Both WAN and LAN looks like same. They are entirely different networks interconnected. Let us discuss here all about Computer networks, WAN vs LAN, and much more.
Computer Network:
A computer network is a small group of computers that works on standard communication protocols over a digital bi-directional interconnection. The primary purpose of a computer network is to share resources provided by the communication endpoints named network nodes.
The interconnection between the network nodes are established using wires, optical cables, wireless radio communication technology, else telecommunication networks.
The computer network is the backbone for many applications and services such as World Wide Web, printer and fax sharing, email, and other applications like instant messaging. Internet is the best example for computer networks from different component groups working under a single address space.
What are the Types of Computer Networks:
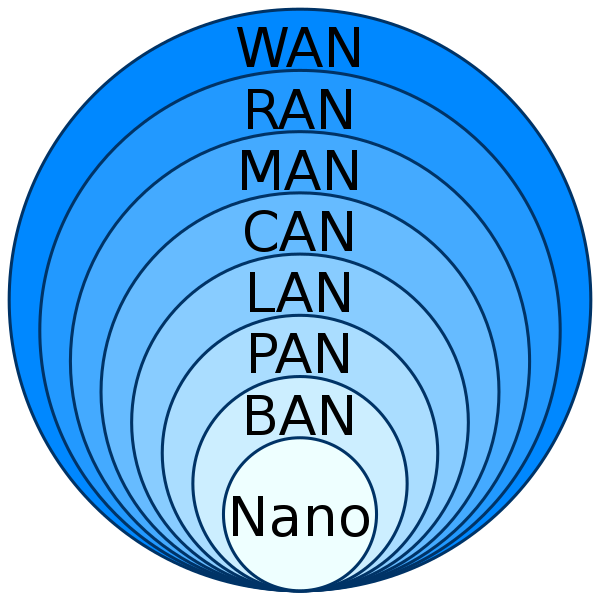
Based on the network properties such as features, physical capacity, institutional purpose, user access, access rights, and more, they are classified further. The main property for classification is its physical extent. There are different computer network structures employed universally.
 They are:
They are:
- NanoScale Network
- Personal Area Network called PAN
- Local Area Network usually called LAN
- Home Area Network called HAN
- Storage Area Network named SAN
- Campus Area Network named CAN
- Back Bone Area Network
- Metropolitan Area Network called MAN
- Wide Area Network called WAN
- Enterprise Private Network
- Virtual Private Network called VPN
- Global Area Network named GAN
- Internet Area Network called IAN
Let us discuss every network in brief.
NanoScale Network:
The nanoscale network is called as Nanonetwork. It is a network of interconnected nanomachines. The distances between the nanomachines within the network are tiny. And they are anything between a few hundred nanometers to few micrometers. They can perform very limited work such as computing, storing, sensing and actuation.
The nanoscale network is mainly employed in nanotechnology and biomedical science. The network is routed either on electromagnetic communication or molecular communication. It extends communication to tiny sensors and actuators that are operating in a biological system in the environment.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
PAN is a computer network among computers and other devices such as fax machines, scanners, printers, tablets, digital assistants, and game consoles. The connected devices are close to one person. The reach of the Personal Area Network extends to the maximum of about ten meters distance.
The PAN may be wireless or wired. An example of a wired PAN is interfacing such as Firewire, Thunderbolt, and USB. The wireless PAN (WPAN) uses Bluetooth, ZigBee, IrDA, and Infrared communications. Several types of WPAN operate on the ISM band also.
Local Area Network
Local Area Network connects system devices within a limited geographical area such as Home, Office, Institution, etc. Each connected device in the network is a node. Node is nothing but a redistribution point or a communication endpoint. Wired local area network entirely relies on Ethernet.
ITU-T and G.hn standard clearly stipulate the specification for the wires to be employed. It uses coaxial cables, telephone lines, and power lines too. The main characteristic of the Local Area network is its high-speed data transfer. But, it is limited to that geographical area where it is working. A local area network can be connected with a wide area network with the help of a router.
Home Area Network
HAN or a Home area network is a residential Local area network used for communication between digital devices in the home. They are usually in a small number of personal computers and accessories of an individual at home. The vital function of HAN is sharing of internet access through a DSL service provider.
A home network relay on a gadget that establishes a physical layer, data link layer, and network layer that helps to connect with other internal devices in the HAN. They can use either wired or wireless technologies to connect the nodes. The wireless is the primary option due to its easy installation and few other factors.
Therefore HAN is of two types, namely Wired PAN and Wireless PAN. The Wireless PAN is further subdivided into Low-Rate Wireless PAN. Because of convenience and reliability, many people are using Cloud services for their HAN. There are few downsides to using HAN.
They are:
- Wireless signal loss
- Leaky Wi-Fi system
- Electrical Grid Noise, since PAN relay on Powerline communication technology
Storage Area Network (SAN)
The SAN is always referred to as the network behind the servers.In addition, It is the simplest dedicated network for data storage.
Besides, It is a combination of hardware and software. It is a special-purpose network. SAN is a dedicated network to access data storage. SAN is primarily used to access storage devices like disk arrays, tape libraries, and more.
The storage devices are accessible to servers so that the devices look locally attached to the operating systems. In simple terms, SAN is a network of storage devices that are not accessible by any other devices not included in SAN. Due to its high cost and complexity, SAN discontinued already.
It has its own networking devices, such as SAN switches. Storage Area Network is usually built with redundancy; therefore, SAN switches are connected with redundant links.
Campus Area Network (CAN)
CAN is nothing but interconnections of Local Area Network with a limited Geographical area such as the campus of a university, government establishment, or enterprise.
For example, a university campus needs to link various departments, academic colleges, libraries, student hostels, conference halls, technology centers, training centers, and more. CAN is a network larger than LAN but smaller than MAN or WAN. The range of CAN is a maximum of 5 kilometers.
Back Bone Area Network
It is a part of a computer network infrastructure that provides an exchange of information between different subnetworks. It can tie diverse networks together within a building or across other buildings or wide areas. The backbone network is designed certain critical factors are taken into account.
Its capacity is greater than that of the individual networks connected to it. An example of the backbone network is Internet Backbone. Back Bone Area Network is further divided into Distributed Backbone Network, Parallel Backbone Network, Serial Backbone Network, and Collapsed Backbone Network.
Note: Parallel backbones are more expensive because of the extensive cabling involved. But it increases efficiency and fault tolerance.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
MAN is a more extensive network that spans over a city or a larger campus. It interconnects users with resources in the geographical region of the size of a metropolitan area. MAN is also used to describe linking several local area networks in that metro area by using point-to-point connections between them.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network is a computer network that covers larger geographical areas such as countries, continents, etc. It uses telephone lines, cables, and others. WAN uses communication channels provided by common carriers such as telephone companies.
It functions at three layers, namely the physical layer, data link layer, and network layer. The definition of a wide area computer network is spanning regions, countries, or even the world. But in practice, it is used to transmit data over long distances and between different networks. It is used to connect local area networks and other types of networks. It is often built on leased lines.
Enterprise Private Network
Enterprise Private Network is called intranet. It is a network built by a single organization built to interconnect its office location, such as factories, headquarters, remote offices, etc., to share data. Intranet is exclusively for the employees of a particular organization.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
VPN is an overlay computer network in which a few of the links between nodes are carried by virtual circuits in some larger network like the Internet. The data link layer protocols of the virtual network are tunneled through the Internet. It is a secured communication through the public Internet. It does not have explicit security features such as content encryption. The topology of VPN is a little complicating than the point to point. It uses dedicated circuits or tunneling protocols over existing networks. The advantage of using it is, the resources are accessed remotely using VPN. VPN is a point-to-point connection, and it does not tend to support broadcast domains.
Global Area Network (GAN)
GAN is a network used to support mobile communication across wireless Local area networks, satellite coverage areas.
Internet Area Network(IAN)
IAN is a computer network that connects voice and data nodes within a cloud environment over IPs. It eliminates the geographical boundaries of the network entirely because the service is virtualized. IAN offers users secure access to the data from anywhere, at any time, via an internet connection.
WAN Vs LAN
Understanding WAN:
Wide Area Network that covers larger geographical areas. Internet is the best example of that. Some other WAN networks run across the Globe for military and government purposes.
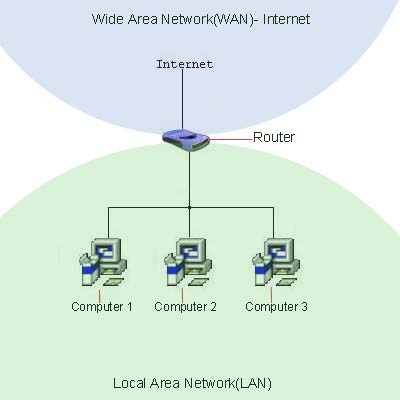 They interconnect their offices and data centers using this technology. In easy terms, a wide area network is a bundle of enormous local area networks coupled together.
They interconnect their offices and data centers using this technology. In easy terms, a wide area network is a bundle of enormous local area networks coupled together.
And they communicate with each other. Therefore WAN is a network of networks. Internet is one of the largest wide area networks globally. There are various types of WANs employed in the modern world to full fill the needs.
Brief History:
United States Air Force created the first one in 1950. They interconnected their Air force sites with the SAGE radar defense system. The main objective of Semi-Automatic Ground Environment is to control, coordinate and operate North American Aerospace Defense Command against any Russian air attack. A massive network of computers, displays, radar systems, dedicated hotlines, teleprinters, telex, and telephones linked together.
In the 1960s, ARPANET was employed by the United States department of defense. ARPANET is the first wide area packet switching network that implemented the TCP/IP protocol. SAGE and ARPANET are the technical foundation for the modern Internet. It interconnected four nodes, namely the University of California in Los Angeles, Stanford Research Institute, University of California, and Utah.
X.25 Protocol
The first WANs interconnected offices with terminals to mainframe and minicomputers. The Nodes are point-to-point connections from offices to data centers. Later it was adapted to personal computers. Then X.25 protocol and T1/E1 circuits are employed in those days.
In later 1980, a stripped-down version of X.25 protocol, Frame Relay employed in a wide area network. Frame relay comes with error correction. Frame Relay detects an error and drop-down that erroneous packet.
It simplified the protocol at each switching Node. It is a packet-switched technology that works on T1/T3 circuits bandwidth are at 128 kbit/s. Later, Frame Relay was replaced by ATM.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Asynchronous Transfer Mode handles traditional high data traffic and real-time, low latency voice and video data. ATM networks become much faster. A 1500 byte (12000-bit) full-size Ethernet frame takes only 1.2 µs to transmit on 10 Gbit/s across the network.
In the late 1990s, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) replaced the ATM, a routing technique in WAN. Still, this technology is employed in large-scale enterprises. MPLS protocols direct data from one Node to the next Node with the help of short path labels instead of long network addresses to bypass complex lookups in the routing table. MPLS supports a wide range of access technologies, such as T1/E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL.
SD-WAN
Then SD-WAN was introduced. Software-defined wide-area networking improved the user experience tremendously. It consists of business-grade IP-VPN, broadband internet, wireless service, and more. SD-WAN forward traffic automatically and dynamically to the best and appropriate path based on network conditions.
Wide Area Network Routers:
The WAN routers are nothing but Edge routers or Border routers. It routes the data packets between various wide area locations and allows the guest to access the carrier network. An edge router is a gateway to the inbound traffic into your network; therefore, it needs to protect and secure the IP traffic from other edge and core routers. The border routers strictly follow all the latest WAN protocols such as SONET/SDH (PoS), Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), ATM, and Frame Relay. Simply the border routers or the edge routers offer packet forwarding between other edge and core routers and manage traffic without packet loss and traffic congestion.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN is Software-Defined Networking in a wide area network. It simplifies the management and operation of a wide area network. It de- links the networking hardware from its control mechanism as and when needed for efficient data management. They are designed to address network problems. SD-WAN makes the wide area network architecture easier to deploy, operate and manage. It supports multiple connection types, such as MPLS, Last Mile Fiber Optic Network, or high-speed cellular networks. SD-WAN technology prioritizes QoS, bandwidth priority, dynamic path selection, security, automatic switchover, online traffic engineering, and quality performance.
WAN Types:
There are various types of wide area network, and they are:
- Pocket Switching
- TCP/IP protocol suite
- Router Network
- Overlay network
- Packet over SONET/SDH (PoS)
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Frame Relay
Pocket Switching:
The Pocket Switching is a method of grouping data and doing data transmission. In addition, Pocket switching is a reapplication of basic dynamic allocation techniques employed in tape switching systems, mails, and telegrams.
Besides, Pocket switching broke the message into several pockets and send them independently in triplicate using networking hardware directly to the destination. They are reassembled at the destination end.
The pockets are made up of identifying header and payload. Every pocket is verified in a process at the receiving end. The packets are verified, compared, and confirm with at least two copies match.
If any mismatch is found, a fresh request is made for a packet to be resent. It is the primary basis for data communication in worldwide computer networks. Packet switching optimizes the use of channel capacity and minimizes the transmission latency to communication.
TCP/IP Protocol Suite:
TCP/IP protocol suite is an internet protocol suite with conceptual models which have certain communication protocols on the Internet. It has foundational protocols such as Transmission control protocol (TCP) and internet protocol (IP). The internet protocol suite makes end-to-end data communication possible. It specifies how the data should be packetized, address, transmit, route, and receive.
The internet protocol is organized into four abstraction layers. They are called link layer, internet layer, transport layer, and application layer.
Router Network:
The objective of the Router is to connect multiple networks and forward the packets intended to the attached networks or remote networks.A router is a networking gadget employed to interconnect LANs to form a wide area network. The IP routers use IP addresses to determine where to forward the packets. It does the traffic directing functions on the web. When a data packet comes in, the Router reads the network address information in the header and then decides the right destination.
Then using the decision, it sends the packets to the following network using the information in its routing table or routing policy. When multiple routers are used in an interconnected network, they exchange information about the destination address using the routing protocol. Besides, each Router builds up a routing table- a list of routes between two computer systems on the interconnected networks. The Router is working on two functional processing units working simultaneously, namely, the control plane and the forwarding plane.
Control Plane and Routing:
The control plane of the Router maintains the router table. For that, it uses static routes or by learning the routs dynamically using the routing protocol. Then it finalizes the route directives and forwards that directive (forwarding information base) to the forwarding plane. The forwarding plane forwards the data packets between incoming and outgoing interface connections. It reads each packet’s header data, matches the destination entries supplied by the control plane, and directs the packet to the outgoing network.
The Router that connects the local area network with a Wide area network is called a border router, or gateway router. The Router is a three-layered device.
Overlay Network:
An overlay network is a data communication network in which software is used to create virtual networks layered on another network. For example, the Internet is over-laid on the telecommunication network. It is a bit complex network. Nowadays, a wide area network is the basis for more overlaid networks constructed to permit routing of messages to destinations not specified by IP. They use distributed hash tables to route the messages to the destination.
Packet over SONET/SDH (POS):
Packet over SONET/SDH (PoS) is one of the most popular protocols used primarily for WAN transport. These communication protocols transmit packets in the form of the point-to-point protocol over SDH or SONET. Both are standard protocols for communicating digital data using lasers. The most crucial aspect of POS is to support sending IP pockets over wide area networks.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
It is scalable and protocol-independent. Multiprotocol Label Switching is a routing optimizing technique employed in a wide area network. It directs data packets from one Node to the next Node based on short path labels rather than the long network address to avoid complex lookups.
Therefore it increases the speed of the traffic flow. MPLS identifies virtual paths between distant nodes rather than endpoints. MPLS supports T1/E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL. The advantage of MPLS is its ability to support multiple service models and perform traffic management. It works in conjunction with Internet protocol and its routing protocols like IGPs.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM):
Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a switching technique that is superseded by IP-based technologies. It uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing to code data into tiny, fixed-sized cells. It can handle multiple types of traffic, including voice, video, and data, in a network without using any separate overlay networks.
ATM can handle both usually data traffic and real-time low latency content like voice and video data. It uses the features of packet switching and circuit switching networks. ATM was designed to focus on a low jitter network interface.
Frame Relay:
Frame Relay is the standardized technology that is employed in a wide area network. It specifies the physical and data link layers of the channels using the packet switching technique. Earlier it was used to transport across ISDN infrastructure. The network service providers implement frame relay for voice and data as encapsulation techniques to send and receive data between LAN over WAN.
The Frame Relay network sends data over a frequently changing path using wide area network protocols in transparent mode to the end-users. It puts data in variable-sized units called frames and leaves any necessary error correction data at the endpoints. The endpoints have to detect and retransmit dropped frame sequences. Its Relay switches create virtual circuits to connect remote LANs to a wide area network. Frame Relay aims to provide cost-efficient data transmission.
WAN Optimization:
Wide Area Network Optimization employs a variety of techniques, including compression, protocol optimization, equalizing, traffic handling, local caching, latency optimization, and de-duplication. These will help to improve packet delivery and traffic control, allowing network bandwidth. WAN optimization is a subject of extensive research.
Understanding LAN:
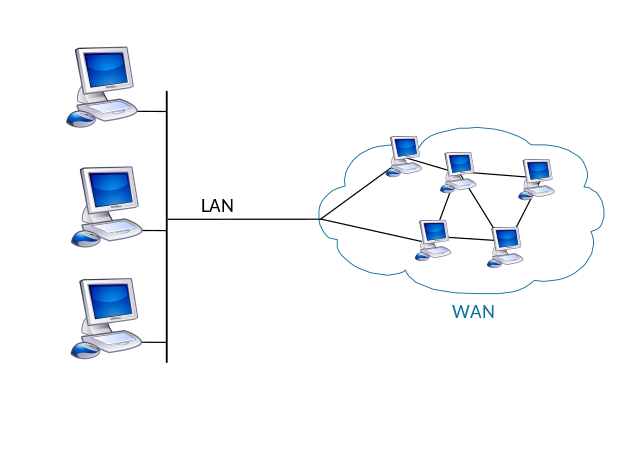 LAN is a computer network that interconnects computer systems confined to a limited area. It comprises Ethernet cables, access points, switches, routers, and other components that help to connect internal servers, web servers, other local area networks, and wide area networks such as the Internet. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two c ways to establish Local Area Network Connection.
LAN is a computer network that interconnects computer systems confined to a limited area. It comprises Ethernet cables, access points, switches, routers, and other components that help to connect internal servers, web servers, other local area networks, and wide area networks such as the Internet. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two c ways to establish Local Area Network Connection.
There are two types of LANs. They are WLANs and Wired LANs. A wired LAN uses Switches, Ethernet cabling to connect end nodes and servers, and IoT devices to the telecommunication network. The Wired Local Area Network can be managed with a single switch with enough Ethernet ports to interconnect all the network devices.
But in bigger establishments, thousands of devices and gadgets are required to connect. Therefore it needs additional hardware, software, and proper configuration to optimize the network correctly. Consequently, it needs a virtual local area network to connect.
Ethernet LAN is a shared medium. In an organization, if too many devices are connected to a single Local Area Network, the amount of broadcast traffic will be heavy. The broadcast of a single device will be heard by all devices connected to the network.
How Signals Sent:
This broadcast traffic can create bottlenecks and unwanted congestions. To counter; this heavy broadcast traffic of sent and received signals on a network, it needs to be split into multiple VLANs. If it is split into multiple virtual networks, the broadcast signals will be sent and received and heard within that network. The virtual network removes the broadcast overhead and thereby avoids performance issues.
If devices of various VLANs need to speak with each other, then it needs a Layer3 switch to send and receive traffic among them. It is termed inter-VLAN routing. Since larger enterprise networks need to break up the network into small VLANs, they require hundreds of Layer 3 switches that need to be deployed throughout the network.
Instead of these routers, now people are employing integrated layer three routing capabilities into network switches to create a layer switch. With these capabilities, the Layer 3 switch can work as a switch and do inter-VLAN routing in a single hardware tool.
Wireless LAN (WLAN)
Wireless Local Area Network is a wireless computer network that interlinks fewer devices using wireless communication to form a Local Area Network. It is limited within the premises. It allows the user to move freely within the building with the ability to remain connected to the network. Through a gateway, WLAN can be connected to Wide Area Networks such as the Internet.
The latest WLANs are based on IEEE 802.11 standard to transport data between end nodes and the network using wireless spectrum. In most cases, WLAN is preferred because of its convenience and flexibility, and cost-saving. It avoids unnecessary cable running throughout the premises.
Most of the users use mobile devices such as Smartphones and Tablets; therefore, they prefer WLAN for connectivity. Now WLANs deploy infrastructure mode. In this mode, wireless clients such as tablets and smartphones connect to the WAP to join the network. The WAPs are usually fixed and provide service to their client’s nodes within the range. Some networks use multiple WAPs using the same SSID and security protocol. WAP usually have a wired network connection and may have wireless connections to other WAPs also.
Basic LAN Setup:
Any operating with internet protocol version IPV4 or IPv6 networking capabilities can be used for LAN setup. Some gadgets such as personal computer and Laptop come with an Ethernet port can be connected to a network gateway such as Router. Besides, with an inbuilt Wi-Fi chip or Wi-Fi adapter that can be easily connected to a WLAN.
A basic wired Local Area Network needs an administrator to connect the end device to LAN. For this connection, you need an Ethernet cable (Cat5 or Cat6). Once connected, they start communicating with each other in the same network. For administering a Wireless setup, you need a wireless access point, namely WAP. WAP can be configured to broadcast the network service identifier (SSID). And they required authenticating to the network using Wi-Fi authentication methods. Some of the authentication options are WAP2 Enterprise and Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 pre-shared key.
Types of LAN:
Based on the classification followed in the distribution methods in Local Area Network, it is of four types. They are:
- Ethernet
- Token Ring
- Token Bus
- Fiber Distributed DATA Interface (FDDI)
Ethernet is a distribution method most people use in the wired network. A token is a circular ring pattern. With the help of tokens passed through them, authenticate and establish a connection among them. Token Bus is used in connecting devices in Coaxial cables, and the connection is established via the token. With FDDI or Fiber Distributed DATA Interface, faster network connectivity can be established on Fiber optic cables and high-speed copper cables.
Ethernet:
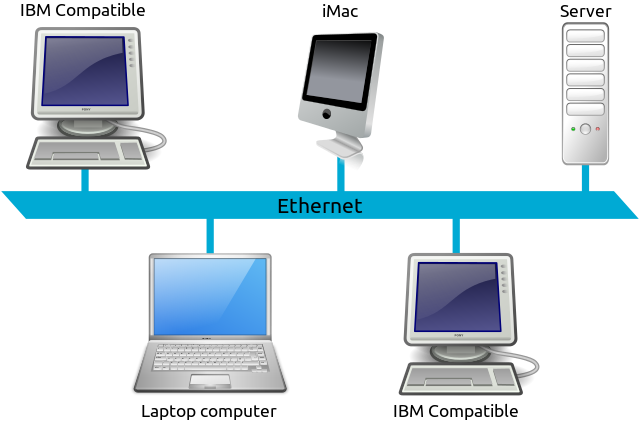 The Ethernet is a family of wired computer networking technology used in local area networks and wide area networks. In addition, Ethernet widely used in homes and small establishments and work well with wireless Wi-Fi technologies.
The Ethernet is a family of wired computer networking technology used in local area networks and wide area networks. In addition, Ethernet widely used in homes and small establishments and work well with wireless Wi-Fi technologies.
It is a network protocol that controls the data flow in a local area network. In this cabled network, users can transfer data at a rate of more than 10Mgabits per second. Usually, it checks for the medium to transfer data between the network devices; if it is available, then the connection is established.
Working:
When the connected devices need to communicate with each other on the network, they need to detect the carrier. If the carrier is available, then they will start sending and receiving data among them. When a sender sends a data packet in the network, all the connected devices in the network receive the packet and check whether it is meant for them.
Then the actual recipient receives the data packet. Until then, the sender has to wait. The communicating data over Ethernet is divided into shorter pieces called frames. And, each frame contains the sender and receiver addresses and error-checking data to check and remove the damaged data frame. Usually, the higher layer protocol triggers retransmission of the lost frame once it is detected and discarded.
The Ethernet includes a data link layer, a 48-bit Mac address adopted by other IEEE 802 networking standards, including IEED802.11 (Wi-Fi) protocol including FDDI. Ethernet was improved to include higher bandwidth, with improved medium access control utilization, varying physical media. And the coaxial cable was replaced with point-to-point links connected by repeaters and switches. In the latest Ethernet, each station communicates with the switch, and the switch forwards the traffic to the destination node. In this method, the collision is reduced. Collision is only possible when the Node and switch attempt to communicate at the same time.
Token Ring
Token Ring is a type of local area network in which all the connected devices are in a ring arrangement. The connected devices form a circle, and they receive tokens as per their requirement. The token is a three-byte frame, and it is passed around the Ring of workstations or the servers. That three-byte frame contains starting delimiter at the beginning of the frame.
And the access control, which contains the priority field, reservation field, token bit, and monitor bit. At the end of the frame is the ending delimiter.Token passing is a channel access method to provide fair access to each workstation. It eliminates the collision of contention-based access methods.
Token Ring works on access priority. And certain nodes have priority over the token. Multiple identical MAC addresses can be supported on the Token Ring network. It has difficulties in handling device failure and adding new stations to a network.
It is more complex than the Ethernet and requires some special processor and firmware for each interface. Work stations on Token Ring are logically organized in a ring topology with sequential data transmission.
Every work station in a Token Ring network can be an active or passive monitor station; since there can be only one active monitor on a ring at a time. The active monitor is chosen through the monitor contention process. A newer version of Token Ring is Fast Token Ring is available with a data transfer rate of 100Mbps. The Token Ring was a successful technology in a corporate environment but is replaced with the latest versions of Ethernet.
Token Bus:
Token Bus was developed and introduced by IBM. It is a network implementation with token ring protocol over a virtual ring on a coaxial cable. A token is passed around the network endpoints. The endpoint device which possesses the token only can transmit at that time. If the nodes that possess the token do not have anything to send, the token is passed to the next Node in the virtual ring network.
Each Node must know the address of its neighbors in the Ring; therefore, special protocols need to notify the nodes about the connections to and disconnection from. There is no collision; therefore, two or more devices can send data on the Bus simultaneously and the transmitted data saved from destroying.
Due to difficulties in Token Ring, Token Bus has taken momentum. Token Bus protocol was created to combine the benefits of a physical bus network. It was standardized by IEEE standard 802.4. It is mainly used for industrial applications. The main difference between Token Bus and Token Ring is that the endpoints of the Bus do not meet to form a physical ring. Token Bus was first introduced for industrial automation. GM first used it for manufacturing protocol.
Fiber Distributed DATA Interface (FDDI)
Fiber Distributed DATA Interface (FDDI) uses optical fiber as the standard underlying physical medium. Later, it used copper cable as the medium, named Copper Distributed DATA Interface (CDDI). Fast Ethernet replaced FDDI, which offers the same speed of 100Mbits per second.
The network can be extended to the range of up to 200 kilometers. FDDI is a Ring based token network; it does not use the Token Ring protocol. It is a product of the American National Standard Institute. FDDI contains two rings, one as primary and the second one as a secondary backup. If the primary Ring fails, the secondary Ring plays the role. If the network does not need the backup, then the secondary Ring also will carry data.
Secondary Ring can boost the capacity to 200 Mbits per second. The dual Ring can extend up to 100 Kilometers. FDDI requires this dual Ring of trees network topology because the dual Ring actually passes through every connected device and requires every Node in the network remain continuously operational. FDDI-2 is for long-distance voice and multimedia communication.
All the Local Area Networks discussed above have their own merits and demerits. They have their own specification. They have their own purpose of use and have their limitations and issues.
LAN Topology:
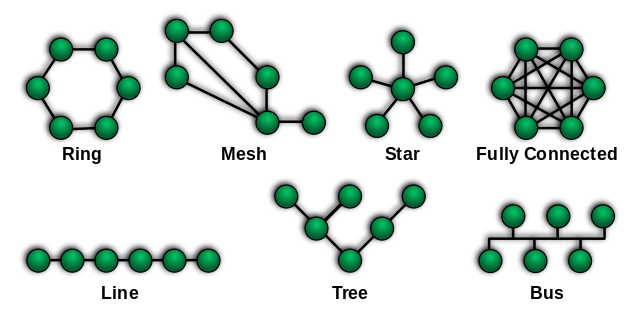 The major topologies of Local Area Network are divided into two broad categories. They are physical and Logical topologies. They are:
The major topologies of Local Area Network are divided into two broad categories. They are physical and Logical topologies. They are:
- Physical Bus Topology
- Physical Hub of Star Topology
- Ring Topology
- Physical Mesh Topology
- Star-Bus Topology
- Star- Ring Topology
Bus Topology:
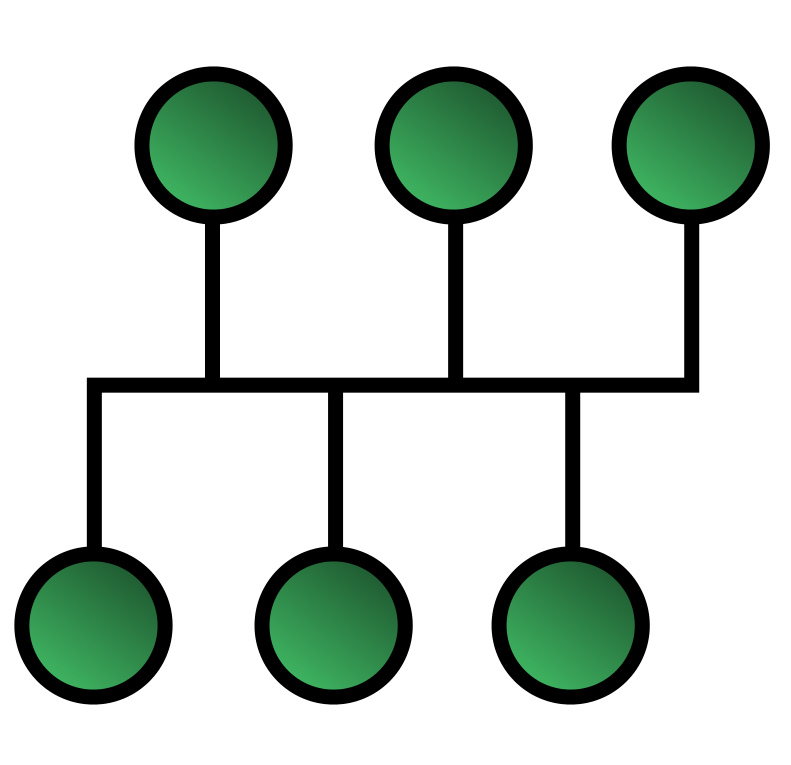 In the Bus topology, all the end nodes, including servers and computers connected to a single network cable called a Bus. All the nodes in the Bus have equal access to the trunk. This is achieved with short drop cables or direct T connectors. Source node sends data signal.
In the Bus topology, all the end nodes, including servers and computers connected to a single network cable called a Bus. All the nodes in the Bus have equal access to the trunk. This is achieved with short drop cables or direct T connectors. Source node sends data signal.
That is broadcast to all the other nodes via a bus cable. Even though the message is broadcast, the intended receiver only receives the signal. The recipient accepts the signal if the MAC address or the IP match. The data transmission occurs one way.
If the message is missed or not recognized, it reaches the end of the Bus and dissipates at the terminator.
The network is very easier, simple, and economical.
It is easy to install. It adheres to all industry standards. The bus network is difficult to re-configure. It isn’t easy to troubleshoot since everything happens on a single medium. Any breakdown of cable may lead to an adverse effect on the network.
Star Topology:
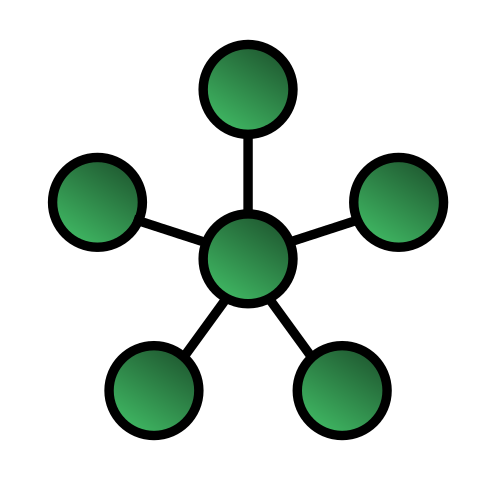 All the nodes are connected to the central node in the Star Topology network, and they are not interconnected. Each Node has a point-to-point connection to the central hub. The central controlling Node has dedicated legs pointing to all nodes.
All the nodes are connected to the central node in the Star Topology network, and they are not interconnected. Each Node has a point-to-point connection to the central hub. The central controlling Node has dedicated legs pointing to all nodes.
They need to send the messages to the central node, and the central Node takes the responsibility of sending the data to the right destination. This type of network prevents collisions and keeps the line always free from traffic and open for communication.
Star topology is a little challenging to install, but each end node has its dedicated line meant for work. It needs more cabling work. It is easy to re-configure and troubleshoots.
Defected data are automatically isolated to the failed segment. The advantage of this topology is that if one end node fails, it cannot send or receive data, and the remaining star network functions normally. The disadvantage is if the central hub or the switch failed then the entire network system will fail.
Ring Topology:
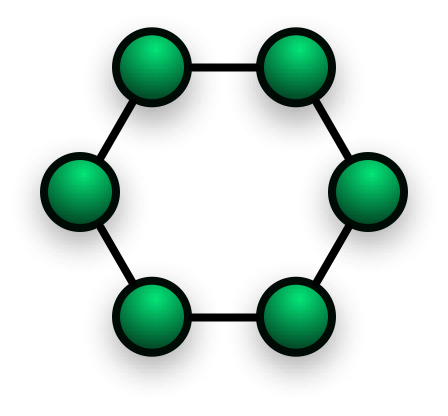 Ring Topology network the nodes are interconnected to form a closed loop. Each Node on the Ring can communicate with either side with the help of the token. The nodes with the tokens are allowed to pass data.
Ring Topology network the nodes are interconnected to form a closed loop. Each Node on the Ring can communicate with either side with the help of the token. The nodes with the tokens are allowed to pass data.
In this topology, the central Node is eliminated; therefore no need for a network server to control the other devices. Data sent to the Node to Node in an organized manner. The data is transmitted around the Ring with the token passing technique.
Each Node checks the messages for matching destination addresses. If the destination address doesn’t match, it regenerates the message and passes it to the next Node on the Ring. Once the Ring is configured, then it isn’t easy to modify or re-configure.
It is easy to troubleshoot. An internal feature helps to identify the problematic Node in the network. Rings may be unidirectional with traffic transmit either clockwise or anticlockwise, or in bidirectional. It functions better than Bus topology under heavy network load. One malfunctioning node can create problems for the entire network. Bandwidth is shared on all links between the nodes.
Mesh Topology:
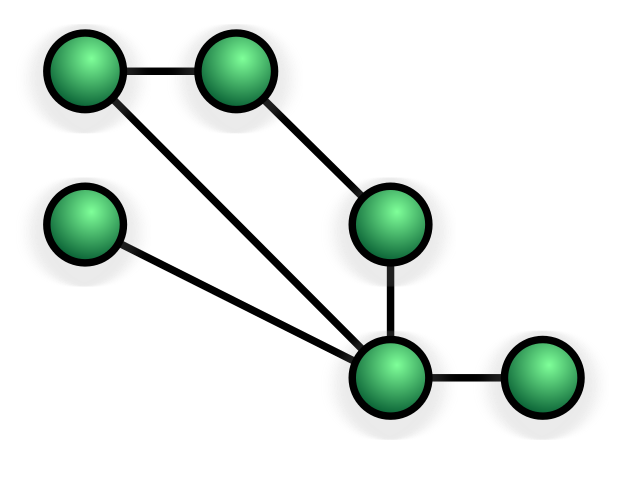 All the Nodes are connected with every other Node individually by cable. This configuration offers redundant paths to the network. Even if one Node is failed, the network won’t get affected.
All the Nodes are connected with every other Node individually by cable. This configuration offers redundant paths to the network. Even if one Node is failed, the network won’t get affected.
The significant advantage of Mesh topology is its backup capabilities because of multiple paths in the network. The Nodes are independent, and the lack of dependency on each Node allows them to participate in data relay. Mesh network dynamically self-organize and self-configure.
Therefore it reduces the installation overhead. The ability to self-configure enables the dynamic distribution of workloads, particularly when a few nodes failed. These properties contribute to fault tolerance and minimize the maintenance overheads. ATM is the best example of mesh topology. It is difficult to install and re-configure if there are more number of devices are participating. It relays the data either by using flooding technology or the routing technique.
Star-Bus Topology
Star-Bus Topology is a hybrid network topology in which star networks are interconnected through the bus network. Besides, tree networks are hierarchical, and each Node can have more child nodes. If any of the computers fail in the network, that won’t affect the communication between the other nodes in the system.
But if the star node is affected, the entire system nodes connected to the star could not communicate with the other system nodes. From the controlling point, each of the star network’s uplink ports is connected with the help of drop cables.
Star- Ring Topology:
In the Star-Ring network, the system nodes are connected to the central components using drop cables as in a star network. However, the component nodes are wired to form a ring network. In it, if a single system node fails, that will not affect the network. Because of token passing, each of the Nodes has equal priority in communicating with others. The spokes of the rings are point to point connection to the central hub to individual nodes.
Local Area Network (LAN) Security:
Network security starts with authentication with a username and password or, otherwise, one-factor authentication. With two-factor authentication or three-factor authentication, you can add more safety and security to the network. Besides authentication, the firewall enforces access policies to prevent unauthorized access. The intrusion prevention system component helps to prevent intrusion.
Anomaly-based intrusion detection systems also monitor unusual traffic, and they can detect active attackers, both inside and outside attackers, who can compromise the system. The communication between two hosts can be encrypted to maintain security and privacy. Honeypots are deployed as an early warning and surveillance tool. Honeypots effectively decoy network-accessible resources.
How Does LAN Work-
LAN closely follows Open System Interconnection Model (OSI Model). It partitions the data flow in a communication system into seven abstraction layers. Each intermediate layer serves a class of functionality to the layer above it. The communication protocol standardizes the classes of functionality. The data to be transmitted is composed by the topmost layer of the transmitting device into a protocol data unit.
The PDU is passed to the next layer and is named a service data unit. SDU is concatenated with the header, footer, or both and then passed on to the next layer. This process continues till it reaches the bottom-most layers from which data is transmitted to the receiving device.
At the receiving end, the data is passed from the lowest to the highest layer as a series of SDUs. They are successfully stripped off the layer header, footer, or both until they reach the topmost, where we get the received data.
Let us discuss the working of the following layers alone to avoid repetition.
- Physical Layer
- DATA Link Layer
- Network Layer
Physical Layer:
The physical layer transmits raw data bits over physical data links connecting the network node. The bits stream maybe code words or symbols, and these are to be converted into a signal transmitted by the transmission medium. They physical layer is a procedural interface to the transmission medium. The bit has the details about the properties of the connectors, broadcast frequency, line code, and other parameters specified by the physical layer.
The physical layer is the primary layer under laying higher-level functions of a network. The functions can be implemented to it through different hardware technologies of varying characteristics. The physical layer translates communication requests from the data link layer into hardware-specific operations to send or receive them in the form of signals. The physical layer supports the higher layers that are responsible for the generation of logical data packets.
It performs bit-by-bit symbol-by-symbol data delivery over the physical transmission medium. It is responsible for spectrum frequency allocation, specification of signal strength, bandwidth, etc.; the transmission medium may be electrical, optical fiber, or wireless IR communication link.
Emloyed, Link coding in this layer to convert data into electrical signals. To optimize reliability and efficiency, signal processing techniques such as pulse shaping, error correction coding, equalization extra are further added to improve reliability.
DATA- Link Layer:
The Data link layer is the second layer of OSI modeling of computer networking. This protocol layer transfers data between nodes on the network across the top layer. The data link layer is the base for the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities.
It is concerned with the local delivery of data frames between the nodes on the same network level in the network. The Datalink protocols specify how devices detect and recover from collisions and mechanisms to avoid or reduce them.
Network Layer:
Network Layer helps to route the data across the network. This layer provides functional and procedural means of transferring data packets from one Node to the others connected in different networks.
This layer is a medium to which many nodes can be connected. Every Node has an address, and it permits the nodes to stay connected and transfer messages to the connected nodes.
If the Data link layer messages are too large, then it the responsibility of the Network layer that implements the delivery by breaking up the messages into several parts and sending them independently, and at the receiving end, the network layer of the Node reassemble the fragments into the original message. Its layer management protocol has the functions defined, such as management annex, ISO7498/4.
Applications of LAN:
The following can be the broader applications of LAN:
- Housekeeping Applications
- Educational Services
- Resource Sharing
- Office Administration
Resource Sharing: Local area networks employed school and university environments, hospital libraries as it allows sharing of resources like data, scanners, printers, and other sharable utilities. It serves users at home to access the Internet.
Central Control of Equipment and Data: It works as a control center of types of equipments and data.
It is widely used in manufacturing industries where the central server coordinates the activities of other men and machinery.
It is employed in Office administration. The connection to administration offices for easy access of necessary files is possible with it.
Easy Connection of Equipment from Different Vendors: High-speed LANs are typically used to connect many slower networks.
Housekeeping applications: Lan can easily handle acquisition, cataloging, and circulation control.
Educational Programs and Services: Distance education and other study programs can be handled with LAN at the reader’s own pace.
Advantages of LAN:
Resource sharing:
Sharing resources like hard disk drives, DVD drives, printers, scanners, Fax machines, and other connected peripherals made easy with LAN. Anyone in the connected network can access those resources in the primary server without any trouble.
Software sharing:
With the help of LAN software, sharing is possible. A single server with the licensed software can be shared among network systems of the same network. It minimizes the overheads on purchasing more individual licenses for each connected system.
Easy communication:
LAN users can quickly exchange data and information. Since all of the data and information are stored on only one central server, any LAN user can access them at any time. And the user can share the same with the other users in the same network. It ensures that the data and information are sent and delivered to the right person on the network.
Centralized DATA:
The user data is stored in the central server. Therefore any workstation in the particular network can access the data with their user accounts and passwords.
Improved Security:
All input data are stored in the local server of the LAN. Therefore it is more secured and is updated whenever the users access them via LAN. Besides, you can impose additional security protocols to allow or deny particular users and specific data.
Internet Sharing:
LAN can share the internet connection to all the network end node systems. One connection to the Internet can be used to share the connection with all other systems in the LAN.
Computer System Identification:
For easy identification, each computer on the Local area network is assigned a MAC address. Usually, the Mac address is used when in the packet header when sending and receiving the data. This Mac address is stored in the network adapter of the motherboard. You can use this MAC address for computer system identification.
Disadvantages of LAN:
Implementation Overhead: The operational cost is minimum in LAN. Even though LAN saves a lot of money in resource sharing, the initial setup cost is very high due to special software and other hardware procurement.
Policy Violation: All critical information and DATA are stored in the server; the administrator needs to protect it from any intrusion. Therefore administrator needs to check the personal data of each connected computer in the network. It may lead to policy violations.
Security: Gaining access o the systems in the LAN network is easy. Therefore, it is imperative to stop unauthorized access, thereby protecting the server’s data from intruders. Consequently, it is crucial to implement the correct set of rules and privacy policies to protect the server from unauthorized access.
Maintenance: Since multiple devices are connected to the LAN and the work for a long time, they may face any hardware issues and system failure. Hence Local Area Networks need an administrator to handle the problems.
Coverage: Its coverage is limited to 10 Kilometers or so.
Crashes: The central server is the LAN architecture’s brain that controls and manages all the connected systems in the network. If the server encounters any system errors, then it adversely affects the other computers in the network. And none of the data and information in the affected server is accessible to the other computers in the network.
Malware and Viruses: Virus and malware are hazardous in the LAN-based network. If one attached computer is infected with viruses and malware, it can quickly spread to the remaining connected systems within the network.
LAN vs WAN:
Where we have listed significant difference between WAN vs LAN
| LAN-Local Area Network | WAN- Wide Area Network |
| LAN network covers a small geographical area such as homes, offices, and groups of buildings | WAN network covers more expansive geographical areas that can span across the Globe. It allows for a much larger and more intricate network. |
| It connects local devices to each other. | WAN connects LANs to each other. WAN is an interconnected network of LANs |
| Uses Ethernet for connectivity | Uses Frame Relay and X.25 for longer distance connectivity |
| It uses the following networking technologies such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet Cables, Token Ring, and Fiber Distributed Data Interface, FDDI, TCP/IP, etc | It uses networking technologies such as Optical wires, modems, routers, switches, bridges, wireless broadband, and Satellite. |
| Data transfer protocols are Ethernet cable and IEEE 802.11 | Data transfer protocols are PPP, HDLC, and Frame Relay. |
| Setup Cost is lesser since it needs to connect the peripheral within a small area. | The setup cost is Higher since it needs to connect remote and far-off places too. |
| Higher DATA transfer is possible | Lower DATA transfer when compared to LAN |
| It may be a private entity | It may be private, public or both |
| Works on Higher Speed. Its transmission speeds can easily reach or exceed 1Gbps, which can be hundreds of times faster than the average WAN. | WAN Speed is significantly lesser compared to LAN |
| Delay in Propagation is Lesser since it covers the lesser area | Delay in propagation is greater since it covers a broader area |
WAN vs LAN -(Conti-)
|
LAN |
WAN |
| Fault Tolerance is higher | Fault Tolerance is lesser |
| Designing and Maintaining it is easy | Designing and Maintaining it is difficult |
| Local Area Network can use both Layer 1 and Layer 2 devices. | Wide Area Network uses Layer 3 devices |
| LAN uses Hubs, Repeaters, Switches, and Bridges | WAN uses Multi-Layer Switches and Routers |
| Higher Scalability and Security, Reliability | Lesser Scalability and Security, Reliability when compared with Local area networks |
| It has Higher Bandwidth. Currently, Local Area Networks works at bandwidth speeds of 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps. | It has Lesser Bandwidth. Currently, Wide Area Networks runs on bandwidths of 20 Mbps to 100 Mbps |
| Less congestion | More congestion |
| Ethernet cables, like the Cat5, Cat5e, and Cat6, and Cat6a, are used to connect Nodes to the network. | Using High-quality Copper submarine cables to connect the networks |
| Local area network operates on the principle of broadcasting | Wide area network operates on the principle of point-to-point |
| It experiences lesser data transmission errors | It experiences more data transmission errors as compared to the local area network. |
| Signal Deterioration is nil. | Signal Deterioration is there. |
| The range is around 1 Kilometer or less | The range is around 10000 kilometer or more |