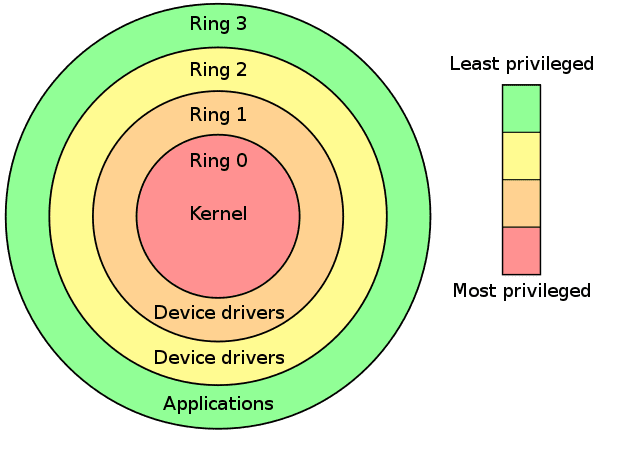
Introduction to the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP)
The Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is a fundamental concept in information security. It aims to limit access rights and permissions to only those necessary for users to perform their job functions. In other words, users are granted the least privilege needed to complete their tasks. That helps to minimize the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. The Principle of Least Privilege is a cybersecurity best practice. And it is a fundamental tenet of a zero-trust security strategy. It enhances the security of an application, network, or technology environment.
The concept of POLP is based on the idea that the more access a user has, the more damage he could potentially cause. Users can misuse that access or his credentials are compromised. Organizations reduce the attack surface by limiting access to only what is necessary. Besides, these limit the potential damage from security incidents. In cybersecurity, the Principle of least privilege is the best practice of restricting account creation and permission levels to only the resources a user requires to perform an authorized activity.
In this article, we will explore how POLP works. What are its benefits? And let us know how it can be implemented in different organizations to improve their information security.
It is the principle or a security architecture that is designed so that every entity is granted the minimum system resources and authorizations that the entity needs to perform its function.
Definition of POLP
The Principle of Least Privilege is the fundamental principle of Zero Trust Network Access. The Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is a security principle that dictates that every user or process in a system should have only the minimum level of access, permissions, or privilege. That is necessary to perform their job functions. The principle is based on the premise that limiting access reduces the risk of unauthorized access, misuse, and potential damage to the system or organization. POLP is a critical component of access control and authorization. It is also used to protect confidential information, prevent data breaches, and maintain the integrity of a system.
What is the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP)?
The principle of least privilege is also referred to as the principle of minimal privilege (POMP) or the principle of least authority (POLA). It is considered a best practice in information security. The principle of Least Privilege is often referred to us as POLP. It is a cybersecurity concept. It refers to the concept and practice of restricting access rights to user accounts and computer processes to only those resources that are absolutely required to perform activities.
The POLP model entails enforcing the minimal level of user rights. That allows the users to perform their routine functions. It also applies to processes, applications, systems, and devices. And each should have only those permissions required to perform an authorized activity. The Least Privilege enforcement requires a way to manage & secure privileged credentials centrally, along with flexible controls. That can balance cybersecurity and compliance requirements with operational & end-user needs. It minimizes the permissions so that the organizations can limit the harm if a security breach occurs. It also limits the risk of privilege abuse by limiting the privileges granted to users or applications.
Explanation of How POLP Can Prevent Security Breaches
It is a critical component of a comprehensive security strategy that prevents security breaches in several ways.
It is a fundamental principle of information security. It prevents security breaches by limiting access rights and permissions to only those necessary for users to perform their job functions. This principle is based on the idea that the more access a user has, the more damage they could cause. They can misuse that access or their credentials are compromised. Therefore, limiting access to only what is necessary is critical to a comprehensive security strategy.
Limiting the Attack Surface
One way that POLP prevents security breaches is by limiting the attack surface. The attack surface refers to the points of entry that attackers use to access sensitive data, systems, or networks. It reduces the number of entry points. Or limit the access of users to only what is necessary. Thereby, organizations reduce the attack surface. And PLOP makes it more challenging for attackers to gain access. This makes it less likely for security breaches to occur. It also reduces the impact of successful security incidents.
Reducing the Impact of Security Incidents
Another way that POLP prevents security breaches is by reducing the impact of security incidents. If a user’s account or credentials are compromised, the damage that can be caused is limited by the least privilege principle. For instance, if a user has read-only access to a database, a hacker who gains access to that user’s account will be limited to reading the data. And the hacker won’t be able to make changes or delete data. It reduces the impact of the security incident. And it prevents or limits the potential damage caused by the security breach.
Preventing Insider Threats
It also prevents insider threats. Insider threats refer to employees or contractors with malicious intentions who could intentionally or unintentionally cause harm to the organization. Limiting users’ access to only what is necessary for their job functions prevents insider threats. Restricting the ability of employees to access sensitive data or systems, they don’t need to perform their duties can limit the damages.
Enforcing compliance
It helps organizations meet regulatory and compliance requirements. It ensures that users only have access to the data and systems they need to perform their job functions. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI-DSS requires organizations to maintain data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Limiting access and permissions to only those necessary for users to perform their job functions help organizations meet these requirements.
It is a critical component of information security that prevents security breaches. And it limits the potential damage from security incidents. Further, it prevents insider threats and ensures compliance with regulations. It limits access rights and permissions to only those necessary for users to perform their job functions. Limiting access rights reduces the attack surface. It maintains the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. Further, it protects their systems and networks from unauthorized access.
How does POLP Work?
POLP is a security principle that ensures that users or processes have access only to the minimum level of resources and permissions necessary to perform their job functions. It minimizes the potential damage that could be caused by a user or process in the event of a security breach or accidental mistake.
So, to understand how POLP works, it’s important to understand the concept of access control. Access control is a process that restricts access to resources or data within a system. It ensures that only authorized users have access to the data, systems, or networks needed to perform their job functions. Access control is implemented at different levels, such as physical, network, application, and data access.
It is a specific type of access control. This one grants the minimum level of access required for each user or process to perform their duties. It limits the access of users or processes to only the resources or data that they need to perform their tasks. If a user’s account or credentials are compromised, the damage that can be caused is limited by the least privilege principle.
To implement POLP, an organization needs to perform the following steps:
Identify and Classify the Resources
The first step is to identify and classify the resources. The resources are data or systems that require access control. Identifying sensitive data includes identifying sensitive data, systems, or networks that need to be protected from unauthorized access.
Identify and Classify the Users
The second step is to identify and classify the users who need access to the resources. It is identifying their job functions, roles, and responsibilities. By doing this, an organization determines the level of access required for each user.
Grant the Minimum Level of Access
After identifying the resources and users, an organization grants the minimum level of access necessary for each user to perform their job functions. It means that users are only granted the permissions they need to perform their duties and no more.
Review and Update Access Regularly
Access control is an ongoing process. And access needs to change over time. It’s important to regularly review and update access to ensure that users still require the same level of access. And it needs to revoke access when it’s no longer needed.
By implementing it, an organization reduces the risk of unauthorized access, misuse, and potential damage to the system or organization. POLP helps organizations to meet regulatory and compliance requirements, protect confidential information, and prevent data breaches. Also, it helps to maintain the integrity of a system.
It is a security principle restricting access to the minimum level required for each user or process to perform their duties. By limiting access, an organization reduces the risk of security breaches. And it protects their sensitive information. Implementing POLP is an important step in securing a system and maintaining data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Explanation of Access Control and Authorization
Access control and authorization are essential concepts in computer security. They protect resources and data within a system from unauthorized access.
It is the process of limiting access to resources, data, or systems. This one involves using various security mechanisms and policies to control who can access a system or a specific resource within a system. Access control is implemented at different levels. The limiting levels employed are physical access, network access, application access, and data access.
It is the process of granting or denying access to a specific resource or data within a system. It is based on the access control policies. Authorization determines whether a user or process has the necessary permissions to access a resource. Authorization is implemented through various methods. The methods are Role-Based Access Control or RBAC, Mandatory Access Control or MAC, Discretionary Access Control or DAC, and Attribute-Based Access Control or ABAC.
In RBAC, access to resources is granted based on the user’s role or job function. In MAC, access to resources is determined by system administrators based on the classification of the data or resource. In DAC, access to resources is granted based on the discretion of the resource’s owner. In ABAC, access to resources is granted based on attributes assigned to a user or process. Those attributes are their location, time of day, and device.
Access control and authorization work together to ensure that only authorized users or processes can access resources and data within a system. By implementing access control and authorization policies, organizations protect sensitive information. And they prevent data breaches and maintain the integrity of a system.
Explanation of Access Control and Authorization in POLP
Access control and authorization are fundamental components of the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) security principle. POLP is a specific type of access control that limits the access of users or processes to only the resources or data that they need to perform their tasks.
In POLP, access control and authorization work together. And they ensure that users or processes are granted the minimum access required for each task. Access control restricts access to resources, data, or systems. It is based on the user’s role, job function, or other attributes. Authorization is then used to grant or deny access to a specific resource or data within a system based on access control policies.
For example, an organization has a database that contains sensitive customer information. The access control policies are set up to restrict access to the database. It restricts access to only those users who need to access it to perform their job functions. Access to the database is granted based on the user’s role, job function, and other attributes. The authorization policies are then set up to grant or deny access to specific data within the database based on the user’s level of access.
If a user’s account is compromised, It ensures that the damage that can be caused is limited by the least privilege principle. The user will only have access to the minimum level of resources. And the user has the permissions necessary to perform their job functions. It minimizes the potential damage that the user could cause. In the event of a security breach or accidental mistake happens.
By implementing access control and authorization in POLP, an organization ensures that users or processes are only granted access to the resources or data that they need to perform their tasks and no more. It reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Further, it reduces misuse and potential damage to the system or organization. POLP helps organizations meet regulatory and compliance requirements. It protects confidential information. Further, it prevents data breaches. And it maintains the integrity of a system.
Discussion of Permissions and Levels of Access in POLP
In it, permissions and levels of access are crucial. It ensures that users or processes have the minimum access required to perform their tasks.
Permissions refer to the specific actions a user or process can perform on a resource or data within a system. Permissions are granted or denied based on the access control and authorization policies.
Levels of access refer to a user or process’s access to a resource or data within a system. Access levels are classified as read-only, write, execute, or delete. It depends on the type of resource or data.
In POLP, users or processes are only granted the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. It means that a user only needs to read data from a resource. They will not be granted write or delete permissions. Similarly, if a process only needs to execute a specific command, permission will be granted for that process only. It will not be granted permission to access other resources or data within the system.
POLP limits the permissions and levels of access. It ensures that users or processes can only perform actions necessary for their job functions. Thus, it reduces the risk of unauthorized access, misuse, or damage to the system or organization.
In addition, it helps organizations meet regulatory and compliance requirements. The requirements include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It ensures that only authorized users or processes can access sensitive data and resources.
Implementing permissions and levels of access in POLP is crucial. It ensures that users or processes have the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. Thereby, it reduces the risk of security breaches and maintains the integrity of a system.
Examples of How POLP Can Be Implemented in Different Scenarios
It is implemented in various scenarios to reduce the risk of security breaches. And it is implemented to maintain the integrity of a system. Here are some examples of how POLP can be implemented in different scenarios:
Operating Systems
POLP is implemented in an operating system by using access control mechanisms. The access control mechanisms are user accounts, groups, and permissions. User accounts are created for each user. Also, groups are created to group users with similar access requirements. Permissions are then assigned to the user accounts and groups to control access to files, directories, and other system resources. For example, a user account could be granted read-only access to a specific file or directory. Whereas another user account could be granted read and write access. In addition, operating systems can also use privilege separation to separate privileged and non-privileged processes. It ensures that non-privileged processes cannot perform privileged operations.
Cloud Computing
In a cloud computing environment, it is implemented by using cloud service provider access control mechanisms to control access to cloud resources. Cloud service providers offer access control mechanisms. They are access policies, roles, and permissions to control access to virtual machines, databases, storage accounts, and other cloud resources. Access policies define who can access a particular resource. Their roles define a set of permissions for a specific job function. and the permissions define what actions can be performed on a resource. Cloud administrators use these access control mechanisms to ensure that users and processes have only the access they need to perform their job functions.
Web Applications
In a web application, it is implemented by using role-based access control (RBAC) to control access to application features and functionality. RBAC assigns users to roles based on their job functions. And each role is then granted a specific set of permissions to perform certain actions within the application. For example, a customer service representative might view and modify customer information, while an administrator might have access to modify system settings. By using RBAC, web application administrators ensure that users have only the access they need to perform their job functions and no more.
Database Management
In a database management system, it is implemented using access control mechanisms. The access control mechanisms are user accounts, groups, and privileges to control access to data. User accounts are created for each user, and groups are created to group users with similar access requirements.
Privileges are then assigned to the user accounts and groups to control access to tables, views, and other database resources. For example, a user account could be granted read-only access to a specific table. While another user account could be granted read and write access. In addition, database administrators can also use database views to control access to sensitive data. It ensures that users have only the access they need to perform their tasks.
Implementing POLP in different scenarios requires identifying the resources and data users or processes need to access. It is setting up access control and authorization policies. And it limits the permissions and levels of access to the minimum required for each task. By doing so, organizations can reduce the risk of security breaches. And they can prevent data loss. Further, they can maintain the integrity of their systems.
Benefits of POLP
Implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) provides several benefits to an organization, including:
Improved Security
POLP limits the permissions and access levels of users. And it allows processes only what is necessary. Further significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and unauthorized access. It means that even if an attacker gains access to a system, they will only have limited access to resources. And, therefore, will not be able to compromise the entire system.
Reduced Data Loss
POLP helps to prevent data loss by ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive data. It reduces the risk of accidental or intentional deletion or modification of critical data.
Increased System Integrity
It also helps maintain the integrity of a system by preventing unauthorized changes to critical system files and configurations. It limits the permissions and access levels of users and processes. It ensures that changes to system files and configurations are made only by authorized personnel.
Compliance with Regulations
Many industries and organizations are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate access control mechanisms to protect sensitive data. Organizations implement POLP to ensure that they comply with these regulations and avoid potential penalties.
Improved Accountability
It also helps improve accountability within an organization by providing an audit trail of all system access and activity. It enables administrators to identify any unauthorized access attempts and take appropriate action.
Implementing POLP can provide several benefits to an organization. It includes improved security, reduced data loss, and increased system integrity. Further, it helps organizations to comply with regulations and improve accountability. It limits permissions and access levels to only what is necessary. Thereby organizations significantly reduce the risk of security breaches. And they block unauthorized access and ensure their critical data and systems’ confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Improved Security
One of the most significant benefits of implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is improved security. POLP helps organizations to reduce the risk of security breaches and unauthorized access. It limits the permissions and access levels of users and processes to only what is necessary for their specific tasks.
By limiting the access of users and processes, it prevents unauthorized modification of critical system files and configurations. It ensures that users and processes can only access the resources needed to perform their tasks. This means that even if an attacker gains access to a system, they will only have limited access to resources. Therefore, the hacker will not be able to compromise the entire system.
In addition, it also helps organizations to identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities more easily. It limits the permissions and access levels of users and processes. So that organizations can more easily identify any unusual or suspicious activity on their systems. That can be an indication of a security breach or attempted unauthorized access.
Implementing Principle of Least Privilege can significantly improve the security posture of an organization. And that help protects against various threats, including malware, hacking, and insider threats.
Reduced Data Loss
Another significant benefit of implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is reduced data loss. POLP ensures that only authorized users have access to sensitive data. That reduces the risk of accidental or intentional deletion or modification of critical data.
It limits the access of users and processes to only what is necessary. It helps organizations to protect their data from unauthorized access or modification. This means that even if a user’s account is compromised, the attacker cannot access sensitive data since they do not have permission to access it.
In addition, POLP helps organizations to prevent accidental data loss. For example, suppose a user accidentally deletes a critical file or unintentionally modifies an important document. In that case, Principle of Least Privilege can limit the damage by ensuring that the user only has access to the resources that they need to perform their tasks and no more.
Organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data loss and ensure their critical data’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability by implementing POLP. It prevents financial loss, reputational damage, and other negative consequences. That can result from data breaches or accidental data loss.
Increased System Integrity
Implementing, the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) helps to increase the integrity of a system. Limiting the permissions and access levels of users and processes to only what is necessary. POLP ensures that only authorized personnel can change critical system files and configurations.
It helps to prevent unauthorized modifications to critical system files. That results in system failures, crashes, and other types of disruptions. It limits access to system files and configurations. And it ensures that changes to these files are made only by authorized personnel who have been trained and approved to make such changes.
Furthermore, it prevents accidental modifications to critical system files and configurations by limiting access to only necessary information. Principle of Least Privilege prevents well-intentioned but inexperienced users from making changes that could have unintended consequences.
Overall, implementing POLP can help organizations to maintain the integrity of their systems and ensure that critical system files and configurations are protected from unauthorized or accidental modifications. It prevents system failures, data loss, and other negative consequences. That can result from unauthorized modifications to critical system files.
Compliance with Regulations
Implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) helps organizations to comply with various regulations and standards. Many regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation or GDPR and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard or PCI DSS, require organizations to implement access controls. It limits the permissions of users and processes to only what is necessary.
Organizations ensure that they comply with these regulations and standards by implementing POLP. And it avoids potential fines or other penalties for noncompliance. In addition, implementing POLP helps organizations to demonstrate to auditors and other stakeholders. They have implemented appropriate security controls and are taking steps to protect sensitive data.
Furthermore, implementing it helps organizations comply with internal policies and procedures. By limiting access to only what is necessary, organizations ensure that their employees follow established procedures and do not circumvent security controls for convenience or expediency.
POLP helps organizations to comply with various regulations and standards. And it demonstrates that they are taking appropriate steps to protect sensitive data. In addition, it maintains the security of its systems.
Improved Accountability
Another benefit of implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is improved accountability. It limits the access of users and processes to only what is necessary. POLP help organizations track and audit the actions of their employees and other system users more effectively.
The users are granted access only to the resources needed to perform their tasks. So it becomes easier to track and monitor their actions. It helps the organization to detect and investigate suspicious activities that happen. And it identifies any unauthorized or malicious activities that could lead to data breaches or other security incidents.
In addition, it helps to establish a clear chain of responsibility and accountability within an organization. By limiting access to only what is necessary, organizations ensure that users know their roles and responsibilities. And the organizations cannot make changes or perform actions outside of their authorized duties.
By implementing POLP, organizations improve accountability and ensure that their employees and other system users follow established policies and procedures. It prevents data breaches and other security incidents. And it ensures that the organization can identify and respond to security threats promptly and effectively.
Implementing POLP
Implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) involves several steps, including:
Identifying System Resources and Access Requirements
The first step in implementing it is identifying the system resources that need to be protected and the access requirements of users and processes. It involves analyzing the system architecture and identifying the data and applications that need to be protected, as well as the users and processes that require access to these resources.
Assigning Access Levels and Permissions
Once the system resources and access requirements have been identified, access levels and permissions can be assigned to users. And permissions for the processes based on the principle of least privilege. It involves granting users and processes only the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Access Controls
Access controls should be regularly reviewed and updated. So that it ensures that they continue to meet the organization’s needs. Further, it should comply with any regulatory requirements. It involves monitoring user activity and adjusting access controls as necessary to address new threats or changes in business requirements.
Providing Training and Awareness
Employees and other system users should receive proper training and awareness programs. Organizations should ensure that their employees understand the importance of access controls. They should know how to use them effectively. It includes educating employees on the risks of sharing passwords, granting unnecessary access, and other security best practices.
Implementing Monitoring and Auditing System
Finally, a monitoring and auditing system should be implemented to track user activity and identify suspicious or unauthorized behavior. It includes implementing tools such as intrusion detection systems, log analysis tools, and other security monitoring tools to detect and respond to security threats promptly and effectively.
POLP requires a proactive approach to security and a commitment to ongoing monitoring and review of access controls. By following these steps, organizations can protect their systems against unauthorized access. And that their users are only able to access the resources that they need to perform their duties.
Identifying System Resources and Access Requirements
The first step in implementing the Principle of Least Privilege is identifying the system resources that must be protected. And the access requirements of its users and processes are to be identified. It involves analyzing the system architecture and identifying the data and applications that must be protected. And also the users and processes that require access to these resources.
Organizations should conduct a comprehensive inventory of all hardware, software, and data assets within their IT environment to identify system resources. It includes identifying servers, workstations, network devices, and other hardware. As well as, all software applications and data repositories need to be identified.
Once the system resources have been identified, access requirements must be determined. It involves identifying the users and processes that require access to these resources. And also, the level of access required to perform their tasks requires identification. For example, some users may require access to sensitive data, while others may only need access to basic applications and services.
It is important to consider internal and external users when determining access requirements. Internal users are employees and contractors. The external users are customers, partners, and other third-party users who require access to the organization’s systems.
In addition, access requirements should be analyzed based on the sensitivity of the data and the risk of unauthorized access. For example, sensitive financial data may require more stringent access controls than less sensitive data.
Identifying system resources and access requirements is a critical step in implementing POLP. By thoroughly analyzing the IT environment and access requirements, organizations ensure that their systems are protected against unauthorized access. And those users can only access the resources they need to perform their duties.
Assigning Access Levels and Permissions
First, system resources and access requirements need to identify. The next step in implementing the Principle of Least Privilege is to assign access levels and permissions to users and processes based on the principle of least privilege.
The principle of least privilege states that users and processes should only be granted the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. It means that access controls should be designed to restrict access to sensitive data and applications only to users who require it.
Access controls can be implemented at various levels, including:
Physical Access
Physical access controls limit access to system resources based on physical location. The physical access controls are locks and biometric authentication to restrict access to data centers and other sensitive areas.
Network Access
Network access controls limit access to system resources based on network traffic. The network access controls are firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other network security tools.
Application Access
Application access controls limit access to specific applications and data based on user roles and permissions. The application access controls are user authentication and authorization, role-based access control, and other application-level security measures.
Data Access
Data access controls limit access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions. They are data encryption, data masking, and data loss prevention (DLP) tools.
Access controls should be implemented based on the principle of least privilege. That means that users and processes should only be granted the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. Access controls should be regularly reviewed and updated. It should ensure that they continue to meet the organization’s needs and comply with any regulatory requirements.
Assigning access levels and permissions is a critical step in implementing POLP. By granting users and processes only the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. So that organizations reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. And they ensure that their systems are protected against internal and external threats.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Access Controls
Regularly reviewing and updating access controls is critical to implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP). Access controls should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that they continue to meet the organization’s needs. And they comply with any regulatory requirements.
Access controls should be reviewed and updated whenever there are changes to the IT environment. The change in environment may include introducing new hardware, software, or data repositories or changes to user roles and responsibilities. It ensures that access controls remain effective and up-to-date. It ensures users can only access the resources they need to perform their duties.
In addition, access controls should be reviewed and updated regularly. It needs to identify any potential security vulnerabilities or weaknesses. It involves conducting regular security audits, penetration testing, or vulnerability assessments to identify gaps in the access control system.
When reviewing and updating access controls, it is important to consider the following:
User Roles and Responsibilities
Access controls should be based on user roles and responsibilities. It should be updated whenever there are changes to these roles.
Data Sensitivity
Access controls should be designed to restrict access to sensitive data. And it should be allowed to those users who require it.
Compliance Requirements
It should comply with any regulatory or legal requirements. They apply to the organization.
Security Vulnerabilities
Access controls should be reviewed regularly to identify potential security vulnerabilities or weaknesses. And it ensures that they remain effective in protecting against unauthorized access.
Regularly reviewing and updating access controls is essential for maintaining the security and integrity of an organization’s IT environment. It ensures that access controls are up-to-date and effective. And the organizations reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. And it ensures that their systems remain secure and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Providing Training and Awareness
Providing training and awareness is another important aspect of implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP). Users and employees should be trained on the importance of POLP. They should be trained in risks associated with overprivileged access and how to properly use access controls to protect sensitive data and systems.
Training should cover the following topics:
Understanding Access Controls
Users should understand how access controls work. They should know the importance of granting users only the access they need to perform their job duties.
Identifying Sensitive Data
Users should be trained on how to identify sensitive data. They should know the importance of protecting this data from unauthorized access.
Password Security
Passwords should be kept secure. And the users should be trained on best practices for password management. Users must use strong passwords, change passwords regularly, and not share passwords with others.
Reporting Suspicious Activity
Users should be trained on how to report suspicious activity. The suspicious activity may be any of the following; attempted breaches, phishing emails, or other security incidents.
Compliance Requirements
Users should be trained on any regulatory or legal requirements for the organization. They should train how access controls meet these requirements.
In addition to providing training, organizations should raise awareness about the importance of POLP through various channels, such as email newsletters, posters, and other forms of communication. These reinforce the message about the importance of access controls. It ensures that users remain vigilant about security threats.
Providing training and awareness is a critical component of implementing POLP. It ensures that users understand the importance of access controls. And train the users to use them effectively. With it, organizations reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. And it ensures that their systems remain secure and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Implementing a Monitoring and Auditing System
Implementing a monitoring and auditing system is an important aspect of implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP). A monitoring and auditing system detects and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. And it provides valuable insights into user behavior and potential security threats.
A monitoring and auditing system should be designed to track user activity, log access attempts, and detect unusual behavior. It should also have to track monitoring user login attempts, tracking file access, and modification. And it should also detect changes to system configurations.
Auditing help organizations identify areas where access controls may be insufficient. And Auditing provides insights into potential security vulnerabilities. For example, auditing may reveal that certain users have been granted more access than needed to perform their job duties or that a certain group of users is attempting to access sensitive data they are not authorized to view.
When implementing a monitoring and auditing system, it is important to consider the following:
Log Retention
Organizations should determine how long logs will be retained. They should ensure that logs are backed up and securely stored.
Analysis and Reporting
The monitoring and auditing system should be designed to provide reports and analysis. That reports can be used to identify potential security threats and areas where access controls may need to be strengthened.
Regular Review
The monitoring and auditing system should be reviewed regularly. It should ensure that it remains effective in detecting and preventing unauthorized access. And it should identify any potential areas for improvement.
Compliance Requirements
The monitoring and auditing system should comply with any regulatory or legal requirements applicable to the organization.
Implementing a monitoring and auditing system is essential for maintaining the security and integrity of an organization’s IT environment. Organizations can detect and prevent unauthorized access by monitoring user activity and auditing access attempts. It helps the organizations to identify potential security threats. Further, it ensures that their systems remain secure and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Identifying Privileges That Users Need to Perform Their Job Functions
When implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP), it is important to identify the privileges that users need to perform their job functions. It involves determining the minimum level of access required for each user or group of users. It is based on their job roles and responsibilities.
To identify the necessary privileges, organizations should follow these steps:
Identify Job Roles and Responsibilities
Determine the job roles and responsibilities of each user or group of users within the organization. It involves creating a list of job titles or functional areas and mapping each user to their roles.
Determine Necessary Access
For each job role or responsibility, determine the necessary access required to perform the tasks associated with that role. It involves reviewing the data and systems that the user needs to access. And also the applications or tools required to perform their job duties.
Assign Access Levels
Access levels are based on the necessary access identified in determining necessary access. Based on it, assign access levels and permissions to each user or group of users. It involves assigning user roles with predefined access levels or creating custom access levels based on specific job requirements.
Regularly Review Access Requirements
Access requirements change over time as users take on new responsibilities or new systems and applications are introduced. As such, it is important to review and update access requirements regularly. It ensures that users have the necessary privileges to perform their job duties. It will minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
By identifying the necessary privileges for each user or group of users, organizations can ensure that users have the access they need to perform their job duties. It will minimize the risk of unauthorized access and potential security threats. Regularly reviewing access requirements ensures that access levels remain appropriate and up-to-date. It reduces the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Assigning Privileges Based on the Need
Assigning privileges based on need is a key aspect of implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP). It involves granting users the minimum access required to perform their job functions. It restricts access to resources that are not necessary for their work.
To assign privileges based on need, organizations should follow these steps:
Define Access Requirements
It identifies the resources that each user or group of users needs to access to perform their job duties. The resources are data, systems, applications, and other resources.
Assign Access Levels
Assigning access levels to each user or group of users based on their access requirements. Access levels are read-only access, write access, and administrative access. And other access levels are based on the needs of the user or group.
Review and Refine Access Levels
Regularly review and refine access levels to ensure that users have access to the resources they need to perform their job duties to minimize the risk of unauthorized access. It involves removing access to resources that are no longer needed or granting additional access to users who require it.
Limit Access to Sensitive Data
Sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) and financial data, should be restricted to only those users who require access to perform their job duties. Access to sensitive data should be limited to the minimum number of users required to perform the task.
Monitor Access and Activity
Implementing a system for monitoring access and activity on the network and in applications is crucial in POLP. It will ensure that users are not accessing resources they should not be. It detects and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
Organizations can minimize the risk of data breaches and other security incidents by assigning privileges based on need. And it still allows users to perform their job duties effectively. Regularly reviewing and refining access levels ensures users have the access they need to perform their job duties. It minimizes the risk of unauthorized access. Limiting access to sensitive data and monitoring access and activity further reduce the risk of security incidents.
Monitoring Privileges to Ensure They Are Still Needed and Appropriate
Monitoring privileges is an important aspect of implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) and maintaining a secure environment. By regularly reviewing privileges and access levels, organizations can ensure that they are still needed and appropriate for each user’s job functions.
To monitor privileges, organizations should follow these steps:
Define a Schedule for Reviewing Privileges
Set a schedule for reviewing privileges regularly. It may be quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, depending on the size and complexity of the organization.
Review Privileges for Each User
Review the access levels and permissions for each user to ensure that they are still necessary for their job functions. It may involve removing access to resources that are no longer needed or granting additional access to users who require it.
Ensure That Access is Appropriate
Ensure that the level of access granted to each user is appropriate for their job duties. For example, a user needing only read-only access to a system should not have administrative privileges.
Monitor Access and Activity
Implement a system for monitoring access and activity on the network and in applications. That will ensure that users are not accessing resources that they should not be. It detects and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
Conduct Regular Training and Awareness
Users must be trained and educated on the important access controls and the principle of least privilege. It ensures that users understand the need to limit access to resources. And they are aware of the potential risks of unauthorized access.
By monitoring privileges, organizations ensure that users have the access they need to perform their job duties. It minimizes the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. Regular training and awareness promote a culture of security awareness and ensure that users understand their role in maintaining a secure environment.
Best Practices for POLP
Implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is an important step toward securing an organization’s network and data. Here are some best practices to follow when implementing POLP.
Use Role-Based Access Control
Implementing a role-based access control (RBAC) system ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their job functions. It reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
Implement the Least Privilege at All Levels
The least privilege should be implemented at all levels, including the operating system, applications, and databases. It can reduce the attack surface and minimize the risk of security breaches.
Regularly Review and Update Access Controls
Access controls should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that they are still appropriate for each user’s job function. It minimizes the risk of unauthorized access due to outdated access controls.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) prevents unauthorized access to systems and data. It requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication. So that MFA makes it more difficult for attackers to access sensitive information.
Use Automation to Enforce POLP
Implementing automation ensures that access controls are enforced consistently across the organization. Automation reduces the risk of human error when implementing and maintaining access controls.
Conduct Regular Training and Awareness
Regularly train and educate users on the importance of access controls and POLP. It ensures that users understand the need to limit access to resources. And the users are aware of the potential risks of unauthorized access.
By following these best practices, organizations ensure that they are implementing POLP effectively. They can minimize the risk of security breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
Regular Review of Privileges
Regularly reviewing privileges is an important aspect of implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP). Privileges should be reviewed regularly. It should ensure that users can only access the resources they need to perform their job functions.
Here are some best practices to follow when conducting regular reviews of privileges:
Set a Schedule for Privilege Reviews
Establish a schedule for reviewing privileges based on the risk associated with each user’s job function. For example, high-risk users may require more frequent reviews than low-risk users.
Use Automated Tools to Assist With Privilege Reviews
Automated tools identify privileges no longer needed or have been granted in error. These tools ensure that privileges are consistently applied across the organization.
Review Privileges When Job Functions Change
When a user’s job function changes, their privileges will be reviewed to ensure that they only have access to the resources they need to perform their new job function. It reduces the risk of unauthorized access due to outdated access controls.
Remove Unnecessary Privileges
If a user no longer needs a privilege, it should be removed. It reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Document Privilege Reviews
Documenting privilege reviews ensures that they are conducted consistently. And it can be used as evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements.
Regular review of privileges ensures that access controls are appropriate and effective in limiting access to sensitive data and systems. By following these best practices, organizations minimize the risk of security breaches due to unauthorized access.
Limiting administrative privileges
Limiting administrative privileges is key to implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP). Administrative privileges provide users with high access to systems and data. And it poses a significant security risk if they are not managed properly.
Here are some best practices for limiting administrative privileges:
Use Separate Administrative Accounts
Users should have separate accounts for administrative tasks. That accounts are to be separate from their normal user accounts. It limits the potential for unauthorized access to administrative privileges.
Use Role-Based Access Controls
Administrative privileges should be assigned based on a user’s job function. It should be limited to only the privileges necessary to perform that job function. It ensures that administrative privileges are not granted unnecessarily.
Implement the Least Privilege for Administrative Tasks
Administrative tasks should be assigned the minimum privilege level necessary to perform the task. It limits the potential impact of a security breach or unauthorized access.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication should be required for administrative tasks to provide an additional layer of security. And it reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Audit and Monitor Administrative Activity
Administrative activity should be audited and monitored to ensure that users only access systems and data they are authorized to access. It could identify potential security risks and prevent unauthorized access.
By limiting administrative privileges, organizations can minimize the risk of security breaches. And the limiting privileges minimize unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. Following these best practices ensures that administrative privileges are managed effectively. And it only grants permission to users who need them to perform their job functions.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication is an important security measure. It helps organizations improve their overall security posture. MFA requires users to provide additional forms of identification beyond just a password to access a system or application. It requires users to provide multiple forms of identification. MFA reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if an attacker obtains a user’s password.
Several different types of factors can be used for MFA, including:
Something you know: It can include a password, a PIN, or the answer to a security question.
Something you have: It can include a physical device like a Smartphone or a security token that generates a one-time code.
Something you are: It can include biometric factors like fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scans.
The specific types of factors used will depend on the level of security required. And it also depends on the sensitivity of the data being accessed.
One best practice for implementing MFA is to require it for all users. It is not just those with elevated privileges or access to sensitive data. It prevents unauthorized access across the board. And it reduces the risk of security breaches.
Adopting MFA
Another best practice is to use adaptive MFA. Adaptive MFA is a newer technology that can adjust the level of authentication required based on the user’s behavior or the risk level of the activity being performed. If a user is accessing an application from a known device on a trusted network, they may only be required to provide a password. However, if they are accessing the application from an unfamiliar device or network, they may be required to provide additional forms of identification.
It’s important to make it easy for users to use MFA. Implementing MFA sometimes be seen as a hassle by users. So it’s important to make it as easy as possible for them. It can include using simple and intuitive MFA methods, providing clear instructions, and using single sign-on (SSO) tools to reduce the number of MFA prompts.
Testing and Monitoring
Testing and monitoring are also important best practices for implementing MFA. Like any security measure, MFA should be tested and monitored regularly. It should ensure that it’s working effectively and not causing unnecessary user disruptions. It can include testing vulnerabilities, monitoring for unusual activity, and providing user education and awareness.
In conclusion, implementing MFA can help organizations significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and improve overall security. By following best practices like requiring MFA for all users, using adaptive MFA, making it easy for users, and testing and monitoring regularly, organizations can ensure that MFA is implemented effectively and provides the desired level of protection.
Recap of POLP and Its Importance in Information Security
The principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is a security concept that limits access rights for users and processes to only those resources necessary to perform their job functions. The POLP helps prevent security breaches, data loss, and other security risks by restricting access to sensitive information and systems. It works by implementing access controls and authorizations. And it assigns permissions and levels of access to the users. Further, it regularly reviews and updates access controls.
Implementing the POLP includes improved security, reduced data loss, increased system integrity, compliance with regulations, and improved accountability. To effectively implement POLP, organizations should identify system resources and access requirements, assign access levels and permissions based on need, regularly review and update access controls, provide training and awareness, implement a monitoring and auditing system, identify privileges that users need to perform their job functions, assign privileges based on need. And it monitors privileges to ensure they are still needed and appropriate.
Finally, implementing best practices such as regular review of privileges, limiting administrative privileges, and implementing multi-factor authentication can further strengthen the POLP and improve information security. In conclusion, the POLP is an essential component of any comprehensive information security strategy and should be implemented by all organizations to protect their assets from security threats.
Final Thoughts on How POLP Can Help Organizations Protect Their Data and Prevent Security Breaches
In today’s increasingly digital world, data is one of the most valuable assets for any organization. Therefore, it is critical to protect data from security breaches and other security risks. Implementing the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is an effective way for organizations to reduce the risk of security breaches and data loss.
POLP limits the access rights for users and processes to only those resources necessary to perform their job functions. So that it significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. Moreover, regular reviews and updates of access controls and authorizations strengthen the organization’s security. Further, identifying system resources and access requirements and providing training and awareness to users strengthen the security posture of organizations.
The POLP is an essential concept that organizations should implement as part of their overall security strategy. It helps organizations to protect their data and prevent security breaches. Further, it improves their overall security posture. By following best practices and regularly reviewing access controls and authorizations, organizations ensure that they effectively implement the POLP and minimize the risk of security incidents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is a vital concept that organizations should implement to improve their information security posture. It limits access rights for users and processes to only those resources necessary to perform their job functions. By implementing it, organizations significantly reduce the risk of security breaches, data loss, and other security risks.
Moreover, the security posture of organizations can be improved by regularly reviewing access controls and authorizations. Assigning permissions and levels of access based on need and providing training and awareness to users can further strengthen it.
By implementing the POLP and following best practices, organizations protect their data. It helps to prevent security breaches and comply with regulations. It ultimately helps organizations to build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. Further, it helps to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Therefore, organizations should prioritize the implementation of the POLP. So that they can continuously monitor and update their security measures to stay ahead of emerging security threats.