Silicon Image, one of the founding fathers of HDMI standards, introduced a mobile interconnect in 2008 CES. This interface was termed as MHL or Mobile High-Definition Link. Mobile High-Definition Link is an industry standard that allows Smartphones, tablets, and other portable consumer electronic gadgets to the HDTVs, projectors, etc. Further, it is a consortium of five companies, namely Nokia, Samsung, Silicon Image, Toshiba, and Sony. It is straightforward to use technology that enables the clients to connect various mobile devices and consumer products to the display units such as TVs and monitors. In addition, it offers a zero-lag and flawless connection from mobile devices to TVs.
What is MHL?
This standard was designed in such a way that existing connectors in the device, such as Micro-USB. It eliminated the additional connectors on the device for video sharing. Since the mobile devices have limited space utilizing existing connectors, it is very much helpful. Mobile High-Definition Link connects your mobile device directly through Special MHL-enabled HDMI inputs or through MHL to HDMI adapters. It is connection agnostic.
What Are the Advantages or Benefits of MHL?
The MHL connections transmit control data seamlessly, which means the master remote controls your TV may also control the other connected device. Besides, it offers zero latency, which allows for a lag-free display. The cable can also charge mobile devices up to 40W without any subsequent lag while delivering the content.
The advantage of Mobile High-Definition Link is; it does not define a specific connector to connect your device. Instead, it maps the already existing connectors of your gadgets. For example, it is working perfectly with the USB 2.0 or 3.0. Mobile High-Definition Link protocol works hand in hand with HDMI protocol and the connectors.
Samsung Galaxy S II was the first device that featured Mobile High-Definition Link technology. It is an adoption of HDMI planned for Smartphones and tablets. Besides, it is compatible with HDMI only by using passive cables and adapters. Further, the HDMI socket must be Mobile High-Definition Link enabled. If not, an active adapter is required to convert signals to HDMI.
What is the similarity of MHL with HDMI?
Both of them carry uncompressed HDCP encrypted high definition video and audio. Further, it can carry eight channels of surround sound. Both of them can control all the connected devices with a single remote control with the help of CEC (Consumer Electronics Control)
What is the MHL alternative?
SlimPort is the MHL alternative. SlimPort implements video transmission up to 4k ultra HD and up to eight audio channels over the micro USB connector. In addition, it provides seamless connectivity between DisplayPort, HDMI, and VGA displays.
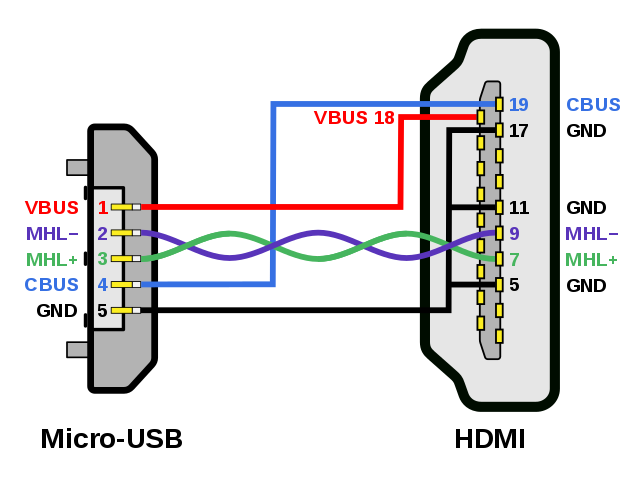
MHL Pin configuration and Working:
MHL ports are dedicated to Mobile High-Definition Link alone. But the standard is designed to permit port sharing with most commonly ports existing in use. The USB port automatically switches from USB to MHL once it recognizes the MHL signals and the MHL sink. An MHL sink can share with a standard HDMI 19 pins receptacle.
The sink needs to provide power maintain the system alive while it is in use. The system uses the default five pins of micro USB port which is typically use for charging the device.
In HDMI, there are 19 pins in total. Out of these 19 pins, Mobile High-Definition Link uses only five pins. One differential pair for data transmission pins, CBUS Channel (bi-directional control channel), power supply pin, and ground.
Since only five pins are used, it is possible to have a much smaller connector on the mobile device and makes the cable thinner as much as possible. MHL port will share USB 2.0 5 pins of Micro USB receptacle.
Working:
Both HDMI and Mobile High-Definition Link differ in the use of power lines. Mobile High-Definition Link 2 and 3 provide 4.5W/900mA of power supply. Whereas; the Super MHL can offer a maximum of 40W power in the supply line. The HDMI expects the maximum power from the source of 55mA for reading the EDID of the display source.
We already discussed that Mobile High-Definition Link is having much lower pin counts than the HDMI. Therefore it does some modification in the transmission of signals and sending and receiving data. In HDMI, pins 15 and 16 are used for DDC, and Pin 13 is meant for CEC. CBUS emulates these functions of DDC and CEC.
This bi-directional bus also carries the MHL sideband channel, which emulates the CEC bus function. MSC takes the role of CEC bus function to help you control the media player on your mobile device with the TV remote control using remote control protocol (RCP) protocol of your mobile phone.
MHL Bandwidth Protocol:
It uses the same TMDS for data transmission as the HDMI. In addition, it uses only one differential pair, whereas HDMI uses four. HDMI uses separate differential pairs for sending video, audio, and auxiliary data. In Mobile High-Definition Link, all these data are transmitted as time division multiplexed in a single MHL data lane. The logical channels are sent in sequence, and the clock signal is sent as a common node signal of the pair.
In the latest Mobile High-Definition Link 3 versions, the clock signals are transmitted separately on the CBUS pin. The same 24-bit mode operates at 2.25 Gbit/s, at a pixel clock rate of 75 MHZ on the multiplex data transmission. It is enough for 1080 interlaced and 720p at 60 Hz. One period of the MHL Clock is equal to the one period of the pixel clock. Further, it can operate in PackedPIxel mode at Three Gbits per second to display 1080 progressively displayed pixels.
In Packedpixel mode, only two channels are multiplexed, and the color signals are sent as chroma subsampled pairs adjacent 16- bits pixels. The adjacent pixels share chroma values with only 36-bits, and the pixel clock is doubled to 150MHZ. In this packed pixel mode, the clock period is doubled so that the MHL clock can transmit twice the number of channels.
Mobile High-Definition Link Version 3 changed to packet-based technology from frame-based technology. It operates at the speed of 6 Gbits per second. The SuperMHL extends this further by carrying the data singles over more than one differential pair up to four with USB C type.
MHL Versions and Specifications:
All its specifications are backward compatible with the previous versions. In addition, it is not tied to a particular type of hardware connector. The first implementation of their version used the five-pin MHL USB connector. Further other proprietary and custom connections are also allowed and accepted.
Version 1:
- It was first introduced and implemented in 2010.
- Supports uncompressed H/d video up to 720p/1080i 60Hz
- Minimum charging supply to 2.5 W (500 mA) between sink and source
- RGB and YCbCr 4:2:2/4:4:4 pixel encoding
- Support for 1080p 60 Hz YCbCr 4:2:2 pixel encoding
- 192 kHz 24-bit LPCM 8-channel surround sound audio
- Supports standard SD and HD color specification
- Supports xvYCC, sYCC601, Adobe RBC, and AdobeYCC601
- HDCP
- MSC includes an in-built remote control protocol
Version 2:
- Minimum charging supply to 4.5 W (900 mA) between sink and source
- Introduced support for 3D videos
- Allowed 1080p 24 Hz 3D video modes
- Included additional sideband channel commands
Version 3:
- Supports 4K ultra HD
- Bandwidth increased from 3 Gbits per second to 6 Gbit per second
- Introduced additional YCbCr 4:2:0 pixel encoding for 4K resolution
- Minimum charging supply to 10 W (2 A) between sink and source
- Supports compressed lossless audio formats
- Speed of bi-directional data channel increased to 75 Mbits per second
- Improved RCP
- Four display units can connect in series
- HDCP 2.2 content protection
- Other features added for simultaneous multiple displays
SuperMHL 1.0:
- Supports 8K Ultra HD 120HZ HDR video with the wide color gamut
- Deep Color support to the maximum of 48-bit color depths
- Backward compatible to 1, 2, and 3 version specifications
- Content on multiple displays when connecting a single source device
- High-Dynamic Range (HDR) support the perfect balance of bright spectral highlights with accurate shadow details
- Enhanced audio performance for immersive surround sound including Dolby Atmos, DTS:X, 3D audio, and an audio-only mode too
- Included object-based audio formats
- Remote Control Protocol extended to multiple Mobile High-Definition Link devices together
- Introduced reversible 32- pin SuperMHL connecter
- Higher charging power of 40 W (20V/ 2A)
- Bandwidth increased by using multiple A/V lanes
- Supports visually lossless video compression standard
- Supports MHL Alt Mode for the USB Type-C specification
- Eight display units can connect in series
MHL Types of connectors Employed:
Micro-USB-to-HDMI (five-pin):
For this first implementation, there are two types of connection depending on whether the display device supports Mobile High-Definition Link or not.
Passive Cable:
The passive cables allow the Mobile High-Definition Link supporting devices to connect directly to the Mobile High-Definition Link enabled display devices and AV receivers via an Mobile High-Definition Link enabled HDMI port. Mobile High-Definition Link signaling use through the connectors over the cable when providing charge upstream to the mobile device.
Active Adapter:
With the help of the active adapter, Mobile High-Definition Link devices can connect to HDMI display devices that do not have the Mobile High-Definition Link capability by converting their signal to HDMI. Most of the adapters have an additional micro USB port on them to provide charging for the mobile gadget since HDMI ports do not have sufficient power.
Samsung Micro-USB to HDMI Adapter (Eleven-Pin):
Some of the Samsung products use an 11-pin connector. The additional six pins are to get some functional improvements over the five-pin strategy. The customers need to buy an Adapter since most of them have a standard Mobile High-Definition Link to HDMI adapter. Even Samsung released Mobile High-Definition Link 2.0 adapter that does not require any external power. Their smart adapter for the 2.0 version is an 11- pin connector.
USB Type-C (Alternate Mode)
The alternate mode for the USB 3.1 specification allows the Mobile High-Definition Link-enabled source and display devices to connect through the USB C port. It is backward compatible. Besides, The standard enables simultaneous data transfer.
Moreover, the power charging is up to 40W. Therefore, it allows the connections to use the docks of your Smartphones and laptops. It will enable the devices to connect to other network peripherals while charging. You can use the passive cables both devices supports the Mobile High-Definition Link standard. Otherwise, an active adapter need to be connect both of the devices.
Depending on the bandwidth requirement, the standard uses different numbers of differential pairs to carry TMDS signals. A single lane require for up to 4K /60HZ and two lanes for 4k/120HZ resolutions and more.
- 4K /60Hz over a single lane
- 8K/60Hz over four lanes
- Supports Immersive audio such as Dolby Atmos, Dolby Digital, DTS:X, etc.
- USB 2.0 and USB 3.1 Versions 1 or Version 2
- Power charging
- Use of existing master remote to control Mobile High-Definition Link phone (RCP)
- Backward compatibility with existing Mobile High-Definition Link specifications
32- Pins superMHL:
It can carry six A/V lanes over six differential pairs to utilize the total bandwidth of 36 Gbits per second. Besides, it also enables 40W of power at higher voltage and current.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is “mobile InterConnect”?
In telecommunication technologies, interconnect, or interconnection, is a physical linking network carrier with the gadgets or the facilities that do not belong to that network.
What is Miracast?
Miracast is a wireless communication standard for sending devices to display receivers. In layman’s words, it is the technology HDMI over Wi-Fi. It replaces the cabling of the source and sink. Further, It employs the standard Peer to Peer Wi-Fi Direct. In addition, It creates the connection via WPS. It is more secured with WPA2.
What is the Alt Mode for USB Type C?
Alt Mode for USB Type C enables devices to support simultaneous Mobile High-Definition Link audio-video and further USB 2.0 and USB 3.1 Versions 1 or Version 2 data transfer and power charging over the c type connector.
Can devices with MHL Alt Mode connect to HDMI displays?
Yes, all gadgets supporting MHL Alt Mode over a USB C type connector can use Mobile High-Definition Link to HDMI adapter to connect the HDMI displays.
Does MHL work with all TVs/Monitors/Projectors?
Yes, it works with all Mobile High-Definition Link displays, monitors, and projectors. Besides, you can use an Mobile High-Definition Link cable to avail the features. However, if you have an HDMI display unit, then you need to use an Mobile High-Definition Link-to-HDMI adapter.