Introduction: Why a Reliable Desktop Power Supply Matters
In this comprehensive “Desktop Power Supply Guide,” we aim to shed light on the often-overlooked aspects of desktop power supplies. Whether you’re a seasoned PC builder, a gaming enthusiast, or a casual user, understanding the ins and outs of power supplies is crucial for optimizing your computer’s performance. It may ensure its longevity and safeguard your data.
It is easy to get lost in the excitement of upgrading your CPU, GPU, or RAM, all in pursuit of better performance and enhanced capabilities for your desktop computer. Amidst the jargon of processors and graphics cards, one crucial component often takes a backseat. It plays a vital role in your PC’s overall health and stability – the desktop power supply.
Unsung Hero of Your Computer Setup
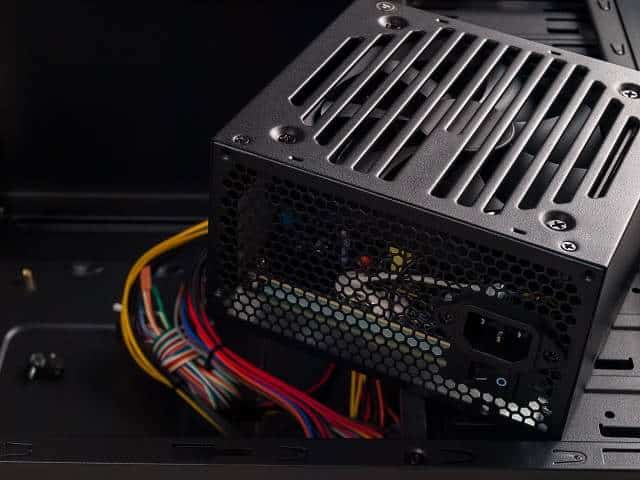
A desktop power supply unit (PSU) is the unsung hero of your computer setup. It provides the lifeblood of electricity required to keep every component running seamlessly. It may seem unassuming and reside in the dark corners of your PC case, but its significance cannot be overstated. A reliable desktop power supply can make the difference between a smooth system and one fraught with crashes, instability, and, worst-case scenario, hardware damage. It offers a trouble-free computing experience.
We will delve into the various components of a desktop power supply and explore the different types available on the market. Let us discuss the significance of wattage and efficiency ratings. Further, let us guide you through the installation process. Furthermore, we will provide insights into maintaining and upgrading your power supply, helping you make informed decisions about this critical element of your PC.
Suppose you have ever wondered about the importance of your desktop power supply or questioned whether it’s time for an upgrade. In that case, this guide is your comprehensive resource to demystify the world of power supplies. Join us as we embark on this journey to empower you with the knowledge and confidence needed to choose the proper power supply for your desktop. We ensure a stable and reliable computing experience.
So, let us uncover the secrets of a reliable desktop power supply unit, the unsung hero of your computing world.
Why a Reliable Desktop Power Supply Matters
Your desktop power supply may not be the most glamorous component of your computer, but it is arguably the most critical. It serves as the foundation upon which your entire PC build rests. And its performance impacts your computer’s functionality, stability, and overall longevity.
Why does a reliable desktop power supply matter?
Stability and Consistency:
A quality power supply provides a steady and consistent flow of electricity to all your computer’s components. It ensures that your CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage devices receive the precise voltage and current they need to operate optimally. Inconsistent power can lead to system crashes, data corruption, and even hardware failures.
Component Protection:
Your power supply is a guardian for your expensive computer parts. It includes built-in safeguards such as surge protection, overvoltage protection, and short-circuit protection to shield your components from electrical damage. A reliable power supply can save your system from irreparable harm in the event of a power surge or voltage spike.
Efficiency and Energy Savings:
Modern power supplies often have efficiency certifications such as 80 PLUS. A more efficient power supply converts more electricity from the wall outlet into usable power for your components. This not only reduces energy consumption but also minimizes heat generation. This minimum heat generation contributes to a cooler and quieter system.
System Reliability:
A low-quality or inadequate power supply can lead to system instability. It may cause your computer to shut down unexpectedly, freeze, or display erratic behavior. These issues can be frustrating and time-consuming to troubleshoot. A reliable power supply minimizes these problems.
Expandability:
A capable power supply is essential if you plan to upgrade your computer by adding more powerful components like a high-end GPU or additional storage drives. It should have sufficient wattage and the necessary connectors to support these upgrades without requiring you to replace them.
Longevity:
A durable power supply can last through multiple computer builds, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Choosing a reputable brand and a well-constructed PSU can save you money in the long run.
Data Safety:
Power fluctuations can result in data loss and corruption. It is especially true if you are in the middle of important tasks or running applications. A reliable power supply reduces the risk of data-related issues caused by unexpected power disruptions.
A reliable desktop power supply is crucial for your computer setup. It ensures the seamless operation of your system. It protects your valuable components. And it contributes to overall system stability and longevity. It is not an area to skimp on when building or upgrading your PC. Let us proceed in this guide; we will delve deeper into the various aspects of desktop power supplies. It helps you make informed decisions to enhance your computing experience.
Understanding the Basics: What Is a Desktop Power Supply?
To comprehend the significance of a desktop power supply (PSU) and make informed choices; let’s start with the fundamental question: What is a desktop power supply?
A desktop power supply is often referred to as a PSU. It is an essential component within your computer system responsible for converting electrical energy from your wall outlet into a form that the various components inside your PC can use. It is the power source for your motherboard, central processing unit (CPU), graphics processing unit (GPU), storage drives, and other peripherals. In other words, it’s the heart of your computer. And it is pumping power to every part of your machine.
Critical Components of a Desktop Power Supply:
- Input Power: The desktop power supply takes electricity from your home’s electrical grid. Depending on your region, it typically uses the standard 110-120V AC (alternating current) or 220-240V AC.
- Conversion: The power supply unit converts the incoming AC power to the DC (direct current) power your computer components need. It accomplishes this conversion through a series of transformers and rectifiers.
- Voltage Regulation: The PSU regulates the voltage to ensure that your components receive a stable and consistent power supply. Most desktop power supplies provide +12V, +5V, and +3.3V rails. Each of them serves different components within your PC.
- Connectors: The PSU has various connectors and cables that deliver power to specific parts of your computer. Common connectors include the 24-pin motherboard connector, 8-pin EPS connector for the CPU, PCIe connectors for graphics cards, and SATA connectors for storage drives.
- Cooling System: A desktop power supply often includes a cooling fan to prevent overheating. Proper cooling is essential for the PSU’s efficiency and longevity.
- Protections: Reliable power supplies incorporate surge protection, overvoltage protection, and short-circuit protection to shield your components from electrical damage.
It’s important to note that desktop power supplies have different wattage ratings and form factors to accommodate various computer configurations. When selecting a PSU for your system, you must consider your components’ power requirements to ensure that your power supply can deliver sufficient wattage.
As you delve deeper into desktop power supplies, you will discover the nuances of power supply ratings, efficiency certifications, and compatibility considerations. These details will help you choose the correct PSU for your specific needs. In the following sections of this guide, we will explore these aspects in more depth, empowering you to make the best choices for your desktop power supply.
Main Components of a Desktop Power Supply
A desktop power supply is a compact metal box tucked away inside your computer case. It is a complex piece of engineering composed of several crucial components that work together to provide your PC with a stable and efficient power source. Understanding these components can help you appreciate the inner workings of your desktop power supply.
Input Connector:
This is where your power supply connects to your home’s electrical grid. In regions with 110-120V AC power, it typically involves a standard three-pronged plug. In 220-240V regions, it might use a different type of plug.
EMI/RFI Filter:
It helps to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI); a power supply often incorporates a filter. This component helps maintain the quality of the power supply’s output.
Rectification and Filtering:
After receiving the input power, it goes through a rectifier, which converts the alternating current (AC) from your wall outlet into direct current (DC). Following this, capacitors are used to filter and smooth the converted power. And that ensures a consistent voltage output.
Transformers:
Transformers are responsible for voltage regulation. They help maintain stable output voltages like +12V, +5V, and +3.3V. These voltages are crucial for the operation of different components within your computer.
Voltage Regulation Circuitry:
Voltage regulation circuitry ensures that the power supplied to your PC components is steady and within acceptable limits. This helps prevent voltage spikes or drops. The voltage spikes can cause damage or instability.
Output Connectors and Cables:
Desktop power supplies come with various connectors and cables designed to deliver power to specific components in your computer. These include the 24-pin motherboard connector, 8-pin EPS connector for the CPU, PCIe connectors for graphics cards, and SATA connectors for storage drives.
Cooling System:
Many desktop power supplies include a cooling system. That is usually in the form of a fan to dissipate heat generated during operation. Proper cooling is essential for the PSU’s efficiency and longevity.
Safety Protections:
A reliable power supply includes features like surge protection, overvoltage protection, and short-circuit protection to protect your components from electrical damage. These protections can prevent catastrophic failures or damage to your PC.
Efficiency Components:
High-quality power supplies incorporate efficiency components to reduce wasted energy and minimize heat production. Look for power supplies with 80 PLUS certification. 80 PLUS certification indicates their energy efficiency.
Modular vs. Non-Modular Design:
Some power supplies come in modular designs. They allow you to detach and reattach cables as needed. This feature enhances cable management by reducing clutter inside your case and ensuring you only use the necessary cables. Non-modular power supplies, on the other hand, have fixed cables. That can sometimes lead to a messier interior but tends to be more cost-effective.
Active Power Factor Correction (PFC):
Many modern power supplies incorporate active PFC. PFC improves the power factor of the PSU. This feature enhances the efficiency of the power supply. That results in less power waste and reduced strain on your electrical circuit.
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures):
The MTBF rating indicates a power supply’s reliability. It estimates the average time a power supply is expected to operate without failing. Power supplies with higher MTBF ratings are generally more reliable.
Form Factor:
Desktop power supplies come in different form factors to fit various PC cases. Common form factors include ATX, Micro-ATX, and SFX. Choosing a power supply that matches your case’s form factor for proper installation is essential.
Quality Capacitors:
The capacitors inside a power supply play a vital role in voltage regulation and overall performance. High-quality power supplies use durable capacitors designed to withstand continuous operation. And they offer excellent stability and longevity.
Efficiency Certification:
Consider efficiency certifications like 80 PLUS (80+ Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, Titanium). These certifications indicate how efficiently the power supply converts input to usable power. Higher-rated certifications signify better efficiency. And their higher rating reduces energy consumption and heat generation.
Fans and Noise Levels:
The cooling fan within the power supply is responsible for dissipating heat. Some power supplies are designed to operate silently, while others may produce more noise. Consider your preference for a quiet PC and the power supply’s noise level when selecting one for your Build.
Understanding these components and features will help you make informed decisions when choosing a desktop power supply for your computer. The right power supply ensures that your system operates reliably and efficiently. And it also contributes to the overall performance and longevity of your PC. In the following sections of this guide, we will explore factors like wattage, efficiency ratings, form factors, and the importance of cable management to further assist you in selecting the perfect power supply for your specific needs.
Types of Connectors and Ports
Desktop power supplies feature a variety of connectors and ports to deliver power to the different components of your computer. Understanding these connectors is crucial when selecting a power supply and during the assembly of your PC. Let us explore the most common connectors and ports you will encounter.
24-Pin ATX Connector:
The 24-pin ATX connector is the primary power connector that supplies power to the motherboard. It provides essential voltages, including +3.3V, +5V, and +12V. It ensures the motherboard and its components receive stable power.
8-Pin EPS Connector:
The 8-pin EPS (or CPU) connector provides power to the central processing unit (CPU). High-performance CPUs may require additional power for stable operation. Some power supplies offer a 4+4-pin configuration that can be split if your motherboard requires an 8-pin connector.
PCIe Connectors:
These connectors deliver power to your graphics card. Depending on your graphics card’s power requirements, you’ll find 6-pin, 8-pin, or 8+8-pin (6+2-pin) PCIe connectors. Be sure your power supply has the necessary PCIe connectors for your GPU.
SATA Connectors:
SATA connectors power your hard and solid-state storage drives. These connectors are slim and easily recognizable. That makes them ideal for modern storage devices.
Molex Connectors:
Molex connectors are versatile and can be used for various peripherals, including fans, older hard drives, and certain cooling accessories. They are less common in modern systems. But they can still be found in some power supplies.
Peripheral Connectors:
These connectors are a broad category that includes Molex connectors and various other connectors like Berg connectors. They are used for various peripherals and accessories but are becoming less common in modern power supplies.
Floppy Drive Connector:
The floppy drive connector is a relic from the past and is almost obsolete in modern systems. It is used for powering floppy disk drives.
CPU Fan and Chassis Fan Connectors:
Some power supplies come equipped with connectors for fans. These can help with cable management by powering fans directly from the power supply instead of the motherboard.
On/Off and Reset Switch Connectors:
Some modular power supplies may include connectors for the power and reset switches on your computer case. These connectors allow you to manage these functions through the power supply itself.
Modular Connector Ports:
You will find corresponding ports for connecting the detachable cables in modular power supplies. This feature allows you to customize your cable setup. It reduces clutter inside your PC case and improves airflow.
When choosing a power supply, ensuring it has the right connectors for your specific components and configuration is vital. Careful consideration of your system’s power needs and the connectors required for your motherboard, CPU, GPU, and other devices will help you make the best choice. Understanding these connectors will simplify cable management during the installation of your power supply. That will result in a neater and more efficient build.
Types of Desktop Power Supplies
When it comes to desktop power supplies, you have a range of options to choose from. Each caters to specific needs and system configurations. Understanding the various types of desktop power supplies can help you select your PC build. Here are the most common types:
ATX Power Supplies:
ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) power supplies are the standard choice for most desktop computers. They are compatible with full-sized and mid-sized tower cases. They come in different wattage ratings to meet various power requirements.
SFX Power Supplies:
SFX (Small Form Factor) power supplies are designed for compact cases and Mini-ITX systems. They are smaller and often have a form factor suitable for mini and micro ATX cases.
TFX Power Supplies:
TFX (Thin Form Factor Extended) power supplies are smaller and thinner than SFX units. They are primarily used in slim or low-profile desktop cases and small form factor PCs.
Flex ATX Power Supplies:
Flex ATX power supplies are highly compact and designed for mini PCs and HTPCs (Home Theater PCs). They balance size and performance and fit in tiny cases.
Modular Power Supplies:
Modular power supplies are known for their cable management flexibility. They come with detachable cables. They allow you to connect only the cables you need. This reduces clutter and enhances airflow within your PC case.
Non-Modular Power Supplies:
Non-modular power supplies, on the other hand, have fixed cables. While they are typically more affordable, they can lead to a messier interior due to unused cables, especially in smaller cases.
Semi-Modular Power Supplies:
Semi-modular power supplies strike a balance between the two. They have some fixed essential cables, like the 24-pin ATX and 8-pin EPS connectors. And they possess detachable cables for additional peripherals.
Fully Modular Power Supplies:
Fully modular power supplies offer complete cable management flexibility. All cables are detachable. And this gives you total control over cable arrangement. This is ideal for PC builders who prioritize cable management and aesthetics.
Multi-Rail and Single-Rail Power Supplies:
Power supplies can be categorized into multi-rail and single-rail designs. Multi-rail power supplies distribute power across multiple rails, which can be more stable in specific scenarios. Single-rail power supplies provide all the power from a single rail. It simplifies cable management but requires careful consideration of power distribution.
Standard and High-Performance Power Supplies:
Some power supplies are designed for basic, everyday computing, while others are geared toward high-performance gaming or workstation systems. High-performance power supplies are often rated with higher wattages and efficiency certifications.
Selecting the correct type of desktop power supply depends on your specific requirements. Those requirements are the size of your case, the power needs of your components, and your preferences for cable management and efficiency. When choosing a power supply, consider your current configuration and any potential future upgrades to ensure that the power supply can meet the demands of your PC.
ATX Power Supplies
ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) power supplies are the most commonly used type. And it is the widely available type of desktop power supply. These power supplies adhere to the ATX form factor standard. They are designed to fit standard ATX and mid-tower cases. Here are some key features and considerations when it comes to ATX power supplies:
-
Standard for Most Desktop PCs:
ATX power supplies are the go-to choice for typical desktop computers. They come in a variety of wattages. That makes them suitable for various systems, from budget PCs to high-performance gaming rigs and workstations.
-
Wattage and Efficiency:
ATX power supplies are available in various wattage ratings. That is typically ranging from 300W to 1000W or more. The wattage you need depends on your system’s components. Consider the total power consumption of your CPU, GPU, drives, and other peripherals to select an appropriate wattage.
-
Efficiency Ratings:
Look for ATX power supplies with efficiency certifications like 80 PLUS (80+ Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, Titanium). These certifications indicate the power supply’s efficiency in converting electricity from the wall outlet to usable power for your components. Higher-rated certifications denote better efficiency. And that Higher-rated certified one can save you on energy costs and reduce heat generation.
-
Connectors and Cables:
ATX power supplies come with a standard set of connectors, including a 24-pin ATX motherboard connector and various PCIe, SATA, and Molex connectors. Ensure your power supply has the necessary connectors for your components, such as your motherboard, graphics card, and storage drives.
-
Cooling and Noise Levels:
ATX power supplies often feature cooling fans to dissipate heat. Some models include intelligent fan control systems to adjust fan speed based on temperature and load. Consider your preference for a quiet PC when selecting an ATX power supply, as the noise level can vary between models.
-
Single vs. Multi-Rail Design:
ATX power supplies may come in single-rail or multi-rail designs. Single-rail power supplies provide all the power from a single rail. That simplifies cable management. Multi-rail power supplies distribute power across multiple rails. That can be more stable but requires careful consideration of power distribution.
-
Form Factors:
ATX power supplies are primarily designed for standard ATX cases. They can also fit into mid-tower and some small form factor cases. Check your case’s compatibility before purchasing an ATX power supply.
-
Reputable Brands:
When choosing an ATX power supply, select reputable brands that produce high-quality, reliable units. Well-known brands often provide warranties and better customer support. And that will ensure a hassle-free experience in case of any issues.
ATX power supplies are versatile and suitable for most desktop systems. They are an excellent choice for users looking to build or upgrade a standard PC. It offers various options to meet different power requirements and budgets. When selecting an ATX power supply, be sure to consider your specific system needs, including the total power consumption and the efficiency requirements, to ensure optimal performance and reliability for your PC.
SFX Power Supplies
SFX (Small Form Factor) power supplies are designed for compact desktop cases and Mini-ITX systems. These power supplies are smaller and more compact than standard ATX units. And that makes them a perfect fit for cases with limited space. Here’s what you need to know about SFX power supplies:
-
Compact Design:
SFX power supplies are significantly smaller than ATX units. This makes them ideal for Mini-ITX and small form factor (SFF) PC cases. They are often more depth- and height-friendly to accommodate the space limitations of smaller cases.
-
Wattage Options:
SFX power supplies are available in various wattage options. It is typically ranging from 300W to 800W or more. Despite their smaller size, they can provide sufficient power for various system configurations, including gaming and media center setups.
-
Form Factors:
You’ll find SFX-L (SFX Large) power supplies in addition to the standard SFX form factor. SFX-L units have the same width and height as standard SFX but are slightly longer. This additional length allows for larger cooling fans. That is potentially improving cooling efficiency and reducing noise.
-
Efficiency Ratings:
Unlike ATX power supplies, SFX power supplies can come with efficiency certifications like 80 PLUS. These certifications can impact energy consumption and heat generation.
-
Connectors and Compatibility:
SFX power supplies have connectors suitable for Mini-ITX motherboards, GPUs, and storage drives. Ensure that your power supply has the required connectors for your specific components. It is essential to check the compatibility of the SFX power supply with your SFF case.
-
Cooling and Noise Levels:
Given their compact size, SFX power supplies may feature smaller cooling fans, leading to slightly higher noise levels than larger ATX power supplies. Some SFX power supplies include fanless or semi-fanless designs for quieter operation.
-
Modular Options:
SFX power supplies are available in both non-modular and modular designs. Modular SFX power supplies offer cable management flexibility. It allows you to connect only the necessary cables and reduce clutter in your compact case.
-
Reputable Brands:
As with any power supply, choose a reputable brand known for producing reliable units. Quality is paramount, especially in smaller systems where space and airflow are at a premium.
SFX power supplies are the solution for PC builders seeking to create small form factor systems that are both powerful and space-efficient. When opting for an SFX power supply, carefully consider your case’s compatibility and your system’s power requirements to ensure a seamless and efficient build. These power supplies are the cornerstone of compact and portable desktop systems. They are ideal for gaming, HTPCs, and any scenario where space-saving is a priority.
Modular vs. Non-Modular Power Supplies
One key decision when choosing a desktop power supply is whether to opt for a modular or non-modular unit. Each type has its advantages and considerations, so it is crucial to understand their differences.
Non-Modular Power Supplies:
Non-modular power supplies come with a fixed set of cables and connectors. These cables are permanently attached to the power supply. And you cannot detach or remove them. Here are some key points to consider regarding non-modular power supplies.
Cost-Effective: Non-modular power supplies are often more budget-friendly than their modular counterparts. This makes them an attractive option for those looking to save on the overall cost of their PC build.
Limited Cable Management: Since the cables are fixed, you must use all of them, even if your components do not require all the connectors. This can result in extra cables cluttering the inside of your case. That is potentially affecting airflow and aesthetics.
Simplified Installation: Non-modular power supplies are straightforward to install. You don’t have to worry about connecting the right cables, as all the necessary cables are already attached.
Recommended For: Non-modular power supplies are often recommended for entry-level or budget builds. In the cable, management, and aesthetics are not top priorities.
Modular Power Supplies:
Modular power supplies provide flexibility when it comes to cable management. They come with detachable cables. That allows you to connect only the cables needed for your specific components.
Here’s what you should know about modular power supplies:
Cable Management: Modular power supplies offer excellent cable management options. Since you only use the necessary cables, your case has less clutter. That will lead to better airflow, improved aesthetics, and easier troubleshooting.
Reduced Clutter: Modular power supplies are precious in small form factor cases or builds where space is limited. They enable a neater, more compact build.
Higher Cost: Modular power supplies are typically more expensive when compared to their non-modular counterparts due to their added convenience and flexibility.
Recommended For: Modular power supplies are often recommended for mid-range and high-end computer builds. In high-end builds, cable management, airflow, and aesthetics are priorities. They also benefit builders who want the freedom to customize their cable setup.
Semi-Modular Power Supplies:
Some power supplies fall between the categories of modular and non-modular. Semi-modular power supplies have specific essential cables permanently attached. The permanently attached are the 24-pin ATX and 8-pin EPS connectors. And they allow flexibility with other cables. This design strikes a balance between convenience and cost-effectiveness.
When choosing between modular and non-modular power supplies, consider your budget, the aesthetics of your Build, and your cable management preferences. A modular power supply can be a worthwhile investment for a cleaner and more organized build. But, non-modular units are a cost-effective choice, particularly for entry-level or budget systems. Semi-modular power supplies offer a compromise for those who want a balance between convenience and cost.
Power Supply Ratings
Understanding power supply ratings is crucial when selecting a desktop power supply for your computer. These ratings provide insights into the performance and efficiency of the power supply. Here are the key ratings to consider:
-
Wattage (Output Capacity):
Wattage is perhaps the most critical rating when choosing a power supply. It represents the maximum power the power supply can deliver to your components. To select the appropriate wattage, consider the power requirements of your CPU, GPU, storage drives, and other peripherals. Choosing a power supply with a wattage that exceeds your system’s power needs by a comfortable margin is recommended to accommodate future upgrades and ensure stable performance.
-
Efficiency Ratings (80 PLUS Certification):
Efficiency ratings indicate how efficiently the power supply converts electricity from the wall outlet into usable power for your components. The most common efficiency certification is the 80 PLUS standard, which includes various levels: 80+ Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, and Titanium. The higher the certification, the more efficient the power supply is in reducing wasted energy and heat production. A more efficient power supply can save money on electricity bills and help maintain a cooler and quieter system.
-
Voltage Rails:
Power supplies use different voltage rails to deliver power to various components in your computer. Standard voltage rails include +12V, +5V, and +3.3V. The power supply’s ability to provide stable voltages is essential for your system’s reliability. Over- or undervoltage can cause instability and damage to your components.
-
Amperage (Current Ratings):
Amperage ratings on the +12V rail(s) are important for determining the power supply’s ability to deliver current to components like the CPU and GPU. High-performance CPUs and graphics cards may require a power supply with specific amperage ratings to ensure optimal performance.
-
Single vs. Multi-Rail Design:
Power supplies can come in single-rail or multi-rail designs. Single-rail power supplies provide all the power from a single rail. It simplifies cable management. Multi-rail power supplies distribute power across multiple rails. That can be more stable but requires careful consideration of power distribution.
-
PFC (Power Factor Correction):
Power Factor Correction (PFC) features many modern power supplies. It helps improve the power factor of the PSU. That is making it more efficient in drawing power from the electrical grid. Active PFC is generally preferred. It can reduce energy consumption and minimize heat generation.
-
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures):
MTBF represents the average time a power supply is expected to operate without encountering a failure. Power supplies with higher MTBF ratings are generally more reliable and less likely to fail.
Understanding these power supply ratings is vital for selecting a unit that meets your system’s power requirements. And they can ensure efficiency and stability. Before purchasing a power supply, carefully assess your system’s needs and consider potential future upgrades to choose a power supply that provides adequate wattage and efficiency for your specific computer build.
Wattage (Choosing the Right Wattage for Your PC)
Selecting the appropriate wattage for your desktop power supply is one of the most critical decisions when building or upgrading your PC. An insufficient power supply can lead to system instability and crashes. An overpowered supply can be a waste of energy and money. Here’s how to choose the correct wattage for your PC:
-
Identify Your Components:
The first step in determining the correct wattage is to list all the components in your PC that require power. These include your CPU, GPU, storage drives, RAM, motherboard, and additional peripherals like cooling fans, RGB lighting, and optical drives.
-
Check Manufacturer Recommendations:
Most component manufacturers provide power requirements for their products. Check the official websites or product manuals to find the power consumption information for your CPU and GPU. These are often the most power-hungry components in your system.
-
Use Online Calculators:
Several online power supply calculators can help you estimate your system’s power needs. These calculators typically consider the wattage requirements of your CPU, GPU, motherboard, drives, and other components. When making your calculations, be sure to include any overclocking or potential future upgrades.
-
Consider Headroom:
Adding a margin of safety, or Headroom, is a good practice for your wattage calculation. A power supply that offers slightly more wattage than your system requires flexibility for future upgrades and ensures stable operation. A common recommendation is to aim for a power supply around 20% higher in wattage than your calculated needs.
-
Efficiency Matters:
Having a higher-wattage power supply than you need provides some flexibility. However, it is also essential to consider efficiency. An oversized power supply operating at lower loads may be less efficient, which can lead to wasted energy. Therefore, it’s essential to strike a balance between wattage and efficiency. Look for a power supply that meets your system’s needs without being excessively overpowered.
-
Budget Constraints:
Budget considerations can also influence your choice. If you’re on a tight budget and your calculations suggest a 600W power supply is sufficient, you might be tempted to opt for a 1000W unit for future-proofing. However, this is not always necessary, and you could instead invest in a high-quality 600W power supply with better efficiency and build quality.
-
Quality Over Wattage:
Remember that the quality of the PSU power supply is just as important as its wattage. A high-quality, lower-wattage power supply can outperform a generic, higher-wattage unit. Quality power supplies provide stable voltage output, efficiency, and safety features, reducing the risk of damage to your components.
By carefully assessing your system’s needs, considering potential upgrades, and balancing wattage with efficiency, you can choose a power supply that provides the correct power for your PC. This is crucial for ensuring your computer build’s stability, reliability, and efficiency.
Efficiency Ratings (80 PLUS Certification)
The efficiency of a power supply is a significant factor to consider when selecting the right one for your desktop computer. A more efficient power supply can save you money on energy bills. In addition, it can generate less heat. Further, it can be more environmentally friendly. The 80 PLUS certification is a standard that helps consumers identify and compare the efficiency of power supplies. Here’s what you need to know:
-
Understanding 80 PLUS Certification:
The 80 PLUS certification is a voluntary program that tests and rates the efficiency of power supplies. The certification is based on a power supply’s ability to convert electricity from the wall outlet into usable power for your components. A higher efficiency rating means less energy is wasted as heat.
-
Certification Levels:
The 80 PLUS program offers several certification levels. Each level denotes a specific level of efficiency:
- 80 PLUS: This is the basic certification level, indicating a power supply is at least 80% efficient at 20%, 50%, and 100% load.
- 80 PLUS Bronze: A Bronze-certified power supply is at least 82% efficient at 20% and 100% load and 85% efficient at 50% load.
- 80 PLUS Silver: Silver-certified power supplies are at least 85% efficient at 20% and 100% load and 88% efficient at 50% load.
- 80 PLUS Gold: Gold-certified power supplies offer 2
- a minimum of 87% efficiency at 20% load, 90% at 50% load, and 87% at 100% load.
- 80 PLUS Platinum: Platinum-certified power supplies provide a minimum efficiency of 90% at 20% and 100% load and 92% at 50% load.
- 80 PLUS Titanium: Titanium-certified power supplies are the most efficient, with at least 90% efficiency at 10% and 100% load and 94% at 50% load.
-
Advantages of Higher Efficiency:
Opting for a power supply with a higher 80 PLUS certification can bring several benefits:
- Energy Savings: More efficient power supplies waste less energy as heat. Thereby they are reducing your electricity bills over time.
- Reduced Heat Generation: A more efficient power supply generates less heat. And that can help maintain lower operating temperatures inside your PC case.
- Eco-Friendly: Improved efficiency is environmentally friendly, as it reduces energy consumption and, consequently, carbon emissions.
-
Matching Efficiency to Usage:
The choice of 80 PLUS certification should align with how you plan to use your computer. If your system runs 24/7 or energy savings are a top priority, a higher certification, like Gold or Platinum, is a good choice. However, if you are building a budget PC and power efficiency is less critical, a Bronze-certified power supply might suffice.
-
High Quality and Efficiency:
Remember that not all high-wattage power supplies with 80 PLUS certifications are the same quality. Besides efficiency, consider factors like build quality, voltage regulation, amperage ratings, and reliability when choosing the right power supply for your system.
Therefore, the 80 PLUS certification is a valuable tool for gauging the efficiency of power supplies. Higher-rated certifications offer advantages in terms of energy savings. They reduce heat generation and eco-friendliness. When selecting a power supply, evaluate your budget and PC usage to determine which 80 PLUS certification level best matches your needs while considering the quality and features of the unit.
Form Factors and Size Compatibility
Selecting the right power supply form factor and ensuring compatibility with your PC case are crucial steps in building a functional and efficient system. Form factors dictate the physical size and shape of the power supply, so choosing the appropriate one is vital for a successful build. Here’s what you need to know:
-
ATX Form Factor:
The ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) form factor is the standard for most desktop power supplies. ATX power supplies are designed to fit standard ATX and mid-tower cases. They come in various wattage ratings to meet various power requirements. When choosing an ATX power supply, check the dimensions and compatibility with your specific case, especially if you have a smaller or compact case.
-
SFX and SFX-L Form Factors:
SFX (Small Form Factor) and SFX-L (SFX Large) power supplies are designed for compact and small form factor (SFF) cases. These cases often have limited space. Therefore, SFX power supplies are smaller and more compact. That makes them a perfect fit for these cases. SFX-L units have the same width and height as standard SFX. But they are slightly longer. Therefore, they can accommodate larger cooling fans for better efficiency and cooling.
-
TFX Form Factor:
TFX (Thin Form Factor Extended) power supplies are even smaller and thinner than SFX units. They are often used in slim or low-profile desktop cases and small form factor PCs. TFX power supplies are suitable for compact office PCs and HTPCs (Home Theater PCs) that require space-saving solutions.
-
Flex ATX Form Factor:
Flex ATX power supplies are highly compact and designed for mini PCs and HTPCs. They balance size and performance and can fit in very small cases. When using a Flex ATX power supply, ensure compatibility with your case’s dimensions and form factor.
-
Compatibility Check:
Before purchasing a power supply, check your PC case’s compatibility with your chosen form factor. Some cases are specific to certain form factors. A mismatch can lead to installation problems or a non-functioning system. Carefully measure the space available for the power supply and verify that the chosen unit fits the case.
-
Custom Form Factors:
Sometimes, you may encounter unique or proprietary form factors, particularly with high-end or custom-built cases. Verifying compatibility with your specific case and its documentation or the case manufacturer’s website is essential.
-
Consider Future Upgrades:
When choosing a power supply form factor, think about potential future upgrades. If you plan to upgrade your system or add high-performance components, you may require a more powerful power supply or one with a different form factor. Assess your long-term goals to ensure your chosen form factor accommodates any future expansions.
The correct power supply form factor is essential for a successful PC build. Consider your case size, future upgrade plans, and compatibility when choosing a form factor. A well-matched power supply ensures efficient power delivery and allows for proper cable management and airflow inside your PC case. That contributes to the overall performance and reliability of your system.
Understanding Form Factors (ATX, Mini-ITX, Micro-ATX)
Form factors are crucial in determining your PC components’ physical size, layout, and compatibility. And that includes the power supply. Here, we’ll explore some of the most common form factors and their characteristics:
-
ATX (Advanced Technology Extended):
- Size: Standard ATX motherboards are typically 12 x 9.6 inches.
- Features: ATX motherboards provide plenty of expansion slots and connectivity options. They are a versatile choice for gamers and enthusiasts who require multiple GPUs, storage devices, and expansion cards.
- Power Supply Compatibility: ATX power supplies are the most common and compatible with standard ATX motherboards. They fit into mid-tower and full-tower cases designed for ATX components.
-
Mini-ITX:
- Size: Mini-ITX motherboards are the smallest, usually around 6.7 x 6.7 inches.
- Features: Mini-ITX motherboards are compact and suitable for space-constrained builds, like HTPCs and compact gaming rigs. They offer fewer expansion slots but still support modern CPUs and GPUs.
- Power Supply Compatibility: Mini-ITX cases typically require SFX or SFX-L power supplies, as these are designed to fit in compact cases. Some Mini-ITX cases may also accept smaller ATX or Flex ATX power supplies.
-
Micro-ATX (mATX):
- Size: Micro-ATX motherboards are intermediate in size, around 9.6 x 9.6 inches.
- Features: Micro-ATX motherboards provide a balance between compactness and expandability. They offer more expansion slots and connectivity than Mini-ITX but are smaller than ATX.
- Power Supply Compatibility: Micro-ATX motherboards are compatible with standard ATX power supplies if the PC case is designed for micro-ATX or ATX components. Some compact mATX cases may require SFX or SFX-L power supplies.
When selecting a power supply for your Build, it’s crucial to match its form factor to your PC case and motherboard. Here’s a quick guide:
- For standard ATX motherboards and cases, use an ATX power supply.
- Mini-ITX cases typically require SFX, SFX-L, or smaller ATX power supplies.
- Depending on their design, Micro-ATX cases can accommodate standard ATX and some SFX or SFX-L power supplies.
Understanding your motherboard’s form factor and the case you intend to use is essential for ensuring a compatible power supply and a successful PC build. Form factor compatibility will dictate whether the power supply fits and affects cable management and airflow, contributing to your system’s overall performance and aesthetics.
Ensuring Compatibility with Your PC Case
Selecting a power supply compatible with your PC case is crucial in building a functional and well-organized system. Misjudging compatibility can lead to problems during installation, cable management challenges, and, in some cases, a non-functioning PC. Here’s how to ensure your power supply is compatible with your case:
-
Check the Case’s Supported Form Factors:
Your PC case’s specifications will typically list the supported power supply form factors. Ensure that your chosen power supply matches one of these supported form factors. Most cases accommodate ATX power supplies. But when you have a smaller case, it may require SFX, SFX-L, or other compact power supply form factors.
-
Measure Available Space:
Measure the physical space inside your case where the power supply will be installed. Check the length, width, and height to ensure enough room for the power supply. Pay close attention to the length, as some power supplies, especially those with high wattage and additional features, can be longer than standard units.
-
Consider Cable Management:
Think about how you will manage the power supply cables. Some cases have dedicated cable management space behind the motherboard tray, while others may have limited room for cable routing. Consider the power supply’s cable length and the space available in your case for neat and efficient cable management.
-
Verify Mounting Points:
Check the case for the power supply mounting points. These are the areas where you’ll secure the power supply in place. Most cases have standardized mounting points for different form factors. However, your power supply must align with these mounting points.
-
Assess Cooling and Ventilation:
Consider the case’s cooling and ventilation. Some power supplies come with fans that exhaust hot air from the unit. Ensure that your case has adequate ventilation to accommodate this airflow. Some cases have bottom-mounted power supply mounts, while others have top-mounted designs. Choose a power supply configuration that aligns with your case’s layout.
-
Double-Check Component Clearance:
In addition to the power supply, consider the clearance for other components like the CPU cooler and graphics card. A larger power supply or non-standard layout could potentially obstruct these components. Ensure there is enough clearance for all your components to fit comfortably.
-
Read User Reviews and Case Compatibility:
User reviews and case manufacturer websites can provide insights into power supply compatibility issues with specific case models. Reading the experiences of other builders can help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure a seamless installation.
-
Plan Ahead for Cable Routing:
Consider the routing of power supply cables within your case. Many modern cases feature routing cutouts, grommets, and tie-down points to help with cable management. If your case has these features, ensure your chosen power supply’s cables are long enough to reach their intended destinations while leaving some slack for ease of assembly.
-
Modular or Non-Modular:
Choosing a modular, semi-modular, or non-modular power supply can impact cable management. Modular power supplies allow you to connect only the necessary cables, reducing clutter. If your case has limited space for cable management, a modular or semi-modular unit can be beneficial.
-
Consider Long-Term Expansion:
Consider potential future upgrades or changes in your system configuration if you add more components like extra storage drives, graphics cards, or cooling solutions. You must ensure your power supply can accommodate these without exceeding capacity. A little extra wattage can provide flexibility for upgrades without replacing the power supply.
-
Verify Compatibility with PSU Shroud:
Some modern cases have PSU (power supply unit) shrouds that conceal the power supply and cables for a cleaner look. Ensure your power supply and cables fit comfortably within the shroud if your case has one. Oversized power supplies or excessive cables can be problematic in such cases.
-
Warranty and Return Policy:
Before finalizing your purchase, review the warranty and return policy of the power supply and the case. This way, you can ensure a hassle-free process if you encounter any compatibility issues or need to make returns or exchanges.
Meticulously check your case’s compatibility requirements and the chosen power supply’s form factor, dimensions, and cable management features so that you will prevent potential issues that could disrupt your PC build. Compatibility ensures that your power supply fits snugly. Further, it ensures your cables are neatly organized and your system runs smoothly with proper airflow. Ensuring compatibility enhances the overall performance and aesthetics of your PC.
By considering these factors and researching your specific case’s compatibility requirements, you can confidently select a power supply that fits seamlessly. It can improve the overall aesthetics and functionality of your PC. Careful planning and compatibility checking will result in a clean, well-organized build that functions at its best and offers the potential for future upgrades.
Cable Management and Connectors
Cable management is a critical aspect of assembling a PC. Well-organized cables not only enhance the aesthetics of your Build but also improve airflow, cooling, and overall system functionality. When choosing a power supply, it is essential to consider the cables and connectors it provides and how they will work with your components and case.
-
Modular, Semi-Modular, or Non-Modular:
The first aspect to consider is whether your chosen power supply is modular, semi-modular, or non-modular.
- Modular: Modular power supplies allow you to attach only the cables you need. This reduces cable clutter and makes cable management more effortless. It is especially useful in cases with limited space for routing cables.
- Semi-Modular: Semi-modular power supplies have essential cables permanently attached (e.g., motherboard and CPU connectors) and modular connectors for peripheral cables (e.g., PCIe and SATA). This offers a balance between convenience and customization.
- Non-Modular: Non-modular power supplies come with all the cables permanently attached. While typically more affordable, they can result in a surplus of cables that may be challenging to manage in smaller cases.
-
Consider Your Components:
Before finalizing your power supply choice, think about the components you’re using and the connectors they require. Consider the following:
- Motherboard: Ensure your power supply has the correct 24-pin ATX motherboard connector.
- CPU: Check for the necessary 8-pin or 4+4-pin CPU power connectors.
- Graphics Card: Verify the number and type of PCIe connectors required for your GPU (usually 6-pin or 8-pin).
- Storage Drives: Ensure the power supply offers adequate SATA and Molex connectors for your hard drives and SSDs.
- Peripherals: If you have additional components like case fans or lighting, ensure enough connectors are available.
-
Cable Length:
Pay attention to the length of the power supply cables. Some cases have routing channels or grommets that require longer cables to reach components farther from the power supply. Please verify that your chosen power supply’s cables are long enough to reach their destinations without strain or unnecessary slack.
-
Cable Sleeving and Aesthetics:
Many modern power supplies come with sleeved or flat cables that not only help with cable management but also improve the overall aesthetics of your Build. Consider the appearance of the cables and whether they match your desired theme or look.
-
Cable Ties and Routing:
Plan out your cable routing before starting the Build. Use cable ties, Velcro straps, or cable management accessories to secure and organize your cables. Proper routing looks cleaner and helps maintain optimal airflow, cooling, and system performance.
-
Safety and Voltage Regulation:
Ensure that your power supply cables are correctly connected and secured. Loose or improperly connected cables can lead to power issues and even damage your components. Also, make sure the power supply provides stable voltage output. Fluctuations in power supply can harm your hardware.
Organizing and managing your cables can significantly impact your PC’s aesthetics, cooling, and performance. Carefully selecting a power supply with the right connectors and cable management options is essential for creating a clean, efficient, and functional build.
Managing Cables for Better Airflow
Effective cable management is not just about aesthetics. It also plays a critical role in maintaining optimal airflow within your PC case. Proper airflow ensures your components stay cool and operate efficiently. Here are some tips for managing cables to improve airflow in your system.
-
Plan Cable Routes:
Before assembling your PC, plan out the routes for your cables. Identify where each cable will go and how it will be routed. Consider the location of your power supply, motherboard connectors, and components such as graphics cards and storage drives.
-
Use Cable Routing Channels:
Many modern cases come with built-in cable routing channels and grommets. Utilize these features to guide your cables neatly from one part of the case to another. These channels help keep cables out of airflow paths and create a cleaner look.
-
Bundle and Secure Cables:
Grouping similar cables together using cable ties, Velcro straps, or cable management accessories is essential. Bundling cables reduces clutter and makes routing more manageable. Secure these bundles to the case using cable tie-down points or clips. That will ensure that cables are not hanging loosely and obstructing airflow.
-
Route Cables behind the Motherboard Tray:
The area behind the motherboard tray is an ideal space for routing and hiding cables. Most cases have a gap between the motherboard tray and the side panel. That provides ample room for routing and concealing cables. This approach keeps the visible side of the case tidy and minimizes obstruction to airflow.
-
Use Modular or Semi-Modular Power Supplies:
Modular and semi-modular power supplies allow you to connect only the cables you need. This reduces cable clutter inside the case and provides more flexibility in managing cable lengths and placement.
-
Keep Cables Away from Fans:
Keep your cables well clear of cooling fans. Cables that obstruct fans can disrupt airflow and lead to increased temperatures. Ensure that no cables are directly behind the intake or exhaust fans.
-
Minimize Excess Cable Length:
Excess cable length can lead to clutter and blockage of airflow. When using modular power supplies, select appropriately sized cables for your case. Some power supplies also offer cable kits with custom-length cables for cleaner routing.
-
Avoid Sharp Bends and Kinks:
Avoid making sharp bends or kinks in your cables, as this can obstruct airflow and damage cables over time. Route cables with gentle curves and avoid tight turns.
-
Test Fit Components:
Before finalizing your cable management, test fit components to ensure that cables do not interfere with installing components like graphics cards, CPU coolers, or storage drives.
-
Regular Maintenance:
After assembling your PC, periodically check and maintain your cable management. Over time, cables may shift or become loose, impacting airflow. Make adjustments and re-secure cables as needed to maintain proper airflow.
Effective cable management improves airflow and cooling and makes your PC easier to upgrade and maintain. A clean, organized interior improves your components’ performance and longevity and enhances your PC build’s overall aesthetic appeal.
Types of Connectors
Let us explore in detail the various types of connectors commonly found in desktop power supplies:
-
24-Pin ATX Connector:
- Purpose: The 24-pin ATX connector is often called the primary connector. It provides power to the motherboard, and a critical connection supplies power to the motherboard, CPU, and other components.
- Description: This connector combines a 20-pin connector and a 4-pin connector into a single 24-pin block. It’s designed to be compatible with both 20-pin and 24-pin motherboard sockets.
- Compatibility: All motherboards require a 24-pin ATX connector. However, some older motherboards may only use the 20-pin portion of the connector.
-
8-Pin EPS Connector (4+4 Pin):
- Purpose: The 8-pin EPS connector is also known as the CPU power connector. It supplies power to the CPU. It’s essential for stable CPU performance, especially in high-end systems.
- Description: The 8-pin EPS connector is often divided into two 4-pin halves that can be combined for an 8-pin connection. This design allows compatibility with motherboards that have either 4-pin or 8-pin CPU power sockets.
- Compatibility: High-performance motherboards and CPUs, especially those used in gaming or content creation rigs, typically require an 8-pin EPS connector.
-
PCIe Connectors (6-pin and 8-pin):
- Purpose: PCIe connectors provide power to graphics cards (GPUs). They are essential for GPUs with different power requirements, especially high-end gaming graphics cards.
- Description: PCIe connectors come in two common forms: 6-pin and 8-pin. Some GPUs require a single 6-pin connector, while others, especially high-end models, need one or two 8-pin connectors.
- Compatibility: The number and type of PCIe connectors needed depend on your graphics card’s specifications. Check the GPU manual or specifications for the exact requirements.
-
SATA Connectors:
- Purpose: SATA connectors power storage devices like hard drives, solid-state drives, optical drives, and other peripherals.
- Description: These connectors are relatively flat and L-shaped. They have replaced older Molex connectors for most modern devices.
- Compatibility: SATA connectors are universally used for connecting storage and other devices. That is making them a standard in modern power supplies.
-
Molex Connectors:
- Purpose: Molex connectors are older power connectors that were once prevalent for connecting storage drives, fans, and other peripherals.
- Description: They are rectangular with four pins, often used for older hard drives, optical drives, and fans. Some power supplies still include Molex connectors for compatibility with older devices.
- Compatibility: Molex connectors are less common in modern power supplies due to the widespread use of SATA connectors for similar purposes.
-
4-Pin Peripheral Connectors:
- Purpose: 4-pin peripheral connectors, like Molex connectors, are used for powering fans and older devices like certain case fans, lighting, and peripherals.
- Description: These connectors are generally round and have four pins. It makes them easily distinguishable from other connectors.
- Compatibility: While not as common as SATA connectors, these connectors can be found in some power supplies and are compatible with legacy hardware.
-
Floppy Drive Connectors:
- Purpose: These small, rectangular connectors were initially used to power floppy disk drives. They are now almost obsolete.
- Description: Floppy drive connectors are very small and flat, with four pins.
- Compatibility: You’re unlikely to find these connectors in modern power supplies. The floppy drives are no longer in common use.
When selecting a power supply, ensure it provides the necessary connectors for your specific components like the motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage drives, and other peripherals. Always double-check the compatibility between your components and your power supply’s connectors to ensure a smooth and functional PC build.
Power Supply Efficiency and Heat Management
The efficiency of your desktop power supply affects your energy bills and plays a crucial role in managing heat within your PC case. Understanding power supply efficiency and its impact on heat management is essential for optimizing your computer’s performance and lifespan.
-
Efficiency and Heat Generation:
Power supplies are not 100% efficient. Some electrical energy they draw from the wall is lost as heat during conversion. The less efficient a power supply is, the more heat it generates. Here’s how power supply efficiency ratings, like the 80 PLUS certification, relate to heat management:
- 80 PLUS Certification: Power supplies with higher 80 PLUS ratings (Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, and Titanium) are more efficient and waste less energy as heat. This saves you money on energy bills. It also helps maintain lower operating temperatures inside your PC case.
-
The Importance of Lower Heat:
Excessive heat can have several negative consequences for your computer:
- Reduced Component Lifespan: High temperatures can lead to premature wear and tear on your components. That is potentially shortening their lifespan.
- Performance Degradation: Overheating can cause thermal throttling. Thermal throttling is a process where components like the CPU or GPU reduce their performance to prevent overheating. This leads to decreased system performance.
- System Instability: Extremely high temperatures can result in system instability, crashes, and even damage to components.
-
Efficient Power Supplies and Cooling:
Efficient power supplies not only reduce heat generation. It also positively impacts your system’s cooling solution:
- Less Heat to Dissipate: When a power supply is more efficient, it produces less waste heat that your PC’s cooling system must work to dissipate. This means cooling fans and heatsinks can operate more effectively.
- Lower Fan Speeds: With less heat to manage, your case fans and CPU/GPU coolers may run at lower speeds. Thereby, they reduce noise levels and extend the life of these components.
- Airflow Optimization: Efficient power supplies allow you to focus on optimizing airflow for other components. Therefore, you do not need to divert as much attention to cooling the power supply itself.
-
Choosing the Right Wattage and Efficiency:
Selecting a power supply with the correct wattage for your system is crucial. An oversized power supply operating at lower loads may be less efficient and generate more heat than a correctly sized unit.
- Balancing Wattage and Efficiency: Choose a power supply that meets your system’s power needs without being excessively overpowered. A good practice is to aim for a power supply around 20% higher in wattage than your calculated needs.
-
Quality and Efficiency:
While efficiency ratings are essential, it’s also vital to consider the overall quality of the power supply. A high-quality, lower-wattage power supply can outperform a generic, higher-wattage unit in both efficiency and heat management.
Power supply efficiency directly impacts heat management and system performance. Selecting an efficient power supply with the right wattage for your system is crucial for maintaining lower operating temperatures. It is optimizing cooling. And it ensures the long-term health and stability of your PC. Carefully consider your power supply’s efficiency rating, quality, and compatibility to achieve optimal heat management within your computer.
Benefits of an Efficient Power Supply
Investing in an efficient power supply for your desktop computer offers several advantages, including lower energy bills. Let’s explore these benefits.
-
Reduced Energy Consumption:
Efficient power supplies convert more electrical energy from your wall outlet into usable power for your components. This means less energy is wasted as heat during the conversion process. Consequently, you consume less electricity. That can lead to lower energy bills over time.
-
Environmental Friendliness:
Efficient power supplies are eco-friendly. They reduce the carbon footprint associated with your computer’s operation. As the world becomes more environmentally conscious, using less electricity and generating less heat can contribute to a greener planet.
-
Lower Heat Generation:
Efficient power supplies produce less waste heat. That is advantageous for your PC’s overall heat management. With less dissipated heat, your cooling system can operate more effectively, including case fans and heatsinks. This, in turn, helps maintain lower operating temperatures inside your PC case.
-
Extended Component Lifespan:
High temperatures can wear down and damage components over time. An efficient power supply reduces the heat your components are exposed to. It ultimately extends their lifespan. Your CPU, GPU, and other sensitive components will benefit from more consistent, lower operating temperatures.
-
Reduced Noise Levels:
Cooling fans and heatsinks often have to work harder to manage excess heat. An efficient power supply allows these components to operate at lower speeds. And that reduces noise levels. Your computer can run quieter. And that creates a more pleasant and less distracting computing environment.
-
Stable System Performance:
Efficient power supplies help maintain stable system performance by minimizing the likelihood of thermal throttling. Components may reduce their performance to avoid overheating when they get too hot. That will lead to decreased system performance. You are less likely to encounter performance issues with efficient power delivery and lower operating temperatures.
-
Improved Long-Term Cost Savings:
Efficient power supplies may have a higher initial cost. It has long-term savings on energy bills. And it potentially extended component lifespans. Further, it makes them a cost-effective choice. The initial investment can pay off through reduced electricity costs and fewer hardware replacements.
-
Reliability and Peace of Mind:
Efficient power supplies from reputable manufacturers are often built with high-quality components and warranties. That ensures reliability and peace of mind. They are less likely to fail or cause issues in your system.
An efficient power supply is an investment that offers a range of benefits. The benefits include cost savings, reduced environmental impact, better heat management, and improved long-term reliability. When selecting a power supply, consider its efficiency rating and quality to reap these advantages and enhance your desktop computer’s overall performance and lifespan.
Overheating and Its Effects on PC Performance
Overheating is a common issue in desktop computers that can significantly impact overall system performance and component longevity. Understanding the causes and effects of overheating is essential for maintaining a well-functioning and reliable PC.
-
Causes of Overheating:
Several factors can contribute to overheating in a desktop computer:
- Inadequate Cooling: The most common cause of overheating is inadequate cooling. That can result from insufficient case fans, improperly seated or malfunctioning CPU coolers, or a poorly designed case with limited airflow.
- Dust and Debris: Over time, dust and debris can accumulate on components like heatsinks and fans, impeding airflow and causing temperature spikes.
- Thermal Paste Deterioration: The thermal paste between the CPU and heatsink can deteriorate, reducing its ability to transfer heat effectively.
- Overclocking: Overclocking components like the CPU or GPU can generate excess heat and lead to overheating if not correctly managed.
-
Effects on PC Performance:
Overheating can lead to several negative consequences that impact your computer’s performance and longevity:
- Reduced Performance: Excess heat causes components to throttle. Throttling reduces their performance to avoid overheating. This results in slower CPU and GPU speeds. And it negatively affects gaming and multitasking performance.
- System Instability: Overheating can lead to system instability, including crashes, freezing, and unexpected shutdowns. These issues can result in data loss and disrupt your workflow.
- Hardware Damage: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can damage components. That leads to permanent hardware failures. Commonly affected components include the CPU, GPU, motherboard, and storage drives.
- Noise and Dust Buildup: Overheating often prompts cooling fans to spin faster. It results in increased noise levels. Inadequate cooling can also lead to more significant dust buildup inside your case. And it exacerbates the overheating problem.
-
Preventing Overheating:
To prevent overheating and its adverse effects on PC performance, consider the following measures:
- Proper Cooling: Ensure your PC has adequate cooling with case fans, CPU and GPU coolers, and a well-ventilated case. Monitor fan speeds and temperatures regularly.
- Dust Management: Clean your PC regularly to remove dust and debris from components, fans, and heatsinks. Use compressed air to blow out dust from hard-to-reach areas.
- Thermal Paste Replacement: Periodically replace the thermal paste between the CPU and heatsink to maintain adequate heat transfer.
- Optimal Case and Component Placement: Properly position your case and components to ensure they can access cool, fresh air. Avoid obstructing vents or creating airflow bottlenecks.
- Avoid Overclocking: If you are experiencing overheating issues, consider dialing back overclocked settings to reduce heat production.
-
Temperature Monitoring:
Use software tools like HWMonitor or MSI Afterburner to monitor component temperatures. If you notice temperatures consistently exceeding safe levels, it is a sign that your system requires attention.
Overheating can significantly impact your PC’s performance, stability, and longevity. Regular maintenance and proper cooling solutions are essential to prevent overheating and maintain your computer’s optimal functionality. If you suspect overheating issues, promptly safeguard your system and ensure a smooth computing experience.
Power Supply Safety and Reliability
The PSU is one of the most critical components in your desktop computer. Ensuring its safety and reliability is paramount for your system’s overall health and functionality. Let’s delve into why these aspects are so crucial:
-
Electrical Safety:
The power supply converts and supplies electrical power to your PC’s components. Ensuring electrical safety is essential to prevent accidents and protect your computer and, more importantly, your safety:
- Surge Protection: Quality power supplies have surge protection to safeguard against voltage spikes and power surges, which can damage components. Surge protection is especially vital in areas with inconsistent power quality.
- Short Circuit Protection: In the event of a short circuit, a reliable power supply will shut down to prevent damage or fires.
- Overload Protection: Overloading a power supply can lead to overheating and component damage. Reliable PSUs are equipped with overload protection to prevent this from happening.
- EMI/RFI Filtering: Power supplies may have EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) and RFI (Radio Frequency Interference) filtering to reduce electrical noise that can affect your system’s performance.
-
Component Longevity:
A reliable power supply contributes to the longevity of your components:
- Stable Power Delivery: High-quality PSUs deliver a consistent and stable power supply to your components. This stability reduces the risk of voltage spikes or fluctuations that can damage or reduce the lifespan of your components.
- Component Compatibility: A reliable power supply ensures compatibility with a wide range of components. It provides the necessary connectors and voltage levels required by modern motherboards, CPUs, GPUs, and storage devices.
-
System Reliability:
A dependable power supply is essential for maintaining overall system reliability:
- Reduced System Failures: Power supply failures can result in significant system instability, including crashes and data loss. A reliable PSU minimizes these risks. And it ensures that your PC runs smoothly.
- Efficiency and Heat Management: High-quality, efficient power supplies generate less heat and better manage it. This leads to improved system stability and longevity.
-
Energy Efficiency:
Reliable power supplies like 80 PLUS Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, or Titanium often have higher efficiency ratings. These ratings indicate how efficiently the PSU converts electrical power into usable power for your components. Higher efficiency reduces energy consumption and results in lower heat generation. It also contributes to better cooling and longer component lifespans.
-
Brand Reputation and Warranties:
Choosing a reputable power supply manufacturer with a history of reliable products is essential. Established brands often provide better quality and offer warranties. It gives you peace of mind and support in case of issues.
-
Sizing and Wattage:
Selecting the correct wattage for your system is critical. An oversized power supply operating at low loads may be less efficient and generate more heat. On the other hand, an undersized power supply can cause instability and potentially damage components. Balance is primary when choosing the correct wattage for your system.
A safe and reliable power supply is the backbone of your PC’s stability, performance, and longevity. It ensures electrical safety, component protection, and system reliability. When choosing a power supply, prioritize quality, efficiency, and compatibility to safeguard your investment and enhance your overall computing experience.
Surge Protection and Overvoltage Protection
-
Surge Protection:
Surge protection is a crucial feature in a reliable power supply. Surges are sudden spikes in voltage. That can occur for various reasons, including lightning strikes, power grid fluctuations, or even large appliances turning on and off. These surges can be harmful to your computer’s components. Here’s how surge protection works and why it’s vital:
- Surge Suppressors: High-quality power supplies come equipped with surge suppressors that detect voltage spikes and divert excess energy away from your components. They act as a barrier between your computer and the electrical grid.
- Protecting Your Components: Surge protection safeguards your components, like the motherboard, CPU, GPU, and storage drives, from potential damage caused by voltage spikes. Without surge protection, a power surge could lead to costly repairs or replacements.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your power supply has surge protection provides peace of mind. It is especially crucial if you live in an area prone to electrical storms or power fluctuations. It helps ensure your computer runs smoothly even when the electrical grid experiences turbulence.
-
Overvoltage Protection:
In addition to surge protection, overvoltage protection is another critical feature that helps maintain the safety and integrity of your computer’s components:
- Voltage Regulation: A reliable power supply has voltage regulation circuits that monitor the incoming voltage from your wall outlet. If the voltage exceeds safe levels, the power supply adjusts the output to keep it within a safe range.
- Preventing Damage: Overvoltage protection prevents your components from being exposed to damaging voltage levels. This is especially important in unstable power supplies or environments with frequent voltage fluctuations.
- Safeguarding Data: Power supplies with overvoltage protection help safeguard your data by reducing the risk of sudden power interruptions or voltage surges that could lead to data corruption or loss.
Surge and overvoltage protection are essential for maintaining your computer components’ safety, reliability, and longevity. By investing in a power supply with these features, you significantly reduce the risk of electrical damage and ensure the continued smooth operation of your PC, even in less-than-ideal electrical conditions.
Choosing a Reputable Brand
Selecting a reliable power supply for your desktop computer involves more than considering technical specifications. The brand of the power supply also plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality, safety, and performance of your system. Here’s why choosing a reputable brand is so important:
-
Quality Assurance:
Reputable power supply manufacturers are committed to producing high-quality products. They invest in rigorous testing, quality control, and superior components to deliver power supplies that meet or exceed industry standards. When you choose a well-established brand, you can be more confident that the power supply will perform as advertised.
-
Safety Standards:
Reputable brands prioritize safety. They adhere to strict safety standards and design their power supplies with surge protection, overvoltage protection, short circuit protection, and high-quality components to reduce the risk of electrical issues, fires, or other safety hazards.
-
Reliability and Longevity:
A well-regarded brand is more likely to produce reliable power supplies that have a longer lifespan. Their products are engineered to endure the rigors of daily use and provide consistent, stable power to your components.
-
Customer Support and Warranty:
Reputable brands offer solid customer support and warranties. They stand behind their products and assist in case of issues. When you buy a power supply from a trusted brand, you have peace of mind knowing that you’ll receive help if you encounter problems during installation or operation.
-
Compatibility and Innovation:
Leading power supply manufacturers keep up with the latest technological advancements and ensure compatibility with a wide range of components. This includes providing modular connectors, support for multiple form factors, and compatibility with various motherboards, CPUs, GPUs, and storage devices.
-
Brand Reputation:
Reputable brands have built a positive reputation in the computer hardware industry. You can rely on the experiences and reviews of other users to gauge the quality and performance of power supplies from these manufacturers. Online communities and reviews provide valuable insights into the reputation of specific brands.
-
Product Range:
Established brands often offer a wide range of power supply options. That caters to different wattage requirements, efficiency levels, and budgets. This variety allows you to choose a power supply that precisely fits your needs.
-
Brand-Specific Features:
Certain brands may include unique features or technologies in their power supplies. For example, some brands are known for exceptional noise reduction or custom cabling solutions. Researching brand-specific features can help you find a power supply that aligns with your requirements.
When selecting a power supply, consider established brands such as Corsair, EVGA, Seasonic, Thermaltake, Be Quiet!, and Cooler Master. These brands have earned recognition for their commitment to quality, safety, and performance.
Choosing a reputable brand for your power supply is a wise decision that can significantly influence your computer’s overall performance, safety, and longevity. Invest in a power supply from a trusted manufacturer. And you will enjoy a reliable and hassle-free computing experience.
Upgrading Your Desktop Power Supply
As your computing needs evolve, you might find that your existing power supply is no longer sufficient. Upgrading your desktop power supply can be a necessary and beneficial step to ensure your system can handle new components and deliver stable and reliable power. Here’s a guide on upgrading your power supply:
-
Determine the Wattage Requirement:
Before selecting a new power supply, calculate your system’s wattage requirements. Consider your CPU, GPU, motherboard, storage devices, and other components. Many online wattage calculators can assist you in this process. Ensure the new power supply’s wattage meets or exceeds your calculated needs.
-
Consider Efficiency and Certification:
Efficiency ratings, such as the 80 PLUS certification, play a role in reducing energy consumption and heat generation. Choose a power supply with an appropriate efficiency rating. That should align with your environmental concerns and system cooling requirements.
-
Assess the Physical Space:
Ensure the new power supply will fit within your case. Some cases are designed to accommodate standard ATX power supplies, while smaller cases may require SFX or TFX form factors. Measure the available space within your case and verify that the new power supply’s dimensions are compatible.
-
Check the Connector Compatibility:
Review the connectors your components require. Ensure your power supply has the necessary 24-pin ATX, 8-pin EPS, PCIe, SATA, and other connectors for your motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage devices, and peripherals.
-
Plan for Future Expansion:
Consider future upgrades when selecting a power supply. If you anticipate adding more components or upgrading to a more power-hungry GPU or CPU, opt for a power supply with a higher wattage to accommodate these changes.
-
Modular or Non-Modular:
Decide whether you prefer a modular, semi-modular, or non-modular power supply. Modular and semi-modular power supplies offer flexibility in cable management by allowing you to connect only the necessary cables. And it reduces clutter. Non-modular power supplies come with all cables attached. That may be more cost-effective but could result in excess cables in smaller cases.
-
Choose a Reputable Brand:
Select a power supply from a well-established, reputable brand that produces high-quality, reliable units. Brand reputation matters regarding your power supply’s safety, performance, and support.
-
Review Warranty and Support:
Check the warranty the manufacturer offers, as it can be a crucial factor in case you encounter any issues. A more extended warranty period indicates the brand’s confidence in the product’s durability and reliability. Ensure that the manufacturer provides adequate customer support in case you need assistance.
-
Seek Professional Installation (if needed):
If you are unsure about the installation process or lack the technical knowledge, it’s wise to seek professional help. A qualified technician can ensure the new power supply is installed correctly and safely.
-
Recycle or Sell the Old Power Supply:
Once you have upgraded your power supply, consider recycling or selling your old one. Some retailers and organizations may accept old power supplies for recycling while selling the unit can help recoup some of your investment.
Upgrading your desktop power supply is a significant step in enhancing your system’s performance stability and future-proofing it for component upgrades. By carefully assessing your needs and selecting the correct power supply, you can ensure your computer continues to meet your demands and delivers reliable power to all your components.
Signs It’s Time for an Upgrade
Deciding when to upgrade your desktop power supply is not always straightforward. But clear signs indicate it might be time for a replacement. Here are some common indicators that you should consider upgrading your power supply.
-
Frequent Shutdowns or Instability:
If your computer experiences frequent shutdowns, crashes, or instability, it could be due to an insufficient or failing power supply. Components like the CPU and GPU require stable and adequate power to operate without interruption.
-
Overheating and Component Throttling:
High temperatures inside your PC case can indicate insufficient power or inefficient cooling. If you notice your CPU or GPU frequently throttling its performance to prevent overheating, it might be time for a more capable power supply to help manage the load and heat.
-
New Components or Upgrades:
When you add new components to your system, like a more powerful graphics card, CPU, or additional storage devices, you may exceed the capabilities of your current power supply. An upgrade is necessary to meet the increased power demands of your upgraded system.
-
Unexplained Hardware Failures:
Power supply issues can cause unexplained hardware failures. If you have ruled out other factors and your components are failing prematurely, it’s worth investigating the power supply as a potential culprit.
-
Audible Coil Whine or Electrical Noise:
Unusual noises like coil whine or electrical noise from the power supply can indicate problems. These noises may be annoying and signify that the power supply is struggling to deliver power efficiently.
-
Insufficient Connector Availability:
Modern components require specific connectors like 8-pin EPS connectors or multiple PCIe connectors for GPUs. If your power supply lacks the necessary connectors, it’s time to upgrade to meet your component’s requirements.
-
Inadequate Wattage for Your Components:
Pushing your current power supply to its limits regarding wattage is a clear sign you need an upgrade. Running a power supply at or near its maximum capacity can lead to instability and reduced efficiency.
-
Aging or Generic Power Supply:
If your current power supply is several years old or a generic or low-quality unit that came with your case, it’s a good idea to consider an upgrade. Older power supplies may not meet the power requirements of newer components. Further generic units may lack safety features or quality components.
-
Frequent Overheating and Cooling Issues:
If you frequently battle overheating issues and poor system cooling, it might be due to your power supply’s heat generation. Upgrading to a more efficient and cooler-running unit can help mitigate these problems.
-
Enhanced Efficiency and Features:
Newer power supplies often have better efficiency ratings, modular cable management, and additional features like fan control. An upgrade can provide these benefits if you want to enhance your computer’s performance, improve cable management, and reduce energy consumption.
Recognizing these signs that it is time for a power supply upgrade is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your desktop computer. By paying attention to these indicators, you can decide to replace your power supply when needed. It ensures your system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Tips for a Smooth Upgrade Process
Upgrading your desktop power supply can be straightforward if you follow some essential steps and tips. Here are some guidelines to ensure a smooth upgrade experience:
-
Prepare Your Workspace:
- Clear a well-lit and spacious area to work on your computer. Ensure you have easy access to the case, tools, and the new power supply.
-
Gather the Necessary Tools:
- Have the required tools on hand, including screwdrivers, cable ties, and possibly an anti-static wrist strap to prevent electrostatic discharge.
-
Unplug and Disconnect:
- Before you start, power down your computer. Unplug it from the wall, and disconnect all peripherals and cables.
-
Ground Yourself:
- To prevent damaging sensitive components with electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by touching a grounded metal surface or by wearing an anti-static wrist strap.
-
Document and Label Cables:
- Take pictures of your existing cable connections and label them if possible. This will make reconnecting everything correctly when installing the new power supply easier.
-
Assess Space and Compatibility:
- Considering the required connectors, wattage, and form factor, ensure the new power supply fits your case and is compatible with your components.
-
Remove the Old Power Supply:
- Open your computer case and disconnect all cables from the old power supply. Remove the screws securing it to the case and slide it out.
-
Install the New Power Supply:
- Carefully slide the new power supply into place, secure it with screws, and connect all the cables. Ensure that each component is adequately powered, including the motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage drives, and peripherals.
-
Cable Management:
- Proper cable management is essential for airflow and aesthetics. Use cable ties and routing options in your case to keep cables organized and out of the way of cooling fans.
-
Test the System:
- Before closing the case, plug your computer back in and turn it on. Ensure that all components are functioning correctly and the system boots without issues.
-
Monitor Temperatures:
- Monitor component temperatures, especially the CPU and GPU, to ensure the new power supply doesn’t cause overheating.
-
Check for Any Strange Noises:
- Listen for unusual noises, such as coil whine or electrical noise. It might indicate a problem with the new power supply if you hear anything unusual.
-
Keep the Old Power Supply:
- Store your old power supply in a safe place in case you need it as a backup or if you decide to use it in another system.
-
Dispose of the Old Unit Responsibly:
- If you do not plan to keep the old power supply, consider recycling or disposing of it in an environmentally friendly manner. Many electronics stores and recycling centers accept old power supplies.
-
Register the New Power Supply:
- Register your new power supply with the manufacturer to activate the warranty. This ensures you have the manufacturer’s support in case of any issues.
-
Keep Documentation:
- Store any user manuals, Documentation, and warranty information in a safe place for future reference.
By following these tips, you can ensure a smooth and successful power supply upgrade. It minimizes the risk of damage to your components and ensures that your computer operates reliably and efficiently with the new power supply.
Installing and Connecting a Desktop Power Supply
Upgrading or replacing your desktop power supply is a relatively straightforward process that can significantly enhance your computer’s performance and reliability. To guide you through the installation and connection process, follow these steps:
-
Safety Precautions:
Before you begin, ensure your safety and the safety of your components:
- Turn off your computer and unplug it from the wall outlet.
- Ground yourself to prevent electrostatic discharge by touching a grounded metal surface or using an anti-static wrist strap.
-
Open the Computer Case:
Remove the side panel of your computer case to gain access to the internal components. The method for opening the Computer Case varies depending on your case design. But it typically involves removing screws or sliding panels.
- Disconnect Cables:
Unplug all power cables connected to the old power supply, including those attached to the motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage drives, and peripherals. It’s essential to remember or label the cables to ensure proper reconnection.
-
Remove the Old Power Supply:
- Locate the old power supply, which is usually secured by screws or clips. Remove these fasteners and gently slide out the old power supply from its mounting location.
-
Install the New Power Supply:
- Carefully slide the new power supply into the case, ensuring it aligns with the mounting holes. Secure it with screws to keep it firmly in place.
-
Connect Cables:
- Reconnect the cables to the new power supply. Refer to your labeled cables or your photos to ensure each component receives the appropriate power.
- Start with the 24-pin ATX connector for the motherboard, the 8-pin EPS connector for the CPU, and the PCIe connectors for the GPU. Proceed to connect the cables for storage drives and peripherals.
-
Cable Management:
- Organize the cables inside the case for efficient airflow and a clean appearance. Use cable ties or routing options in your case to keep the cables neat and out of the way of cooling fans.
-
Double-Check Connections:
- Before closing the case, double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and properly seated. Loose connections can lead to system instability.
-
Power On:
- Plug your computer back into the wall outlet, turn it on, and ensure all components function correctly. Check for any unusual noises or errors during the boot process.
-
Monitor Temperatures:
- Monitor component temperatures, especially the CPU and GPU, to ensure the new power supply doesn’t cause overheating issues. Proper cooling is crucial for system stability.
-
Close the Case:
- Once you have confirmed everything is working as expected, close the computer case by reattaching the side panel and securing it with screws or clips.
-
Dispose of the Old Unit:
- If you do not plan to keep the old power supply, consider recycling or disposing of it responsibly. Many electronics stores and recycling centers accept old power supplies.
-
Register the New Power Supply:
- Register your new power supply with the manufacturer to activate the warranty. This ensures you have the manufacturer’s support in case of any issues.
-
Keep Documentation:
- Store any user manuals, Documentation, and warranty information in a safe place for future reference.
Following these steps, you can easily install and connect a desktop power supply. Properly connected power cables, efficient cable management, and attention to safety precautions will help ensure a smooth and successful power supply upgrade or replacement.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Here is a step-by-step installation guide for replacing a desktop power supply.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Replacing or upgrading your desktop power supply is a manageable process when you follow these step-by-step instructions:
Step 1: Safety First
Turn off your computer and unplug it from the wall outlet to ensure your safety and protect your components from electrical damage.
Ground yourself by touching a grounded metal surface or using an anti-static wrist strap to prevent electrostatic discharge.
Step 2: Open the Computer Case
Remove the side panel of your computer case to gain access to the internal components. The method for opening the computer case varies depending on your case design.
Step 3: Disconnect Cables
Unplug all power cables connected to the old power supply. Then, disconnect cables from the motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage drives, and peripherals. Remember or label the cables for proper reconnection.
Step 4: Remove the Old Power Supply
Locate the old power supply, usually secured by screws or clips. Remove these fasteners and gently slide out the old power supply from its mounting location.
Step 5: Install the New Power Supply
Carefully slide the new power supply into the case, ensuring it aligns with the mounting holes.
Secure the new power supply to the case with screws to keep it firmly in place.
Step 6: Connect Cables
Connect the cables to the new power supply. Start by connecting the 24-pin ATX connector to the motherboard, the 8-pin EPS connector to the CPU, and the PCIe connectors for the GPU. Then, connect the cables for storage drives and peripherals.
Step 7: Cable Management
Organize the cables inside the case for efficient airflow and a clean appearance. Use cable ties or routing options in your case to keep the cables neat and out of the way of cooling fans.
Step 8: Double-Check Connections
Before closing the case, double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and properly seated. Loose connections can lead to system instability.
Step 9: Power On
Plug your computer back into the wall outlet, turn it on, and ensure all components function correctly. Check for any unusual noises or errors during the boot process.
Step 10: Monitor Temperatures
Monitor component temperatures, especially the CPU and GPU, to ensure the new power supply doesn’t cause overheating issues. Proper cooling is crucial for system stability.
Step 11: Close the Case
Once you’ve confirmed everything is working as expected, close the computer case by reattaching the side panel and securing it with screws or clips.
Step 12: Dispose of the Old Unit
If you don’t plan to keep the old power supply, consider recycling or disposing of it responsibly. Many electronics stores and recycling centers accept old power supplies.
Step 13: Register the New Power Supply
Register your new power supply with the manufacturer to activate the warranty. This ensures you have the manufacturer’s support in case of any issues.
Step 14: Keep Documentation
Store user manuals, Documentation, and warranty information in a safe place for future reference.
Following this step-by-step guide, you can confidently install and connect a desktop power supply. That ensures a smooth and successful upgrade or replacement process for your computer.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Replacing or upgrading a desktop power supply is usually a straightforward process. You may encounter some common issues during installation. Here’s how to troubleshoot and resolve these problems:
-
Inadequate Power:
Issue: If your system fails to power on or experiences unexpected shutdowns after the power supply upgrade, it could indicate an inadequate wattage for your components.
Solution:
- Double-check your power supply’s wattage to ensure it meets your system’s requirements.
- Verify that all required connectors are correctly connected to the motherboard, CPU, GPU, and storage devices.
- Consider removing any unnecessary peripherals or components that may overload the power supply.
-
Cable Misconnection:
Issue: Reversed or improperly connected cables can lead to boot failures, unexpected errors, or component damage.
Solution:
- Carefully review your cable connections, especially the 24-pin ATX and 8-pin EPS connectors for the motherboard and CPU.
- Ensure that all connector cables are appropriately seated and correctly aligned.
- Refer to your labeled cables or photos to confirm proper connections.
-
Overheating:
Issue: Overheating can occur if the new power supply generates more heat or if cable management obstructs airflow.
Solution:
- Check that your power supply’s fan functions correctly and that cables do not obstruct it.
- Ensure that the cooling system of your CPU and GPU is functioning properly.
- Review your cable management and rearrange cables for better airflow.
-
Noisy Power Supply:
Issue: Some power supplies may produce noise like coil whine, electrical noise, or fan noise.
Solution:
- Coil whine and electrical noise can be challenging to eliminate but are not necessarily harmful. They may decrease over time.
- Fan noise can often be addressed by adjusting fan speed settings in the BIOS or using software provided by the manufacturer.
- If the noise persists and is unbearable, contact the manufacturer for guidance or consider a replacement.
-
Component Errors:
Issue: After the power supply upgrade, your computer may report component errors or issues.
Solution:
- Double-check that all components are correctly powered and that connectors are secure.
- Update or reinstall drivers for components like the GPU, CPU, or motherboard to address any software-related issues.
- If component errors persist, verify that the components are still functioning correctly and consider seeking professional assistance.
-
System Boot Failure:
Issue: Your system may not boot after installing the new power supply.
Solution:
- Ensure that the power supply’s main switch is turned on.
- Verify that the 24-pin ATX connector and 8-pin EPS connector are correctly connected to the motherboard.
- Test your old power supply to check if the issue is related to the new unit. If the old power supply works, it may indicate a problem with the new power supply.
If you encounter any other specific issues during the installation process, consult the user manual provided by the power supply manufacturer or reach out to their customer support. Additionally, online forums and communities can be valuable resources for seeking advice from experienced users who may have encountered similar problems and found effective solutions.
Power Supply Maintenance
Maintaining your desktop power supply is essential to ensure its longevity and reliable performance. Although power supplies are relatively low-maintenance components, a few simple practices can help keep them in optimal condition:
-
Keep it Clean:
Dust and debris can accumulate inside your computer case and on the power supply’s fan and vents. It reduces its efficiency and potentially causes overheating. To keep it clean:
- To prevent dust buildup, regularly dust the interior of your computer case with a can of compressed air or a soft brush.
- Pay attention to the power supply’s fan. Ensure it remains unobstructed. Clean it gently to remove dust if necessary.
-
Check for Loose Connections:
Over time, vibrations and movements may cause power cables to loosen. Periodically inspect and reseat power connectors to ensure a secure connection.
-
Monitor Fan Operation:
The power supply fan is crucial for cooling. Monitor its operation during system boot-up. If you notice any irregularities like loud noise, consider replacing the fan.
-
Inspect for Damaged Cables:
Examine the power supply cables for signs of wear or damage. Frayed or damaged cables should be replaced to prevent electrical hazards.
-
Verify Surge Protection:
Ensure your power supply is connected to a surge protector or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to safeguard it from power surges or outages.
-
Test the Voltage Output:
If you suspect power supply issues, you can use a digital multimeter to test the voltage output of your power supply. However, this is an advanced step and should be done with caution.
-
Replace When Necessary:
Power supplies have a lifespan, and components can deteriorate over time. If you experience repeated issues or instability, consider replacing the power supply.
-
Follow Manufacturer Recommendations:
Consult the manufacturer’s Documentation for specific maintenance guidelines or any recommendations for your particular power supply model.
Remember that power supply maintenance is relatively minimal compared to other computer components. However, taking care of your power supply ensures that it continues to provide reliable and efficient power to your system. Further, it extends its lifespan and helps prevent unnecessary issues or component damage.
Cleaning and Dust Prevention
Dust and debris can accumulate over time inside your computer case and affect the efficiency and cooling of your power supply. Regular cleaning and dust prevention measures are essential to maintain the optimal performance of your desktop power supply. Here is how to keep your power supply clean and dust-free:
-
Dust the Interior:
Regularly dust the interior of your computer case to prevent dust buildup on components, including the power supply. You can use a can of compressed air or a soft brush to remove dust from surfaces, fans, and vents. Turn off your computer and unplug it from the wall before cleaning.
-
Maintain a Clean Environment:
Keep your computer in a clean and dust-free environment to reduce the amount of dust entering the case. Consider placing your computer on a clean surface and avoiding areas prone to excessive dust, like near open windows or vents.
-
Use Dust Filters:
Many modern computer cases come with dust filters on the intake and exhaust areas. If your case has these filters, use them to prevent dust from entering the system. If your case does not have dust filters, you can purchase aftermarket filters and attach them to the intake areas.
-
Positioning Matters:
Place your computer in a way that minimizes dust intake. Elevating your case slightly can help reduce the dust and debris that enters through the bottom or side vents.
- Regular Inspections:
Periodically inspect the power supply’s fan and vents to ensure they are unobstructed and free from dust buildup. Dust can accumulate on the fan blades and reduce cooling efficiency.
-
Maintain a Clean Room:
If your computer is in a room with high dust levels, consider keeping the room clean and well-ventilated. Regular cleaning and dusting of the room can indirectly help reduce dust inside your computer.
-
Scheduled Cleaning:
Create a schedule for cleaning your computer case. Depending on your environment, this could range from every few months to once a year. Consistency is critical to preventing dust buildup.
-
Cable Management:
Neat and organized cable management can help prevent dust from accumulating in hard-to-reach areas within your case. Use cable ties or routing options to keep cables tidy and out of the way.
-
Beware of Static:
While cleaning, be mindful of static electricity, as it can harm sensitive components. Use an anti-static wrist strap or touch a grounded metal surface to discharge any static electricity before touching your power supply or other components.
By adopting these cleaning and dust prevention practices, you can help prolong the life of your power supply, maintain efficient cooling, and prevent dust-related issues that can lead to overheating or power supply failure. Regular maintenance ensures your desktop power supply continues to provide reliable and stable power to your computer components.
Checking for Faulty Components
When experiencing issues with your desktop power supply, it’s essential to consider the possibility of faulty components within your system. Identifying and addressing these components can help ensure your power supply functions correctly, and your computer operates smoothly. Here is a guide on “how to check for faulty components.”
-
Visual Inspection:
Begin by conducting a visual inspection of your computer’s interior. Look for any obvious signs of damaged components like charred cables, burnt connectors, or visibly damaged parts. Be particularly attentive to the power supply cables and connectors.
-
Listen for Unusual Noises:
Power supplies, fans, and other components should operate silently or with minimal noise. Unusual sounds like loud grinding, clicking, or rattling may indicate a problem with the power supply’s fan or other components.
-
Component Testing:
You can test components individually to determine if they are faulty. Focus on the following:
- GPU (Graphics Card): If you experience display issues, test your GPU in another system or replace it with a known working card to check if the problem persists.
- RAM (Memory): Memory-related issues can lead to system instability. Test your RAM sticks one by one or replace them with known working modules to identify any problematic ones.
- Storage Devices: Hard drives or SSDs can cause boot failures or data corruption. Verify their health using diagnostic software or test with a different drive to rule out issues.
- Motherboard: Motherboard issues can lead to power-related problems. Check for visual damage, loose connections, or swollen capacitors. Testing with a known working motherboard can help diagnose problems.
- CPU: CPU-related issues are less common but can lead to system instability. Reseating the CPU, checking for bent pins, or testing with a different processor can help diagnose problems.
-
Monitoring Software:
System monitoring software checks hardware component’s temperatures, fan speeds, and power supply voltages. Sudden fluctuations or abnormalities in these values can indicate issues with specific components or the power supply itself.
-
Replace or RMA Components:
If you identify any faulty components during your tests, consider replacing them or taking advantage of warranties or Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) policies if the components are still under warranty. Ensure you handle the replacement process with care. You need to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and safety precautions.
-
Professional Assistance:
If you are unsure about identifying or resolving faulty components or if you lack the technical expertise, consider seeking professional assistance. Experienced technicians can diagnose and replace defective components efficiently.
By checking for and addressing faulty components within your system, you can eliminate potential sources of power supply issues and maintain a stable and reliable computer. Careful troubleshooting and replacing problematic components will help ensure your desktop power supply functions optimally and your system operates without interruptions.
Power Supply Accessories and Add-ons
Enhancing your power supply setup with various accessories and add-ons can not only optimize your system’s performance. But it also improves its overall functionality and aesthetics. Here are some power supply accessories and add-ons to consider:
-
Cable Extensions and Custom Sleeving:
Cable extensions and custom-sleeving kits can improve cable management. It reduces clutter and enhances the appearance of your build. These kits often include color-coordinated or patterned cables that replace the standard ones that come with your power supply. They are trendy among PC enthusiasts who want a clean, personalized system look.
-
Cable Combs and Organizers:
Cable combs and organizers help keep your cables neat and organized. They hold cables in place. That ensures a clean and well-ventilated system. They are particularly useful for routing and maintaining the correct alignment of multiple cables like those for the 24-pin ATX connector or PCIe power connectors.
-
Power Supply Tester:
A power supply tester is a handy tool for diagnosing power supply issues. It allows you to check if the power supply provides the correct voltage levels to your components. A tester can save you time and frustration by quickly identifying whether your power supply is the source of a problem when your computer experiences boot failures or instability.
-
Fan Upgrades:
While power supplies come with built-in fans, you can further enhance cooling and reduce noise by replacing the stock fan with a high-quality aftermarket option. Look for fans that are specifically designed for power supplies to ensure compatibility.
-
Cable Management Accessories:
Cable management accessories include items like adhesive cable clips, velcro straps, and cable channels that help route and secure your cables for a cleaner and more organized build. Proper cable management improves airflow and makes future upgrades and maintenance easier.
-
Surge Protectors and UPS:
Investing in a surge protector or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) can protect your power supply and other components from power surges, fluctuations, and outages. Surge protectors are essential for safeguarding against voltage spikes, while a UPS provides battery backup to prevent data loss during power outages.
-
Modular Cable Kits:
If your power supply does not come with modular cables but supports them, consider purchasing a modular cable kit. Modular cables allow you to connect only the necessary cables, reducing clutter inside your case and improving airflow.
-
Power Supply Shrouds and Covers:
Power supply shrouds and covers are aesthetic add-ons that hide the power supply and cables from view. They can create a cleaner and more polished look for your system. They are especially popular in cases with tempered glass panels.
-
RGB Lighting:
If you are into aesthetics and customization, add RGB lighting accessories to your power supply setup. These lighting strips or fans can be synchronized with the rest of your system’s RGB components, creating a visually striking and coordinated look.
-
Noise Dampening Accessories:
To reduce system noise, consider noise-dampening accessories like anti-vibration mounts for your power supply or noise-absorbing foam for your case. These can help create a quieter computing environment.
These power supply accessories and add-ons not only enhance the functionality of your power supply but also contribute to your PC’s overall performance and appearance. Whether you want better cable management, additional protection, or a visually appealing system, accessories are available to meet your needs and preferences.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
Ensuring your desktop computer remains operational and protected from unexpected power interruptions is paramount. This is where Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) come into play. A UPS device is designed to provide temporary power during electrical outages, surges, and sags. Let us delve into the critical aspects of UPS units and why they are an essential addition to your power supply setup:
-
How UPS Works:
A UPS consists of a battery and an inverter. When your power supply from the wall outlet is stable, the UPS acts as a pass-through device. It directs power directly to your computer. However, the UPS seamlessly switches to its internal battery power when there is a power interruption or fluctuation. It provides you with a few minutes of electricity to save your work and safely shut down your computer.
-
Types of UPS:
There are several types of UPS units, each with distinct characteristics:
- Standby UPS: This type is the most basic and cost-effective. It provides power directly from the outlet until an outage occurs, at which point it switches to battery power.
- Line-Interactive UPS: Line-interactive UPS units offer voltage regulation to handle small power fluctuations, making them suitable for regions with unreliable power.
- Online UPS: Online UPS units continuously provide power from the battery. They offer the highest level of protection against outages and fluctuations. They are often used in data centers and critical systems.
-
Protection from Power Outages:
The most obvious benefit of a UPS is the protection it provides against power outages. When the electricity supply is disrupted, a UPS can keep your computer running for several minutes. It gives you enough time to save your work and perform a safe shutdown. This prevents data loss and helps avoid potential damage to your hardware caused by sudden power loss.
-
Surge and Spike Protection:
UPS units also guard against power surges and spikes. It can result from lightning, voltage fluctuations, or equipment connected to the same electrical circuit. Surge protection is vital for safeguarding your power supply and other sensitive computer components from voltage spikes that can occur at any time.
-
Voltage Regulation:
Many UPS units offer voltage regulation capabilities. This ensures a steady and safe voltage supply to your computer. And this helps prevent under-voltage (sags) and over-voltage (surges) conditions. Both of these conditions can harm your power supply and other components.
-
Data Protection:
A sudden power loss can corrupt data and even cause hard drive failure. An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) provides a safety net by allowing you to save your work, shut down your computer properly, and prevent data loss or damage.
-
Equipment Longevity:
Regular exposure to power surges and fluctuations can shorten the lifespan of your power supply, motherboard, and other components. By using a UPS, you enhance the longevity of your hardware. It is potentially saving money in the long run.
-
Enhanced Productivity:
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) ensures that power interruptions do not disrupt workflow, allowing you to continue working seamlessly even during brief power outages.
-
Environmentally Friendly:
UPS units are energy-efficient and often incorporate features like power-saving modes. That reduces energy consumption and lower electricity bills.
When selecting a UPS for your desktop computer, consider the wattage requirements of your system and the runtime you need during power outages. A UPS is a valuable addition to your power supply setup. It offers protection, peace of mind, and uninterrupted operation when power interruptions occur.
Power Supply Testing Tools
Power supply issues can lead to various problems in your computer, from system instability to unexpected shutdowns. You can use various power supply testing tools to diagnose and address these issues. These tools help you identify problems with your power supply unit and ensure it delivers the correct voltage levels to your components. Here are some essential power supply testing tools you should know:
-
Multimeter:
A multimeter is a versatile tool that can measure voltage, current, and resistance. You can use a multimeter to measure the voltage output from the power supply connectors to test your power supply. Ensure that the voltage levels match the specifications of your power supply unit. This will help you determine if the power supply delivers your components the correct amount of power.
-
Power Supply Tester:
A power supply tester is specifically designed for diagnosing power supply issues. It typically consists of a small, handheld device with connectors for various power supply cables. You connect the tester to your power supply. And it provides a digital readout of the voltages on the power rails like the +12V, +5V, and +3.3V rails. This can quickly reveal if the power supply is delivering the correct voltages.
-
PSU Load Tester:
A PSU load tester is a more advanced tool simulating a real-world power supply load. It is advantageous if you suspect your power supply may be unstable under heavy loads. Connecting it to your power supply allows you to test its performance under stress and see if it maintains stable voltage levels.
-
Power Supply Diagnostic Software:
Some power supply manufacturers provide diagnostic software that can be installed on your computer. This software can monitor and report the power supply’s performance, like voltage levels and efficiency. It is a useful tool for identifying potential issues and tracking the power supply’s health over time.
-
Oscilloscope:
An oscilloscope is an advanced testing tool that can provide a detailed view of voltage waveforms. It is not a common tool for the average user. Professionals can use it to analyze the power supply’s output voltage quality. An oscilloscope can help detect issues like ripples, spikes, and fluctuations in the voltage.
-
Voltage Monitor Alarm:
A voltage monitor alarm is a simple device that continuously displays the voltages from your power supply. It is particularly useful for real-time monitoring of voltage levels. It helps you detect any sudden changes or drops in voltage.
Using these power supply testing tools, you can diagnose problems and ensure your system receives a stable and reliable power source. It is especially valuable for troubleshooting and preventing potential hardware damage due to power supply issues. When using these tools, always follow safety precautions to prevent electrical hazards.
Conclusion
In computing, the desktop power supply often remains an unsung hero. It is quietly providing the lifeblood of your system. Understanding this crucial component and making informed choices can enhance performance, greater reliability, and peace of mind.
To recap, here are the key takeaways from our comprehensive guide on desktop power supplies:
-
Reliability Matters:
- A reliable power supply ensures stable and consistent power delivery to your components. It reduces the risk of data loss and hardware damage.
-
Understand the Basics:
- Knowing the fundamentals of power supplies, including voltage, wattage, and connectors, is essential for making informed decisions.
-
Main Components:
- Familiarize yourself with the essential components of a desktop power supply, like the 24-pin ATX connector, 8-pin EPS connector, and various cables.
-
Types of Desktop Power Supplies:
- Explore various types, including ATX, SFX, and modular power supplies, and choose the one that suits your needs.
-
Efficiency Ratings:
- Consider power supply efficiency ratings like the 80 PLUS certification. Higher ratings reduce energy consumption and heat generation.
-
Wattage Selection:
- Choosing the right wattage is crucial. Calculate your system’s power requirements to avoid underpowering or overloading your power supply.
-
Form Factors and Compatibility:
- Ensure your power supply’s form factor matches your computer case’s compatibility and dimensions.
-
Cable Management:
- Neat and efficient cable management improves airflow and makes future upgrades and maintenance easier.
-
Power Supply Efficiency and Heat Management:
- Opt for an efficient power supply to save energy and minimize heat generation. An efficient power supply also leads to a longer lifespan and better system performance.
- Safety and Reliability: – Protect your power supply and components with surge and overvoltage protection. Prioritize safety and reliability.
- Choosing a Reputable Brand: – Select a trusted and reputable brand when purchasing your power supply, as reliability and quality vary among manufacturers.
- Upgrading Your Power Supply: – Recognize the signs that indicate it’s time for a power supply upgrade and follow a smooth and safe upgrade process.
- Power Supply Testing Tools: – Consider using power supply testing tools like multimeters, power supply testers, and diagnostic software to diagnose issues and ensure proper functioning.
With this knowledge in hand, you are well-equipped to make informed decisions when it comes to selecting, installing, and maintaining your desktop power supply. By doing so, you will not only ensure the health and longevity of your computer but also enhance your overall computing experience.
Remember that the desktop power supply is more than just a component—the reliable power source keeps your digital world alive and thriving. So, choose wisely and power on with confidence.
Importance of a Quality Desktop Power Supply
The desktop power supply often takes a back seat in the intricate tapestry of computer components. Powerful processors, stunning graphics cards, and high-resolution displays overshadow it. However, the importance of a quality desktop power supply cannot be overstated. It is the unsung hero of your system. It silently powers your components and ensures your computer’s reliability, longevity, and performance. Here’s why a quality power supply should be a top priority for any PC builder or enthusiast.
-
System Stability:
- A quality power supply delivers a consistent and stable voltage to your components. It prevents sudden power fluctuations leading to system crashes and data loss. This stability is crucial for both everyday computing and demanding tasks like gaming and content creation.
-
Component Protection:
- Power surges, sags, and spikes can occur due to various factors like electrical storms and fluctuations in the power grid. A high-quality power supply acts as a shield, safeguarding your components from these potentially destructive events. It reduces the risk of damage to sensitive parts like your motherboard, CPU, GPU, and storage devices.
-
Data Integrity:
- Sudden power interruptions can corrupt data and damage storage devices. A quality power supply, however, gives you precious minutes to save your work and properly shut down during power outages. This protects your valuable data and prevents costly data recovery efforts.
-
Hardware Longevity:
- A dependable power supply can significantly extend the lifespan of your components. It minimizes the wear and tear on your hardware caused by power-related issues. Investing in a quality unit can save you money in the long run. And that will reduce the need for premature component replacements.
-
Energy Efficiency:
- Energy-efficient power supplies reduce your electricity bill and generate less heat. Lower heat output leads to a more comfortable and quieter computing environment. It also contributes to the longevity of your components, as excess heat can degrade them over time.
-
Enhanced Performance:
- Inadequate power supplies can cause performance bottlenecks when they cannot provide the necessary power to your components. This can lead to reduced performance and system instability. A high-quality power supply ensures your components receive the power they need to perform at their best.
-
Reliability and Peace of Mind:
- Quality power supplies are known for their reliability. They are less likely to fail or malfunction, which provides peace of mind and uninterrupted computing. You can rely on your computer to work when you need it most, whether for work, entertainment, or critical tasks.
-
Safe System Building:
- Investing in a reputable power supply reduces the risk of electrical and safety issues during system building. High-quality units adhere to safety standards and have built-in protections against electrical hazards.
Therefore, the desktop power supply is the backbone of your computer system. It quietly ensures that your components receive a reliable and clean power source. A quality power supply is an investment in your PC’s longevity, reliability, and performance. It protects your components. In addition, it safeguards your data and allows your system to operate at its best. When building or upgrading your PC, prioritize a quality power supply to guarantee a stable and trouble-free computing experience. It’s a vital component that deserves recognition as a cornerstone of your computer’s overall performance and reliability.
Additional Resources
As you explore the world of desktop power supplies, it is essential to have access to valuable resources that can aid your decision-making and deepen your understanding of this critical component. These additional resources can be beneficial whether you are looking for specific power supply models or seeking to expand your knowledge of power supply technology.
Recommended Power Supply Models
To assist you in your quest for the perfect power supply for your system, here are some recommended power supply models known for their reliability, efficiency, and performance:
Corsair RM850x:
This model offers 850 watts of power, modular cabling, and 80 PLUS Gold efficiency certification. It’s a popular choice among PC enthusiasts and gamers.
EVGA Supernova 750 G5:
EVGA is well-regarded for its power supplies. And its Supernova 750 G5 is no exception. It features 80 PLUS Gold certification. And it comes with a fully modular design and excellent build quality.
Seasonic Focus GX-650:
Seasonic is known for producing high-quality power supplies. The Focus GX-650 is a 650-watt unit with 80 PLUS Gold certification. It is of fully modular design and silent operation.
Thermaltake Toughpower GF1 850W:
This power supply offers robust performance with 80 PLUS Gold certification. It also provides quiet operation and a fully modular design. It’s suitable for systems with high-power demands.
Be Quiet! Straight Power 11 Platinum 750W:
Be Quiet! This power supply focuses on silent operation, and it doesn’t disappoint. It’s 80 PLUS Platinum certified, fully modular, and built with high-quality components.
Further Reading on Power Supply Technology
If you are eager to delve deeper into the intricacies of power supply technology, the following resources provide in-depth knowledge and insights:
“Power Supply Design Basics” by Texas Instruments:
It offers an overview of power supply design principles. It is an excellent resource for those looking to understand power supply internals.
“80 PLUS Power Supply Efficiency Certification” by 80 PLUS:
Learn about the different efficiency certifications and standards for power supplies. You can discover how they impact energy consumption and heat management.
“ATX Power Supply Design Guide” by Form Factors:
This guide provides detailed information about ATX power supply specifications. It helps you understand the standard that most desktop power supplies adhere to.
Manufacturer Documentation:
Do not forget to explore the official Documentation and user guides your chosen power supply manufacturer provided. These documents often contain valuable information on installation, troubleshooting, and best practices.
By utilizing these recommended power supply models and further reading on power supply technology, you can equip yourself with the knowledge and resources necessary to make informed decisions about your desktop power supply. This ensures a reliable and efficient source powers your system. And it contributes to its longevity and performance.