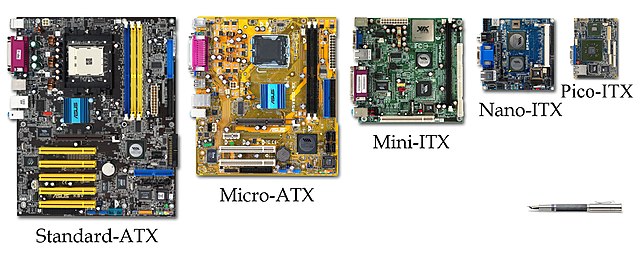
Are you interested in building a PC for gaming or productivity? If yes, then this article is for you. Hence, you can observe the difference between motherboard sizes and PC component sizes (and shapes). As a beginner, it can confuse you a lot. Let us know what is Motherboard Form Factors or motherboard sizes in this blog post.
Once you start a little bit of digging, you will find that several components are compatible with each other. You only need to settle on a CPU, motherboard pairing of the same socket type, and RAM. Once done, you can put these together easily. This article covers different motherboard sizes, pros & cons, and which one you should choose based on your needs.
ATX is a very common term when people discuss motherboards. Do you know what it is? This one is an Intel-coined term which is the abbreviation of Advanced Technology eXtended. It indicates an industry standard related to motherboard and power supply compatibility.
Different Motherboard Sizes or Motherboard Form Factors
Before looking for the best motherboard for a PC build, you should know some facts about motherboards, like size and form factor. Have you decided what you want to build— a small PC, or a standard one, or a full-tower? Based on the needs, you should decide the correct motherboard size to fit in the chassis while still offering the ultimate performance.
If you consider form-factor, use E-ATX, ATX or other large motherboards. These have sufficient space for multiple expansion slots, RAM slots, and other components. So it is possible to produce a strong build. On the flip side, you can have fewer ports for expansion cards, if you go with smaller motherboard options such as a micro-ATX or mini-ITX.
ATX:
This kind of board comes in 305mm in height and 244mm in width, or 12 x 9.6 inches.
If you are planning a build, pairing this with an ATX-compatible PC case is essential. These can be super-towers, or full-towers, or middle-towers, or mini-towers. If these are built to support the ATX format, then the board can fit 10/10 times.
It can run all sorts of systems. This board has at least four RAM DIMMs and supports dual or quad-channel memory. Thus, it can offer enhanced performance in particular applications over a board which is incompatible with this kind of configuration.
The seven expansion slots of ATX boards allows you to run up to four GPUs with Nvidia SLI or AMD Crossfire when the power supply & case are suitable for powering and housing such a system. More expansion slots let you install different upgrades, such as a better network card supporting WiFi, Bluetooth adapters, sound cards, USB hubs, etc.
This motherboard offers manufacturers sufficient space to install large heatsinks, an intricate VRM or voltage regulator module, a bigger rear IO, and more SATA and USB header connectors. These are enough to deliver an improved experience.
But you will find heat issues exist with these motherboards.
The heat problem was so serious that Intel launched a new BTX motherboard series in 2005 to deal with the heat problems and exchange the ATX form factor.
A 24-pin connector with a 6/8-pin connector is used to power these boards for the CPU. Thus, you can run high-end processors. It is even possible to overclock processors on unlocked motherboards.
Pros:
- A complete IO
- Enough room for heatsinks
- Good VRM than smaller boards
Cons:
- Unable to fit into compact form-factor cases
- Costlier than mATX and mini-ITX motherboards
Extended ATX (EATX):
These come in larger sizes measuring 305x330mm (12 x 13 inches rather than 12 x 9.6). Sometimes, these come with dual-socket support, with the help of which it is possible to run two CPUs using the same board. But it isn’t always the case.
Pros:
- Compatible with dual sockets
- More RAM DIMMs and connectors
Cons:
- Fewer products on the market
- Don’t fit in some PC cases
XL-ATX:
Unlike other motherboard sizes, these boards don’t abide by standard width and height. These are very rare, and only some manufacturers released them previously. Except for making strong workstations with more memory DIMMs (up to 8), these don’t offer any clear advantages. That’s why these motherboards are disappearing gradually from the market.
Pros:
- Supports more memory
Cons:
- Can’t fit in most cases
- Very rare
Micro ATX (mATX):
These boards come in a square shape with a measurement of 244x244mm (9.6×9.6 inches). Micro ATX boards contain between 2-4 RAM DIMMs which are suitable for those who want a powerful PC in a compact case. Up to 4 expansion slots allows you to run dual-GPU systems in a few cases. Manufacturers often provide additional features, such as default WiFi with this card type. Therefore, there is no need to use any expansion slots to have this feature.
If it comes to talk about build quality, motherboards which are on par with top-quality ATX boards are available at the same price range. Losing some inputs & outputs provides a smaller form factor. As a result, you can get access to an entirely new lineup of PC cases to build in. If you are going to build in a small form-factor case, you should give sufficient time to cable management for enhanced airflow. Besides, it is essential to invest in the correct components.
Pros:
- Has the ability to get included in more compact cases
Cons:
- Not suitable for high overclocks
Mini-ITX:
These boards measure 170x170mm (6.7×6.7 inches). Mini-ITX boards are the smallest type of board which are still able to run full-sized PC components.
These contain two RAM DIMMs with a single expansion slot. However, it doesn’t support multi-GPU configurations and doesn’t have enough power for running top-quality processors. Therefore, a 4-pin connector is used to power most boards. But it limits the type of hardware that can be run efficiently on a motherboard. As the central processing unit is more power-efficient, you can see many boards letting you overclock.
In most cases, the modern consumer and enthusiast PCs come with Standard-ATX motherboards of 305 x 244 mm or 12 x 9.6 in. You can increase expansion and customize options also. Remember that the component number on ATX boards indicates that these need more power and cooling. If you are looking for an alternative to ATX, then Micro-ATX is an excellent option. It can reduce the board size to 244 × 244 mm or 244 × 205 mm.
For several industrial system builders, Mini-ITX draws an outstanding balance of performance, size, and cooling options. You can find several motherboard sizes and single-board computing (SBC) solutions, such as Raspberry Pi. These offer a package including a motherboard, storage, memory, and onboard processing.
Pros:
- Very compact
- Run a fully-fledged PC
Cons:
- Limited IO
- Not ideal Power delivery for top-quality components
Mini-STX:
The next type of motherboard about which we will discuss is Mini Socket Technology, Extended or Mini-STX motherboards, known as Intel 5×5. The board measures 147 mm×140mm, which is 5.8″× 5.5″ (L×W). NUC or mini-ITX, or other small form factor boards come in a square shape. But this one is 7mm longer from front to rear. As a result, the shape becomes rectangular.
The main motive behind the 5×5 form factor is to offer PC builders a motherboard that I’d equipped with an upgradeable LGA socket that remains under the ultra-compact volume benchmark of one liter. The main intention of Intel behind creating Mini-STX is to produce a platform which was smaller than the basic motherboard designs of that time but still had the hardware to pack a good performance.
As of today, ASRock only produces the motherboard of this form factor still now, and even it doesn’t get updated for the newest Intel sockets. Moreover, the proprietary Nvidia MXM GPU modules which were used with this motherboard have been discontinued. So we can say that this motherboard is almost dead unless ASRock introduces something new.
Nano-ITX:
In 2003, VIA Technologies introduced this form factor. The measurement of this board is 120 x 120 mm (4.72 x 4.72 in). As these saw a few early adoptions in Digital Entertainment, these now support only a few specific hardware components. These are ideal for building small PCs and smart entertainment purposes, including PVRs, smart TVs, or automation.
Pros:
- Budget-friendly
- Compact
Cons:
- Don’t support all standard PC components
Pico-ITX:
VIA Technologies introduced these in 2007. It measures 100 x 72 mm (3.94 x 2.83 in). These boards are deployed in embedded tasks because of their small footprint.
Pros:
- Perfect for small IoT devices
- Less complicated to use
Cons:
- Support a limited range of hardware
Intel NUC:
In 2013, these were launched. The measurement of the board is 101.16 x 101.16 mm (4 x 4 in). These are used widely for consumer and commercial tasks.
What do you know about VRM and Why It’s Critical?
VRM is comprised of MOSFETs, chokes, and capacitors, which are essential in power distribution from the motherboard to the other components. You should know that MOSFET is the abbreviation of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors.
It is essential to confirm that the processor runs efficiently at a stable current. MOSFET amplifies the electronic signal to match the component’s requirements, like the power supply converting the alternating currents to make it direct.
The chokes serve as inductors to limit the direct passing current to a certain frequency. It can ensure a stable voltage when it gives power to the CPU. The working process of transistors is the same.
Pick up a model with an intricate VRM if you decide to purchase a premium gaming motherboard or a clean business-branded model at good prices. You will get better performance when there are more chokes, MOSFETs, and transistors.
Ensure that the upcoming boards come with solid-state transistors. In this regard, you should know that Fluid-based transistors might burst. As a result, these can throw acid onto the components, damage circuits, and cut off power to several board sectors.
Which Motherboard Form Factors Should You Choose?
We have given detailed information regarding the specifications and qualities of the different types of motherboards and their sizes. Now, it’s up to you which motherboard. You should purchase and for which purpose you should use. We have already mentioned that each motherboard has its strengths and weaknesses.
So, which motherboard you should purchase depends on your workflow and the number of PCIe and RAM slots you use. To make your task of buying a motherboard easier, we are going to divide this section into 3 parts.
For Budget PC Build:
People looking for a PC at affordable prices need to keep in mind that a considerable amount of money will go towards the processor and the graphics card. So, you should pick a Micro-ATX motherboard. Remember that rather than other components, processor and graphics cards can have much of an impact on the regular performance. So, these components form the base for storage, memory, and other components. Remember that to use other PC parts completely, you must have a good CPU and GPU.
Therefore, when you are going to buy a PC, invest your money mainly on these two components. However, you should check the quality of other components also. These motherboards are available at 30-40% lower prices than their full-size counterparts.
The best thing is these come with all the major features which ATX motherboards have. But what makes them different is that the full-size ATX boards can offer better thermals due to having more VRM and MOSFET modules physically. It is also capable of physically incorporating more PCIe slots.
Remember that these features are important but not so useful if it comes to talking about budget builds. However, you should know that budget CPUs don’t come with the overclocking headroom which is required for making full use of the VRM solution of ATX boards.
For High-End Gaming PC Build—
Purchasing a full-size ATX motherboard is essential if you have high-end gaming PCs. It can offer up to 7 PCIe slots. Top-quality gaming PCs have a lot of differences from their budget counterparts. People use multiple graphics or expansion cards in their high-end gaming PCs, and it is quite common. If you want the ultimate performance, you should choose overclocked high-end gaming PCs. It indicates that your motherboard must come with a strong power delivery system to fulfill the enhanced power requirements.
Hence, you should select the full-size ATX motherboard. The availability of up to 7 PCIe slots allow you to have many GPUs and install other add-on cards such as capture cards, PCIe SSDs, or 10-gigabit network cards.
For Small Form-Factor PC Build:-
In this case, you should purchase a mini-ITX or micro-ATX motherboard, if you are willing to build a PC with a smaller footprint. People looking for a more minimalist design can choose a smaller mini-ITX or micro-ATX motherboard.
It is the most suitable option for those willing to save a little money & space but want to have the strongest components. Remember that multiple choices are not available when it comes to selecting the motherboard and case. Hence, the cooling and storage might not be as costly as these would be for a larger design.
Whether you are willing to choose the smallest build without selecting a proprietary solution such as an Intel NUC or a Corsair one, you should choose these Mini-ITX motherboards.
Conclusion:
Choosing the motherboard’s sizes depends on personal preference. You should use a small form-factor PC when you work in your home or office. However, mini-ITX boards could be your automatic choice if you are willing to run demanding software with a compact build. In this article, we have discussed the specifications and qualities of the different types of motherboards and their sizes. Now, choose your required one as per your preference.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What size should your motherboard be?
The usual size of the motherboard is 12″ × 9.6″ for ATX.
- What are motherboard sizes in CM?
The size of ATX motherboards is 30.5cm x 24.4cm. You can use these inside mid or full-tower cases.
- What does ATX stand for?
Advanced Technology Extended is the standard form of the term ATX.