple layers of protection to defend against cyber threats.
Layers of Defense-in-Depth
The defense-in-depth strategy typically involves implementing multiple layers of security controls to protect an organization’s network and data. The specific layers of defense can vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and regulatory requirements, but some common examples include the following:
Perimeter Defense
This layer involves securing the organization’s network perimeter by implementing firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and other security technologies. It prevents unauthorized access to the network and protects the organization against external threats.
Identity and Access Management
This layer involves implementing access controls and authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users are accessing sensitive data and resources. Examples of controls in this layer include two-factor authentication, password policies, and user activity monitoring.
Data Security
Data Security protects the organization’s data from unauthorized access or theft. It is achieved by implementing encryption, data loss prevention technologies, and backup and recovery procedures.
Application Security
The application Security layer secures the organization’s software applications by implementing secure coding practices, vulnerability scanning, and penetration testing.
Physical Security
The physical security layer secures the organization’s physical assets, such as servers, data centres, and other critical infrastructure. It is possible to achieve through access controls, video surveillance, and other security measures.
Incident Response
This layer involves having a plan to detect & respond to security incidents promptly and on time. Incident Response includes procedures for incident reporting, containment, investigation, and recovery.
By implementing multiple layers of defense-in-depth, organizations improve their overall security posture. And they reduce the risk of successful cyber attacks. Each layer of defense provides an additional barrier to entry for cyber attackers and helps to minimize the impact of successful attacks.
What is Perimeter defense?
Perimeter defense is the first layer of a defense-in-depth strategy that organizations use to protect their network from external threats. It involves securing the network perimeter by implementing various security technologies to prevent unauthorized access to the network.
The perimeter defense layer typically includes firewalls, intrusion detection, and prevention systems (IDPS). And it has virtual private networks (VPNs). Firewalls act as a barrier between the internal network and external networks or the internet. They inspect incoming and outgoing traffic. And firewalls determine whether to allow or block traffic based on predefined security policies.
IDPS monitors network traffic for signs of suspicious or malicious activity. Malicious activities are attempts to exploit vulnerabilities or perform unauthorized actions. When an IDPS detects an attack, it takes various actions. That is blocking the traffic or generating alerts for further investigation.
VPNs provide secure remote access to the organization’s network by encrypting traffic between the user and the network. It prevents eavesdropping and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Perimeter defense is an essential layer in a defense-in-depth strategy because it establishes a first line of defense against external threats. Organizations control and monitor network traffic by implementing firewalls, IDPS, and VPNs. And they reduce the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
What is Identity and Access Management in Defense-In-Depth Strategy?
Identity and access management (IAM) is a layer in the defense-in-depth strategy that focuses on managing user access to the organization’s network and resources. This layer involves implementing access controls and authentication mechanisms. It ensures that; only authorized users can access sensitive data and resources.
IAM solutions features are user provisioning, role-based access control, and authentication and authorization mechanisms. User provisioning involves creating and managing user accounts, assigning privileges, and defining access policies. Role-based access control (RBAC) provides a way to assign permissions based on user roles and responsibilities. It is rather than assigning permissions to individual users. This simplifies the management of access controls. And it reduces the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
Authentication and authorization mechanisms are also components of IAM. Authentication verifies the user’s identity attempting to access the network or resource. While the authorization determines what resources the user is authorized to access. And what actions they are authorized to perform. IAM solutions include various authentication mechanisms. Those authentications are mechanisms of passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication. And it ensures that only authorized users can access the network and resources.
IAM is an essential layer in the defense-in-depth strategy. It ensures that only authorized users have access to the organization’s sensitive data and resources. IAM solutions help organizations to manage user access better. And it reduces the risk of insider threats and credential theft. Further, it improves their overall security posture.
What is Data Security Layer in Defense-In-Depth Strategy?
Data security is a layer in the defense-in-depth strategy. That focuses on protecting the organization’s data from unauthorized access or theft. This layer involves implementing various technologies and practices. It ensures that sensitive data is stored and transmitted securely.
Some common examples of technologies used in the data security layer are encryption, data loss prevention (DLP), and backup and recovery solutions. Encryption involves converting sensitive data into unreadable form without the appropriate decryption key. It protects data from unauthorized access in case it is intercepted or stolen.
DLP technologies are designed to prevent data leakage or loss by monitoring network traffic and endpoint devices for sensitive data. DLP solutions detect and block unauthorized attempts to access or transfer sensitive data. The sensitive data include credit card numbers, personal information, and intellectual property.
Backup and recovery solutions are also vital components of the data security layer. These solutions ensure that critical data is regularly backed up. And the data can be recovered in case of data loss or system failures. It helps to minimize the impact of data breaches or other security incidents.
Data Security Layer is an essential component of the Defense-In-Depth strategy. It ensures that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access or theft. Organizations better protect their critical data assets by implementing encryption, DLP, and backup and recovery solutions. Besides, they reduce the impact of security incidents.
What is Application Security in Defense-In-Depth Strategy?
Application security is a layer in the defense-in-depth strategy. It focuses on protecting the organization’s applications from vulnerabilities and attacks. This layer involves implementing various security measures. In addition, it ensures that the applications are designed, developed, and maintained securely.
Application security measures secure coding practices, vulnerability assessments and testing, and web application firewalls (WAFs). Secure coding practices involve following established coding standards and guidelines. It ensures that applications are designed and developed with security in mind. Besides, it avoids common coding mistakes. And it implements security controls, such as input validation and access controls.
Vulnerability assessments and testing involve identifying and addressing potential security weaknesses in the application. This one includes conducting regular security assessments, penetration testing, and code reviews. It identifies vulnerabilities and areas for improvement.
Web application firewalls (WAFs) are another critical component of application security. WAFs protect web applications from common attacks, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). WAFs monitor incoming and outgoing traffic. And it applies predefined security policies to block or allow traffic based on the level of risk.
Application security is an important layer in the defense-in-depth strategy. It helps to ensure that the organization’s applications are designed, developed, and maintained securely. It implements secure coding practices and vulnerability assessments. And WAFs better protect their applications from vulnerabilities and attacks. Further, it reduces the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
What is the Physical Security Layer in Defense-In-Depth Strategy?
Physical security is a layer in the defense-in-depth strategy. And that focuses on protecting the organization’s physical assets. The physical assets are facilities, equipment, and personnel. This layer implements various physical security measures. And it prevents unauthorized access, theft, and damage to the organization’s physical assets.
Physical security measures include access controls, surveillance systems, alarms, and security personnel. Access controls restrict entry to the organization’s facilities and equipment to authorized personnel only. This one uses locks, keycards, and biometric authentication to control access to sensitive areas.
Surveillance systems, like video cameras, monitor the organization’s facilities and equipment for suspicious activity. Alarms alert security personnel or law enforcement in case of unauthorized access or other security incidents.
Security personnel, such as guards or patrols, are also an essential component of physical security. They deter potential threats and respond quickly to security incidents.
The physical security layer is an important component of the defense-in-depth strategy. It ensures that the organization’s physical assets get protection from unauthorized access, theft, and damage. It implements access controls, surveillance systems, alarms, and security personnel. The physical security layer protects their physical assets. And it reduces the likelihood of successful physical attacks or thefts.
What Is Incident Response Layer in Defense-In-Depth Strategy
Incident response is a layer in the defense-in-depth strategy. And it focuses on detecting, analyzing, and responding to security incidents. This layer involves implementing various processes and procedures. It ensures that security incidents are detected and handled promptly and effectively.
Incident response measures include incident detection and response plans, incident response teams, and security incident and event management (SIEM) systems. Incident detection and response plans help organizations quickly identify and respond to security incidents. These plans are predefined processes for incident detection, analysis, containment, and recovery.
Incident response teams are responsible for executing the incident response plan. And it is coordinating with other stakeholders, such as IT staff, legal, and law enforcement. These teams include members with specialized skills, such as forensics, incident analysis, and communication.
SIEM systems collect and analyze security event data from various sources, such as network devices, servers, and endpoints. SIEM systems identify potential security incidents in real time. So that incident response teams to quickly respond and mitigate the incident.
The incident response layer is an important component of the defense-in-depth strategy. It helps to ensure that security incidents are detected and handled in a timely and effective manner. The incident response layer implements incident response plans, and the incident response teams and SIEM systems detect and respond to security incidents. It minimizes the impact of such incidents on the organization.
Overview of the Different Layers of Defense-In-Depth Strategy
The defense-in-depth strategy implements multiple layers of security controls to protect an organization’s assets from cyber threats. The different layers of defense-in-depth include:
Perimeter Defense
The Perimeter Defense layer implements security controls; such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and web application firewalls. It protects the organization’s network perimeter from external threats.
Identity and Access Management
This layer implements controls to ensure that only authorized users can access the organization’s systems and data. It implements strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, and manages user access through identity and access management (IAM) solutions.
Data Security
This Data Security layer implements controls to protect the organization’s data from unauthorized access, theft, or corruption. This layer encrypts sensitive data, implementing data loss prevention (DLP) solutions. And it manages access to data through role-based access controls.
Application Security
The application Security layer implements controls to ensure that the organization’s applications are secure and free from vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. This application security layer implements secure coding practices, conducts regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing, and implements web application firewalls (WAFs).
Physical Security
This layer implements controls to protect the organization’s physical assets, such as facilities, equipment, and personnel. This layer implements access controls surveillance systems, alarms, and security personnel.
Incident Response
The incident Response layer implements processes and procedures to detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents promptly and effectively. This implementation includes developing incident response plans, forming incident response teams, and implementing security incident and event management (SIEM) solutions.
By implementing these different layers of security controls, organizations can establish a comprehensive defense-in-depth strategy that protects organizations against a wide range of cyber threats. Each layer provides an additional level of protection. It makes it more difficult for attackers to penetrate the organization’s defenses and steal or compromise sensitive data.
Explanation of Each Layer and Its Purpose
Here’s an explanation of each layer of the defense-in-depth strategy and its purpose:
Perimeter Defense
The perimeter defense layer includes security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and web application firewalls. The purpose of the Perimeter Defense layer is to protect the organization’s network perimeter from external threats, such as hackers and malware. The Perimeter Defense layer filters out unauthorized traffic. And it allows only legitimate traffic to pass through.
Identity and Access Management
The identity and access management (IAM) layer controls and ensures that only authorized users can access the organization’s systems and data. This layer prevents unauthorized access to the organization’s resources, such as confidential data and systems. It ensures that users are authenticated, and their access is limited to only what is necessary for their job.
Data Security
The data security layer controls protect the organization’s data from unauthorized access, theft, or corruption. This layer ensures that sensitive data is protected throughout its lifecycle, from creation to deletion. It implements security controls. The security controls include encryption, data masking, data loss prevention (DLP), and access controls.
Application Security
The application security layer ensures that the organization’s applications are secure and free from vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. The application Security layer protects against attacks that target application vulnerabilities. The vulnerabilities are SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). It implements secure coding practices, conducts regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing, and implements web application firewalls (WAFs).
Physical Security
The physical security layer protects the organization’s physical assets. Some examples of physical assets are facilities, equipment, and personnel. The purpose of this layer is to prevent physical theft, damage, or unauthorized access to the organization’s resources. It implements access controls, surveillance systems, alarms, and security personnel to protect the assets.
Incident Response
The incident response layer’s processes and procedures are to detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents promptly and effectively. The Incident Response layer minimizes the impact of security incidents by detecting them as soon as possible. The Incident Response layer analyzes the incident to determine its scope and severity. It contains the incident to prevent further damage. And it helps to recover from the incident by restoring normal operations and implementing measures to prevent future incidents.
Organizations implement these different layers of security controls. Organizations establish a comprehensive defense-in-depth strategy that provides multiple layers of protection against a wide range of cyber threats. Each layer provides an additional level of protection. They make it more difficult for attackers to penetrate the organization’s defenses and steal or compromise sensitive data.
Examples of Tools and Technologies Used in Each Layer:
Here are some examples of tools and technologies that are used in each layer of the defense-in-depth strategy:
Perimeter Defense
Firewall
A firewall is a network security device. It monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an organization’s established security policies.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPS is a network security system. It monitors network traffic for any signs of possible malicious activity. And IDPS takes action to prevent such activity.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Web Application Firewall is a security system designed to protect web applications from attacks. The attacks are cross-site scripting, SQL injection, and others.
Identity and Access Management
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On is an authentication process. It allows users to enter one set of credentials to access multiple systems or applications.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication is a security system. It requires users to authenticate using two or more different authentication factors. The authentication factors are a password and a fingerprint scan.
Identity Management Systems (IDM)
Identity Management System manages user identities, authentication, and access control.
Data Security
Encryption
Encryption is a process of encoding information to protect its confidentiality.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention is a security system. It prevents unauthorized users from accessing, copying, or sharing sensitive data.
Access Control
Access Control is a process that limits access to specific data to authorized users only.
Application Security
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
It is a security technique that analyzes application source code for security vulnerabilities before it is compiled or executed.
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
It is another security technique. It analyzes applications in real-time as they are running, searching for security vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A web Application Firewall is a security system designed to protect web applications from attacks such as cross-site scripting, SQL injection, and others.
Physical Security
Video Surveillance
Video Surveillance security system captures video footage of an organization’s facilities and assets to deter theft, vandalism, and other physical security risks.
Access Control
Access Control is a process that limits access to physical resources to authorized users only.
Alarm Systems
The alarm system alerts security personnel or authorities in case of attempted unauthorized access or a security breach.
Incident Response
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
The security Information and Event Management system collects and analyzes security-related data from multiple sources to identify
potential security incidents.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems is a network security system. That monitors network traffic for signs of possible malicious activity. And it takes action to prevent such activity.
Forensic Tools
Forensic Tools are a set of tools and techniques used to analyze security incidents and gather evidence for investigation.
These are just a few examples of the tools and technologies used in each defense-in-depth strategy layer. The specific tools and technologies that an organization chooses to use will depend on its specific security needs and requirements.
Benefits of Defense-in-Depth
The defense-in-depth strategy offers several benefits for organizations looking to enhance their cybersecurity posture:
Multiple Layers of Protection
By implementing multiple layers of security, an organization can create a more robust defense against cyber threats. If one layer of defense fails, other layers can provide protection. Thereby it reduces the likelihood of a successful attack.
Reduced Risk of Data Breaches
With multiple layers of protection, organizations reduce the risk of data breaches and the potential loss of sensitive information.
Early Detection and Response to Threats
With intrusion detection systems and security monitoring tools, organizations detect potential security incidents early. And they respond quickly to mitigate any damage.
Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Organizations comply with industry standards and regulations by implementing a defense-in-depth strategy. Industry Standards and Regulations include the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Improved Business Continuity
Organizations reduce the risk of cyber-attacks and ensure that critical business functions can continue in the event of a security incident.
The defense-in-depth strategy provides organizations with a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. It allows them to protect better their data, systems, and reputation against cyber threats.
Explanation of the Benefits of Implementing a Defense-In-Depth Strategy
A defense-in-depth strategy provides several benefits for organizations that implement it:
Improved Security
This strategy offers multiple layers of security. That makes it harder for attackers to penetrate an organization’s network or gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Each layer provides an additional barrier. Thereby it reduces the risk of a successful attack.
Enhanced Resilience
In the event of a security breach, this security strategy mitigates the damage by limiting the scope of the attack. An organization can quickly detect and respond to threats because of its multiple-layer security strategy. It reduces the recovery time of an attack.
Regulatory Compliance
This security strategy helps organizations comply with various regulatory requirements. The regulatory requirements are the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Reduced Costs
While implementing this strategy, initial expenses are costly. But it saves the organization money in the long run. It reduces the risk of a security breach. Therefore by reducing the risk, organizations avoid the costs associated with data loss, system downtime, and reputational damage.
Improved Stakeholder Confidence
It demonstrates an organization’s commitment to cybersecurity. It enhances stakeholder confidence. Customers, partners, and investors are more likely to trust an organization since it has taken steps to protect their data and systems.
It is a security strategy that offers a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. That mitigates risk, complies with regulations, and enhances their overall security posture.
Real-Life Examples of Organizations That Successfully Used Defense-In-Depth Strategy to Protect Against Cyber Threats
Many real-life examples of organizations have successfully used a defense-in-depth strategy. They used it to protect against cyber threats.
Here are a few examples:
JPMorgan Chase
In 2014, JPMorgan Chase suffered a massive data breach that affected 76 million households and 7 million small businesses. After the breach, the company invested heavily in cybersecurity. And they implemented a defense-in-depth strategy. They focused on increased network segmentation and the use of multi-factor authentication. And they deployed more advanced intrusion detection systems. These measures helped the company prevent future attacks and protect customer data.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is a cloud computing platform that many businesses use to store and process data. AWS uses a defense-in-depth strategy. That strategy has multiple layers of security. The layers are firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls. AWS also employs a team of security experts to monitor the platform. And they respond to potential threats.
Australian Signals Directorate (ASD)
The ASD is an Australian intelligence agency. It is responsible for protecting the country’s national security interests. The agency uses a defense-in-depth strategy. That includes multiple layers of security. The layers are firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. The ASD also employs a team of cyber security experts responsible for monitoring the agency’s network and responding to potential threats.
Microsoft
Microsoft is one of the world’s largest software companies. And it has implemented a defense-in-depth strategy to protect against cyber threats. The company uses a variety of security measures. Those measures are network segmentation, access controls, and the use of multi-factor authentication. Microsoft also employs a team of security experts. And these experts monitor the company’s network and respond to potential threats.
These examples demonstrate that a defense-in-depth strategy can effectively protect against cyber threats. By implementing multiple layers of security and investing in advanced security measures, organizations reduce their risk of a security breach and protect sensitive data.
Implementation of Defense-in-Depth
Implementing a defense-in-depth strategy requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of an organization’s security needs. Here are some steps that can help organizations implement a successful defense-in-depth strategy:
Conduct a Risk Assessment
The first step in implementing it is to conduct a risk assessment. This Risk Assessment involves identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities to an organization’s network and data. A Risk Assessment helps an organization determine which security measures are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Develop a Security Policy
Once the risks have been identified, developing a security policy is next. That security policy needs to outline the security measures that will be implemented. The policy should include guidelines for password management, network segmentation, access controls, and other security measures.
Implement Multiple Layers of Security
This strategy requires multiple layers of security to be implemented. These layers include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, data encryption, and other security measures.
Train Employees
One of the critical aspects of implementing a security strategy is to train employees. Organizations must ensure that employees are appropriately trained in security best practices. Training employees involves training on password management, phishing awareness, and other security-related topics.
Regularly Monitor and Test Security Measures
This strategy requires regular monitoring and testing to ensure all security measures work effectively. It includes penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and other security testing methods.
Continuously Improve Security Measures
Finally, organizations should continuously improve their security measures to stay ahead of emerging threats. It involves upgrading security software, implementing new security measures, or improving employee training programs.
Implementing it requires a comprehensive approach to security that involves multiple layers of security. And it needs a commitment to continuous improvement. By taking these steps, organizations can better protect themselves against cyber threats. And they can safeguard their sensitive data.
Best Practices for Implementing a Defense-In-Depth Strategy
Implementing a defense-in-depth strategy is a complex process. That requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to keep in mind when implementing a defense-in-depth strategy:
Develop a Security Plan
Before implementing this strategy, it is essential to develop a comprehensive security plan. That plan must outline the organization’s security policies, procedures, and guidelines. The security plan should also identify potential risks and vulnerabilities. And it needs to guide how to mitigate them.
Implement Multiple Layers of Security
This security strategy requires multiple layers of security to be implemented. These multiple layers are firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, data encryption, and other security measures. It is important to ensure that these security measures are complementary and do not create conflicts or vulnerabilities.
Use Best-of-Breed Security Solutions
When selecting security solutions, it is important to choose best-of-breed solutions. And that is well-tested and proven to be effective. It is also important to ensure that these solutions are regularly updated and maintained.
Regularly Monitor and Test Security Measures
This strategy requires regular monitoring and testing to ensure all security measures work effectively. It may include penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and other security testing methods. Regular monitoring detects potential security breaches before they can cause significant damage.
Educate Employees
Employee training is a critical component of a defense-in-depth strategy. All employees should be trained on security best practices. The training must include password management, phishing awareness, and other security-related topics. Regular security training helps employees identify potential security risks and take appropriate action.
Perform Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits identify potential security vulnerabilities. And it ensures that security measures are working effectively. An independent third-party auditor should conduct audits. And the audits must ensure objectivity and impartiality.
Continuously Improve Security Measures
It requires a commitment to continuous improvement. Organizations should continuously evaluate and improve their security measures to stay ahead of emerging threats. This involves upgrading security software, implementing new security measures, or improving employee training programs.
By following these best practices, organizations can develop a strong security strategy. That protects against a wide range of cyber threats and helps safeguard sensitive data.
Challenges to Implementing a Defense-In-Depth Strategy
Implementing this strategy is essential for protecting against cyber threats. It can also be challenging. Here are some common challenges that organizations may face when implementing a defense-in-depth strategy:
Cost
Implementing it requires significant investment in security tools and technologies. And it needs regular maintenance and updates. This is expensive for organizations, particularly small and medium-sized businesses.
Complexity
This security strategy involves multiple layers of security. That can be complex to manage and maintain. It is important to ensure that all security measures are integrated. And it should be ensured to work together effectively to avoid conflicts or vulnerabilities.
Resistance to Change
Implementing it may require significant changes to an organization’s security policies and procedures and employee training programs. Some employees may resist these changes, particularly if they are accustomed to a different approach to security.
Lack of Expertise
Further, implementing it requires expertise in cybersecurity and knowledge of the latest security tools and technologies. Smaller organizations may not have the resources or expertise to implement this strategy effectively.
False Sense of Security
While a security strategy provides significant protection against cyber threats, it is important to remember that no security measure is foolproof. Some organizations may develop a false sense of security and neglect other critical security measures, such as employee training and regular security audits.
By understanding these challenges and developing a plan to address them, Organizations can implement a defense-in-depth strategy that effectively protects against a wide range of cyber threats.
Tips for Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Successful Implementation
Here are some tips for overcoming the challenges of implementing a defense-in-depth strategy and ensuring successful implementation:
Conduct a Risk Assessment
Before implementing that security strategy, it is important to conduct a comprehensive risk assessment. This assessment needs to identify the specific threats and vulnerabilities facing your organization. With it, you prioritize your security measures and allocate resources effectively.
Develop a Clear Plan
A clear and detailed plan is essential for implementing a defense strategy. This plan should include specific goals, timelines, and responsibilities. And also, it must have contingency plans for addressing any unexpected challenges.
Invest In Training and Education
It is vital to invest in training and education for all employees to ensure the successful implementation of this strategy. This one ensures that everyone understands their role in protecting the organization’s data and systems. And it prevents human error from undermining your security measures.
Prioritize Integration and Interoperability
It is important to prioritize integration and interoperability between security tools and technologies to avoid conflicts and vulnerabilities. This one ensures that your security measures are working together effectively to provide comprehensive protection.
Stay Up-To-Date With Emerging Threats and Technologies
Cyber threats are constantly evolving. So it is important to stay up-to-date with the latest threats and security technologies. With this strategy, you can identify new risks and opportunities for improvement. And it ensures that your strategy remains effective over time.
By following these tips and addressing the challenges of implementing the strategy, organizations can ensure that their systems and data get security against a wide range of cyber threats.
Defense-In-Depth Strategy Limitations and Draw Back
It provides comprehensive protection against cyber threats. But, there are also some limitations and drawbacks to consider. Some of the main limitations and drawbacks include:
Cost
Implementing a comprehensive defense-in-depth strategy is expensive. Since, it often includes investing in multiple layers of security tools and technologies. And also ongoing maintenance and training costs.
Complexity
This strategy is complex to implement and manage, especially if you are using multiple layers of security tools and technologies from different vendors. This one makes it difficult to integrate and optimize your security measures.
False Sense of Security
This strategy provides comprehensive protection against a wide range of threats. But, it also leads to a false sense of security. This may happen if organizations rely too heavily on their security measures and fail to adequately monitor and respond to threats.
User Error
Even with a comprehensive defense-in-depth strategy, human error remains a significant risk factor. Employees may inadvertently compromise security through actions such as using weak passwords or falling victim to phishing scams.
Lack of Standardization
There is no industry-wide standard for implementing a defense-in-depth strategy. Therefore, it is difficult to compare and evaluate different approaches. This lack of standardization also makes it challenging for organizations to ensure that their security measures are effective and up-to-date.
While this strategy provides comprehensive protection against cyber threats, it is vital to be aware of these limitations and drawbacks. And the organizations need to take steps to mitigate them where possible. This one includes investing in ongoing training and education for employees and prioritizing standardization and integration of security measures. And also, monitoring your systems and data closely for signs of threats or vulnerabilities is crucial.
Recap of the Importance and Benefits of Defense-In-Depth Strategy
Here’s a recap of the importance and benefits of a defense-in-depth strategy:
Comprehensive Protection
A comprehensive Protection strategy provides multiple layers of security to protect against a wide range of cyber threats. It is a more comprehensive approach than relying on a single security measure.
Reduces Risk of Successful Attacks
Implementing multiple layers of security reduces the risk of successful cyber attacks and data breaches.
Protects Against Different Types of Threats
Protects against Different Types of Threats have a wide range of security measures. They are such as network security, application security, data security, identity and access management, physical security, and incident response. This one ensures that your organization has enough protection against different types of cyber threats.
Increases Resilience
It increases the resilience of your organization’s security posture. And it enables it to withstand cyber attacks and recover from any resulting damage or disruption effectively.
Meets Regulatory Compliance
Many industry regulations require organizations to implement this strategy as part of their cybersecurity measures. They need to comply with these regulations so that organizations avoid legal and financial penalties, as well as reputational damage.
Overall, this security strategy is a critical component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. It provides comprehensive protection against cyber threats. It reduces the risk of successful attacks. And it increases resilience and ensures regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important in today’s world of interconnected technology. And a defense-in-depth strategy is a crucial component of any organization’s cybersecurity approach. Implementing multiple layers of security measures better protect organizations against the growing threat of cyber-attacks and data breaches.
From perimeter defense to incident response, each layer of defense serves a specific purpose in protecting critical assets and operations. The benefits of this security strategy include comprehensive protection. In addition, it reduces the risk of successful attacks. Besides, it protects the organization against different types of threats. Further, it increases resilience and regulatory compliance.
There are challenges to implementing a defense-in-depth strategy. But, organizations need to take the necessary steps to overcome these challenges. And they need to ensure successful implementation. By doing so, organizations protect themselves against cyber threats, safeguarding their critical assets and operations in a better way.
The threat of cyber-attacks continues to grow; therefore, implementing a defense-in-depth strategy is no longer an option. But it is a necessity. It is time for organizations to take action. And implement it to ensure the security and resilience of their operations.
Call of Action
The threat landscape is rapidly evolving, and cybersecurity is more crucial than before today. By implementing a defense-in-depth strategy, organizations better protect themselves against the growing threat of cyber-attacks and data breaches. This comprehensive approach to cybersecurity involves multiple layers of security measures, from perimeter defense to incident response, working together to create a strong and resilient security posture.
If you have not implemented it in your organization, then it is the right time to do so. Take the necessary steps to assess your organization’s security posture. Identify its potential vulnerabilities and threats. And implement the appropriate security measures to protect against them. Engage with cybersecurity experts and implement best practices to ensure a successful implementation.
Don’t wait until; it’s too late to protect your organization from cyber threats. Implement a defense-in-depth strategy today to ensure the security and resilience of your organization’s critical assets and operations.